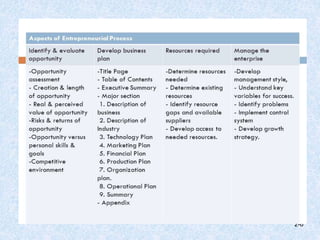
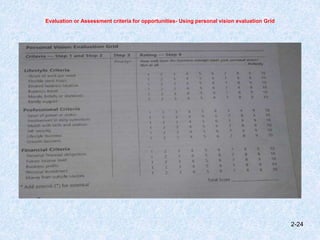
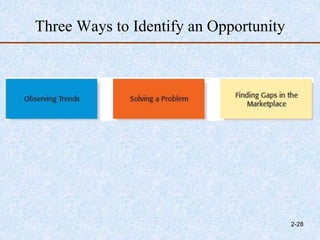
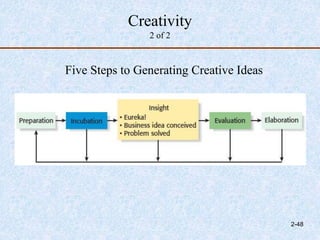
The document discusses entrepreneurship development, focusing on enhancing skills, recognizing opportunities, and stimulating economic growth. It outlines the entrepreneurial process which includes opportunity identification, business planning, resource determination, and enterprise management, while also detailing methods for generating ideas and spotting gaps in the marketplace. Finally, it emphasizes the significance of trends, social networks, and creativity in recognizing business opportunities.