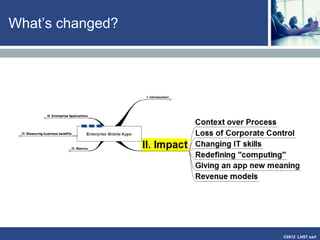
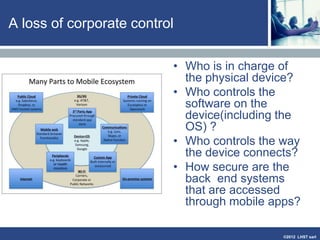
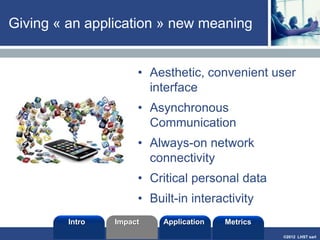
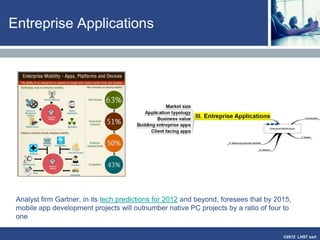
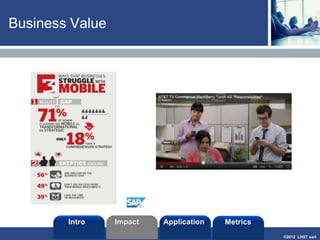
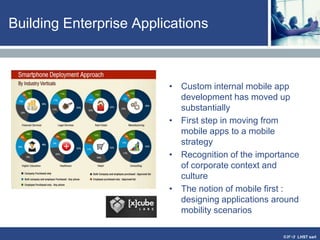
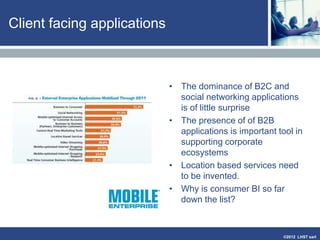
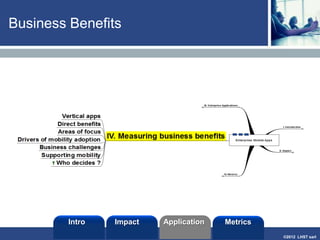
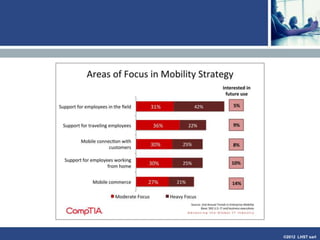
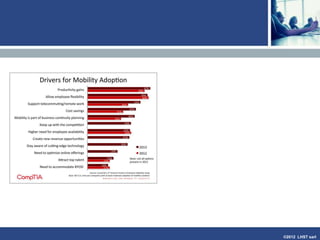
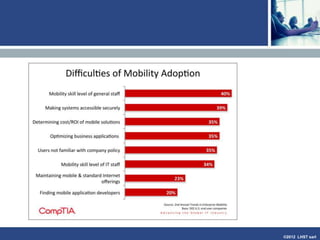
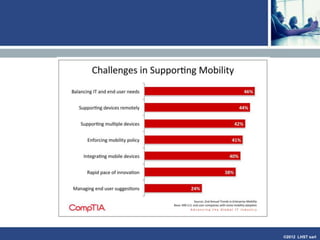
The document discusses enterprise mobile applications. It begins with an introduction to mobile applications and their classification as browser-based, native, or hybrid. It then discusses factors to consider when deciding between web and native apps. Key points made include the size and growth of the app economy, trends in mobile development skills and revenue models, and challenges organizations face in developing enterprise mobile solutions. Benefits are seen as increased efficiency, sales opportunities, and regulatory compliance, but skills gaps and integrating innovation pose challenges.