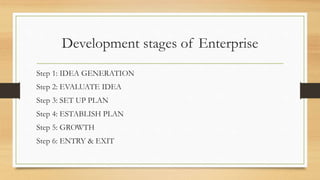
This document provides an overview of entrepreneurship presented by Simran Kaur. It defines key terms like enterprise, entrepreneurship, and entrepreneur. It discusses theories of entrepreneurship and characteristics of successful entrepreneurs like being self-employed, risk-taking, and innovative. Intrapreneurs who create new ideas within companies are also covered. The roles of entrepreneurship in economic development and common problems entrepreneurs face are summarized. The presentation outlines the development stages of starting a new enterprise and differences between entrepreneurs and managers.