The document provides an introduction to the EMCLI (Enterprise Manager Command Line Interface) tool. Some key points:
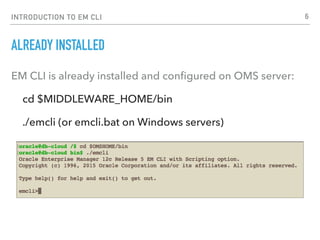
- EMCLI allows accessing Enterprise Manager functionality from a command line instead of the web interface. It comes pre-installed on the OMS server and can also be installed on other machines.
- There are three modes of EMCLI - Standard, Interactive, and Scripting. Scripting mode allows running Python scripts containing EMCLI verbs.
- Over 400 verbs are available across 75+ categories to perform various monitoring and management tasks. Common verbs include get_targets, add_target, update_db_password.
- Python is introduced as the scripting language used with EMCLI in Script












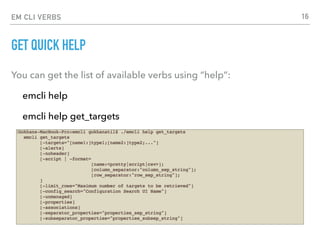
![EM CLI VERBS
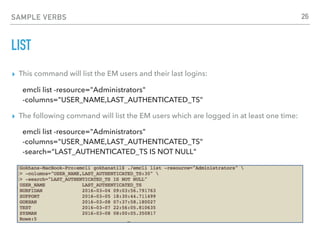
EM CLI VERBS IN STANDARD MODE
In standard mode, EM CLI expect you enter a verb as the first
parameter. Verbs may take zero or more arguments as input.
emcli verb -1st_argument="value"
[ -2nd_ argument="value" ]
[ -3rd_ argument="value" ]
[ -4th_ argument ]
…
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/em13c-writepowerfulscriptswithemcli-ougn-160313134052/85/Enterprise-Manager-Write-powerful-scripts-with-EMCLI-17-320.jpg)





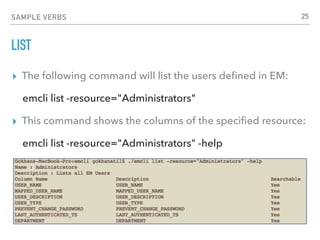



![FUNDAMENTALS OF PYTHON
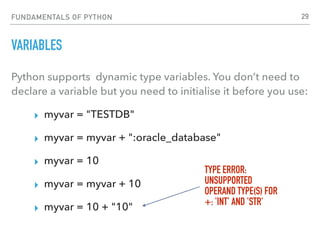
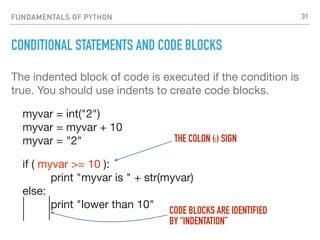
DICTIONARY AND LIST OBJECTS
Dictionary objects, list objects and iterations:
mydict = { 'Name':'Gokhan', 'Age':40 }
mydict['Name'] = "Gokhan"
mylist = ["Joe","William","Jack","Averell"]
mylist[0] = "Joe"
for i in mylist:
print i
SIMILAR TO
JSON. KEY=VALUE
IT WILL PRINT ALL ELEMENTS IN “MYLIST”
ARRAY. USE INDEX TO REACH VALUE
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/em13c-writepowerfulscriptswithemcli-ougn-160313134052/85/Enterprise-Manager-Write-powerful-scripts-with-EMCLI-32-320.jpg)


![EM CLI AND PYTHON
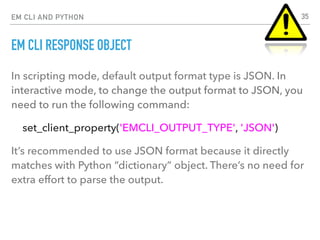
EM CLI RESPONSE OBJECT
Let’s get the response from a verb:
mytargets = get_targets( target="oracle_database" )
type(mytargets.out())
<type 'dict'>
mytargets.out()
{'data': [{'Status': 'Up', 'Warning': '6', 'Status ID': '0', 'Target
Type': 'oracle_database', 'Critical': '64', 'Target Name':
'TESTDB'}, {…}, {…}, {…}] }
36](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/em13c-writepowerfulscriptswithemcli-ougn-160313134052/85/Enterprise-Manager-Write-powerful-scripts-with-EMCLI-36-320.jpg)
![EM CLI AND PYTHON
EM CLI RESPONSE OBJECT
A response always contain a “data” item which is a list object:
type(mytargets.out()['data'])
<type ‘list'>
mytargets.out()['data']
[ {'Status': 'Up', 'Warning': '6', 'Status ID': '0', 'Target Type':
'oracle_database', 'Critical': '64', 'Target Name': 'TESTDB'},{…},
{…}, {…} ]
type(mytargets.out()['data'][0])
<type 'dict'>
37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/em13c-writepowerfulscriptswithemcli-ougn-160313134052/85/Enterprise-Manager-Write-powerful-scripts-with-EMCLI-37-320.jpg)
![EM CLI AND PYTHON
EM CLI RESPONSE OBJECT
We can iterate over the items of the list:
for DB in mytargets.out()['data']:
print DB['Target Name'], DB['Status']
DICT / JSON
LIST (DATA)
DICT
DICT
DICT
DICT
DICT
38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/em13c-writepowerfulscriptswithemcli-ougn-160313134052/85/Enterprise-Manager-Write-powerful-scripts-with-EMCLI-38-320.jpg)

![SAMPLE SCRIPTS
CLEAR STATELESS ALERTS
Save the following code in a file (clearalerts.py) and run it as
“emcli @clearalerts.py”:
if login( username="GOKHAN" ).exit_code()==0:
mytargets=get_targets( targets="oracle_database" )
for DB in mytargets.out()['data']:
clear_stateless_alerts(
target_name=DB['Target Name'],
target_type=DB['Target Type'], older_than="0" )
40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/em13c-writepowerfulscriptswithemcli-ougn-160313134052/85/Enterprise-Manager-Write-powerful-scripts-with-EMCLI-40-320.jpg)
![SAMPLE SCRIPTS
CHANGE DBSNMP PASSWORDS
if len(sys.argv) <> 2:
print "Usage: emcli @change_dbsnmp_passwords.py oldpwd newpwd"
exit()
if login( username="GOKHAN" ).exit_code()==0:
mytargets=get_targets( targets="%_database" )
for DB in mytargets.out()['data']:
try:
update_db_password (target_name=DB['Target Name'],
target_type=DB['Target Type'] ,
change_at_target="yes",user_name="dbsnmp",
old_password=sys.argv[0],
new_password=sys.argv[1],
retype_new_password=sys.argv[1])
except emcli.exception.VerbExecutionError, e:
print e.error()
41](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/em13c-writepowerfulscriptswithemcli-ougn-160313134052/85/Enterprise-Manager-Write-powerful-scripts-with-EMCLI-41-320.jpg)
![SAMPLE SCRIPTS
PROMOTE UNMANAGED DATABASES
lg = login( username="SYSMAN" )
if lg.exit_code() <> 0:
print lg.error()
exit()
utargets=get_targets( "unmanaged", properties=True,
targets="oracle_database" )
for target in utargets.out()['data']:
add_target( name=target['Target Name'], type=target['Target Type'],
host=target['Host Info'].split(';')[0].split(':')[1],
credentials="UserName:dbsnmp;password:xyz;Role:Normal",
properties=target['Properties'] )
POSITIONAL PARAMETERS
42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/em13c-writepowerfulscriptswithemcli-ougn-160313134052/85/Enterprise-Manager-Write-powerful-scripts-with-EMCLI-42-320.jpg)