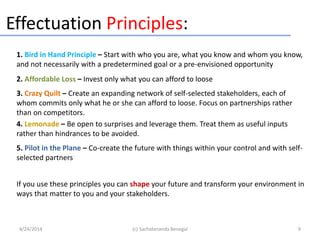
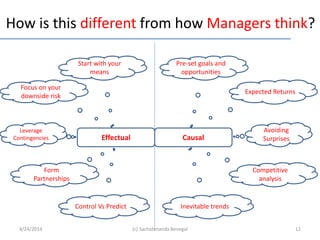
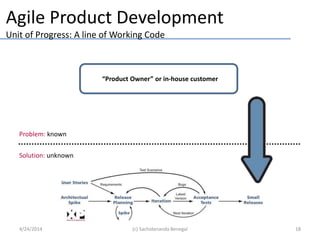
This document discusses entrepreneurship and how entrepreneurs think. It contrasts the causal logic typically used by managers with the effectual logic used by entrepreneurs. Effectual logic focuses on an entrepreneur's means rather than predetermined goals, leveraging contingencies and forming partnerships. The document also discusses lean startup methodology, which emphasizes validated learning about customers through short development cycles of hypotheses, experiments and measuring data. Entrepreneurs play a key role in bringing new firms and markets, but may need managers to help large firms scale over time.