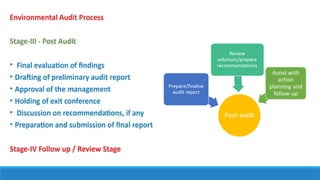
The document outlines the concept and process of environmental audits as a crucial management tool for organizations to evaluate their compliance with environmental regulations. It discusses various types of environmental audits, their objectives, advantages, and challenges faced during the audit processes, particularly in industries like construction and sugar production. A case study on the Kumbhi Kasari sugar factory highlights the importance of environmental audits in reducing pollution and improving resource management for sustainable industrial practices.