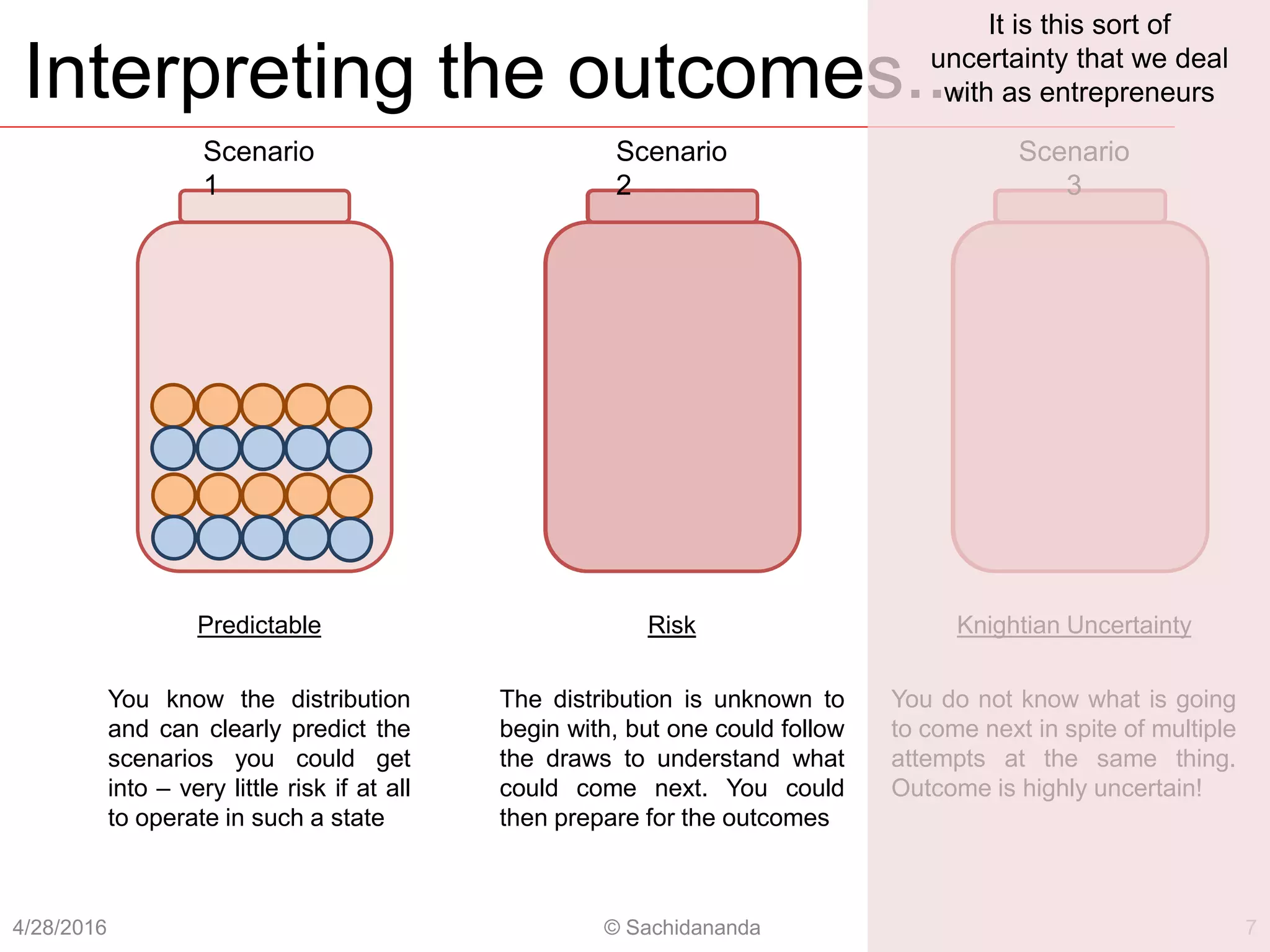
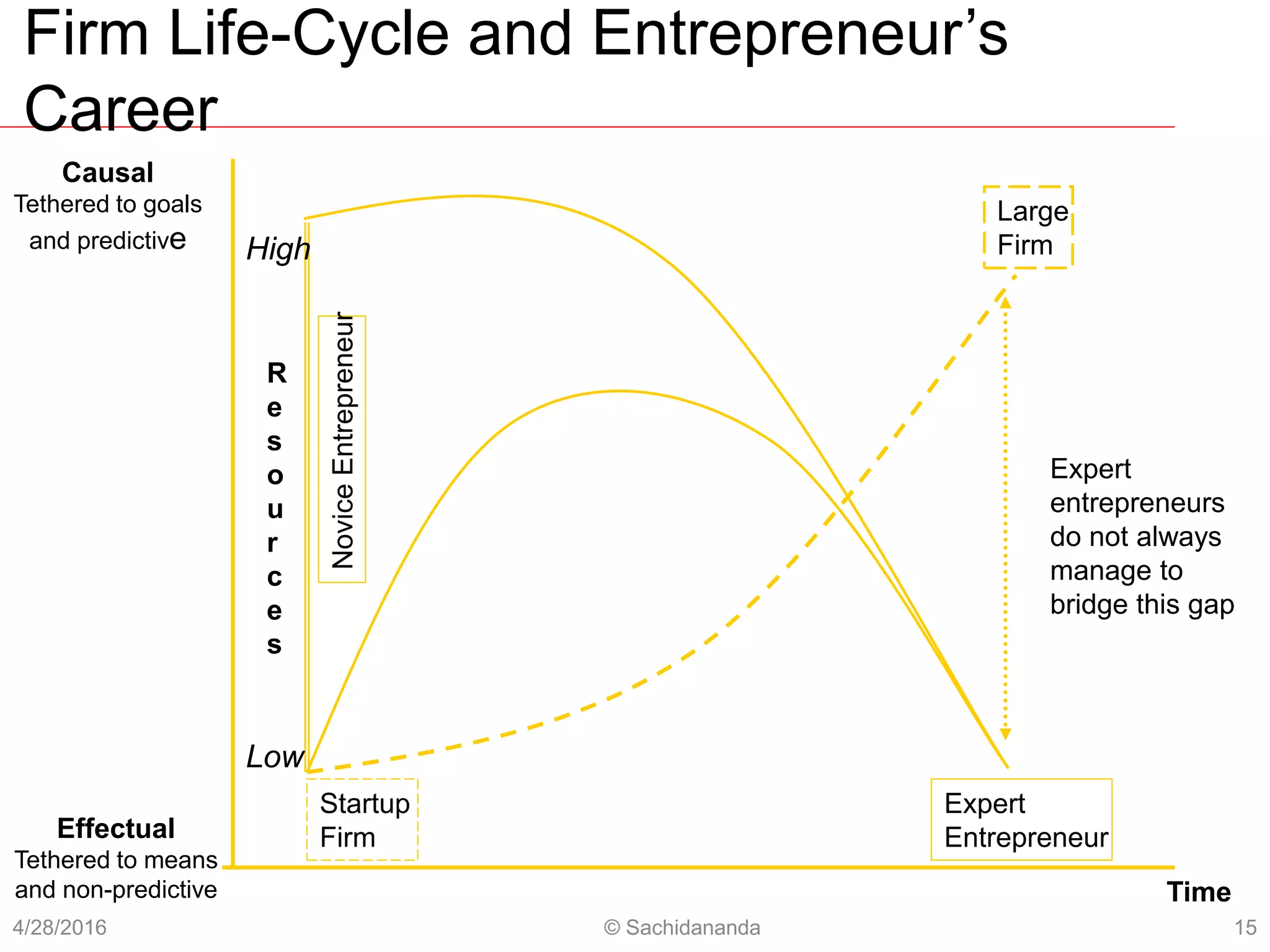
The document discusses how expert entrepreneurs think differently than managers. It presents 5 principles of effectuation that entrepreneurs use - (1) starting with means rather than goals, (2) focusing on affordable loss, (3) leveraging contingencies, (4) forming partnerships rather than competing, and (5) controlling outcomes rather than predicting them. In contrast, managers tend to use causal logic, focusing on pre-set goals, expected returns, and avoiding surprises. The document argues that effectuation offers entrepreneurs more control in unpredictable environments by co-creating the future through stakeholder commitments rather than attempting predictive control.