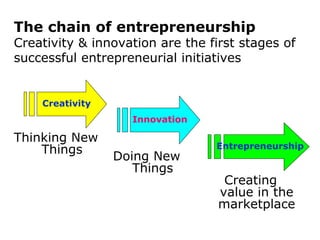
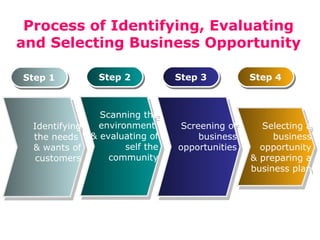
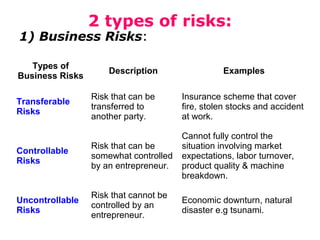
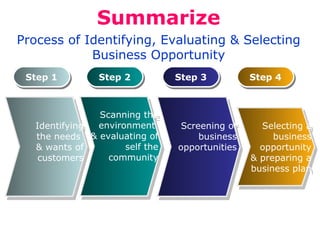
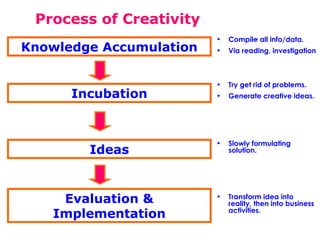
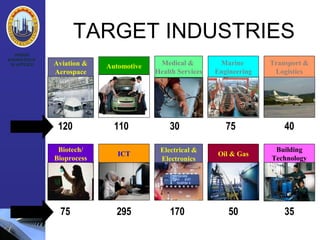
The document discusses the concepts of creativity, innovation, and identifying business opportunities. It begins by defining creativity as generating novel and high-quality ideas and innovation as converting opportunities into marketable products or services. It then outlines a 4-step process for identifying business opportunities: 1) identifying customer needs, 2) environmental scanning and self-analysis, 3) screening opportunities, 4) selecting an opportunity and creating a business plan. Later sections explore methods for generating creative ideas, different forms of innovation, and strategies for encouraging creativity and innovation in business.