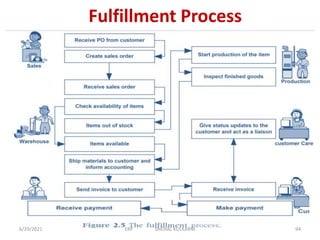
The document discusses various aspects of implementing an ERP system, including strategies, challenges, and approaches. It describes the big bang approach where all modules go live at once, replacing the old system entirely. Alternatively, a phased approach implements modules sequentially. A parallel approach runs the old and new systems simultaneously before a switch. Key factors in choosing an approach include company size, centralized processes, and urgency of the ERP solution. Successful implementation depends on careful planning, change management, training, and addressing challenges like resistance to change.



































![Survey Results – Updated April 1st
• Author[1] recently hosted a survey to find out which
ERP implementation strategies are the most popular
and most successful. With the help of Twitter and our
favorite industry bloggers, he received 85 responses
from organizations that have been involved in an
implementation. His survey was brief and informal with
just four simple questions:
– Which implementation strategy did your organization
choose? Big bang, phased rollout, parallel adoption,
combo of big bang and phased rollout, or other.
– If you selected other, please describe the strategy you
chose.
– Was the implementation a success?
– If you selected no, please explain why.
6/29/2021 39
ERP SNEHAL KULKARNI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-erpimplementation-210629114934/85/Chapter-2-erp-implementation-37-320.jpg)