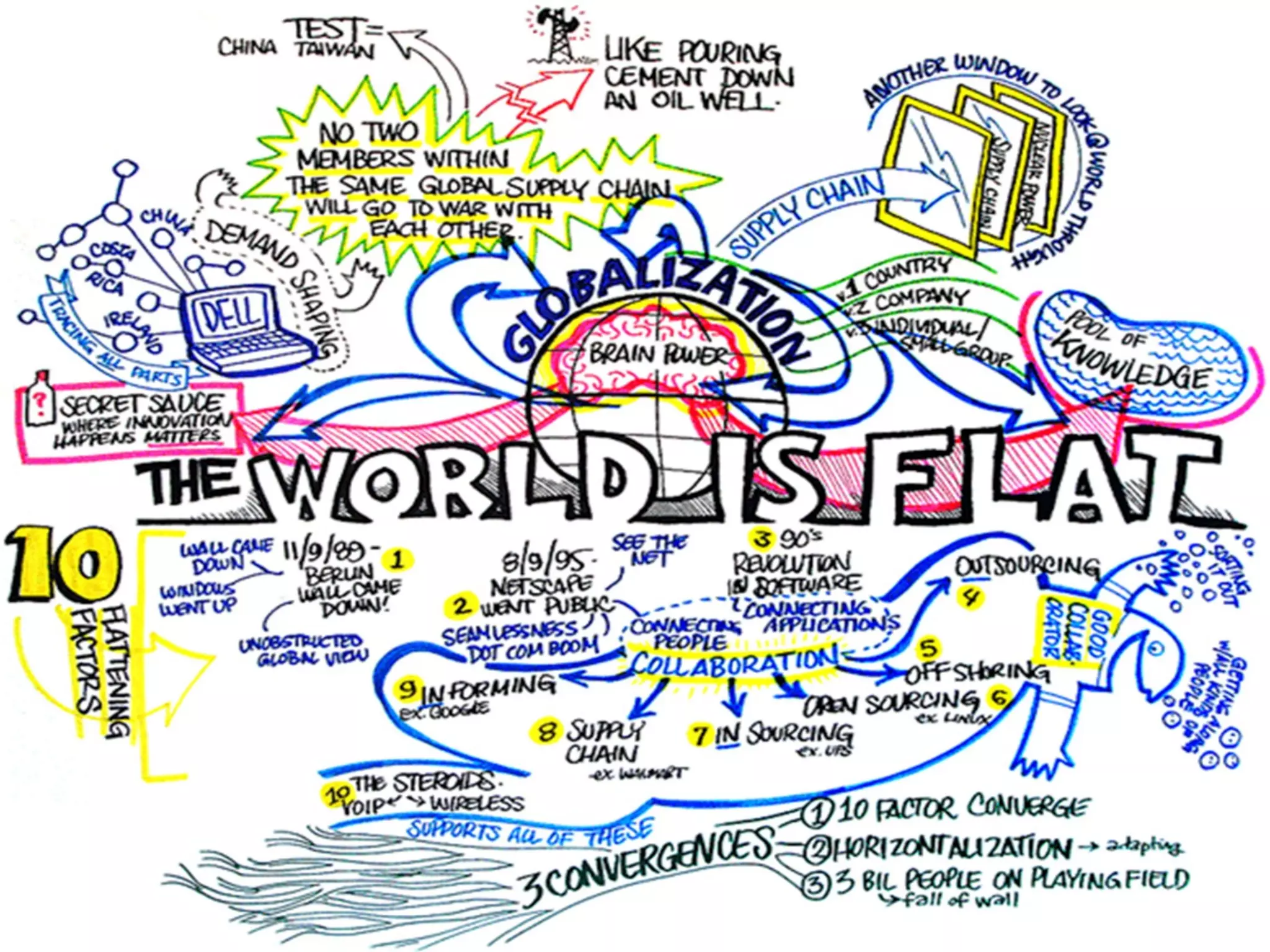
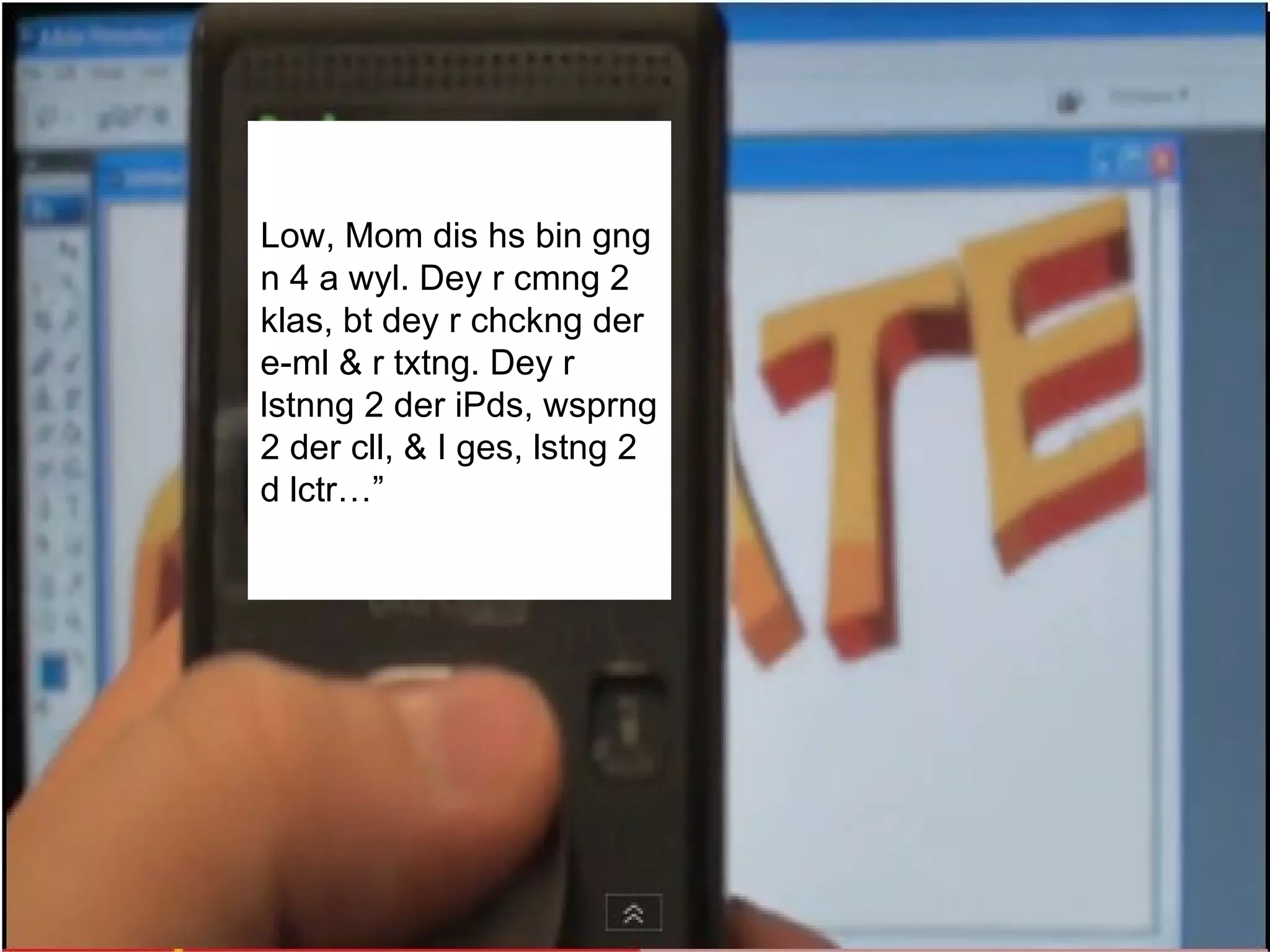
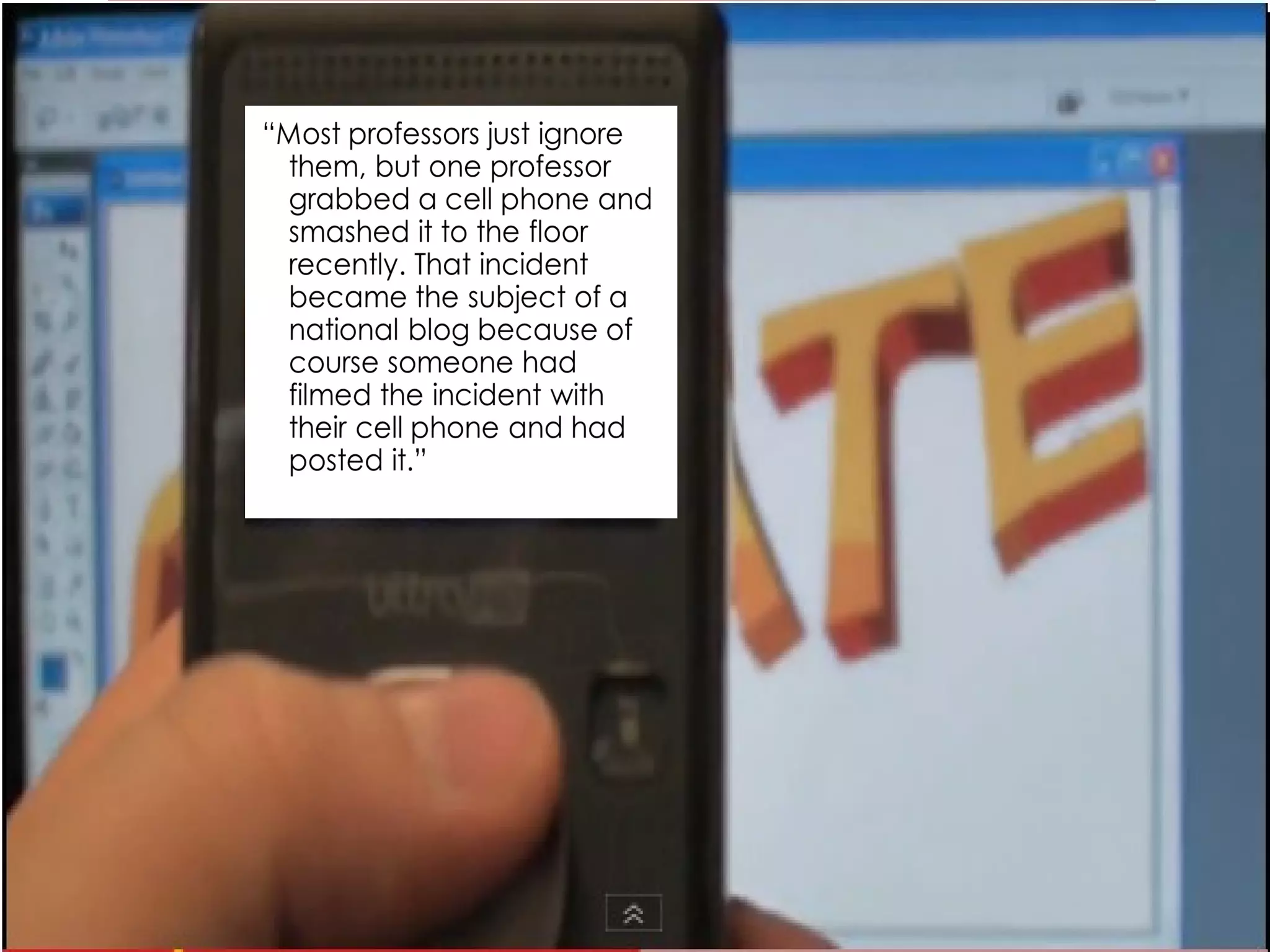
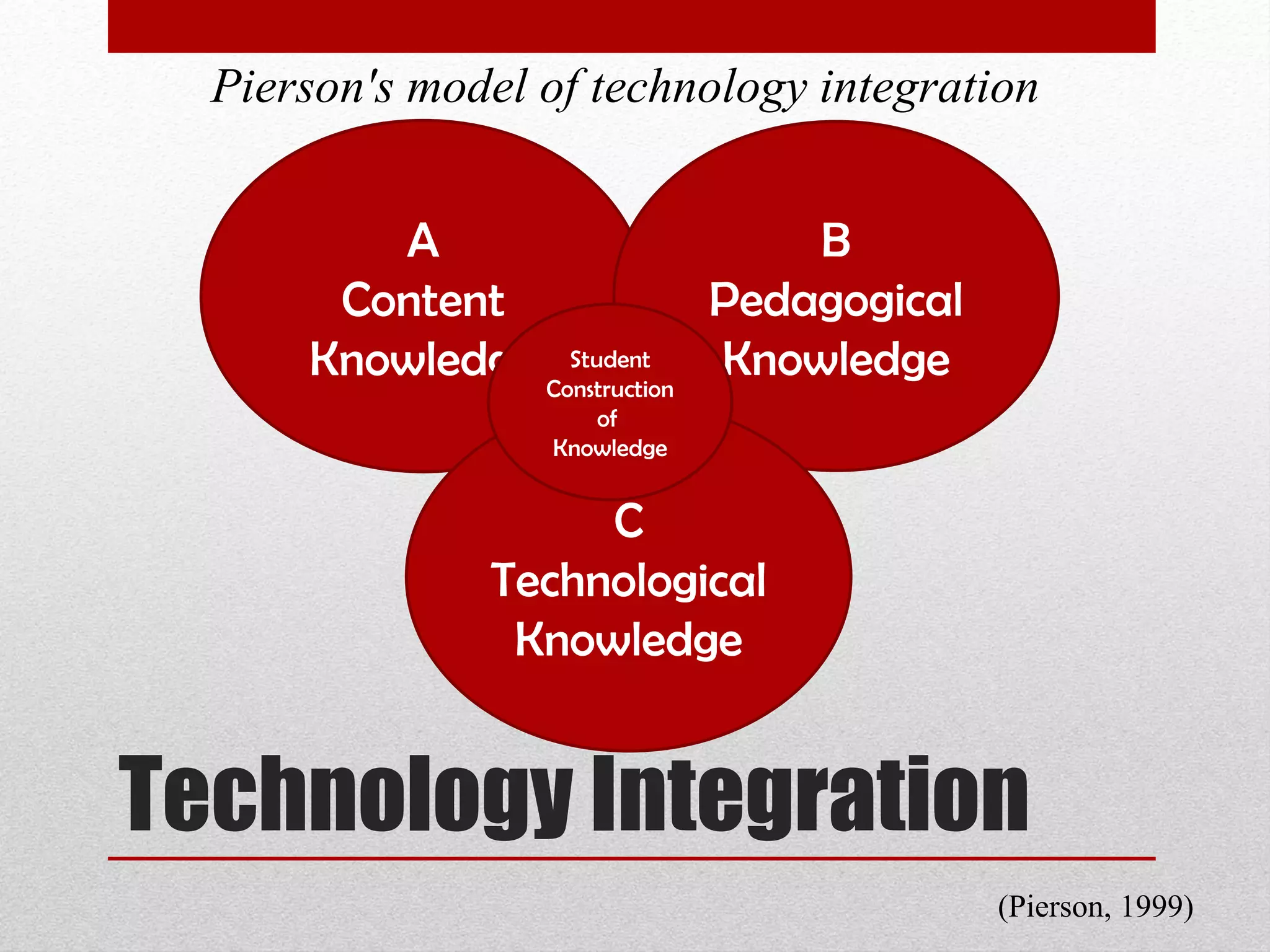
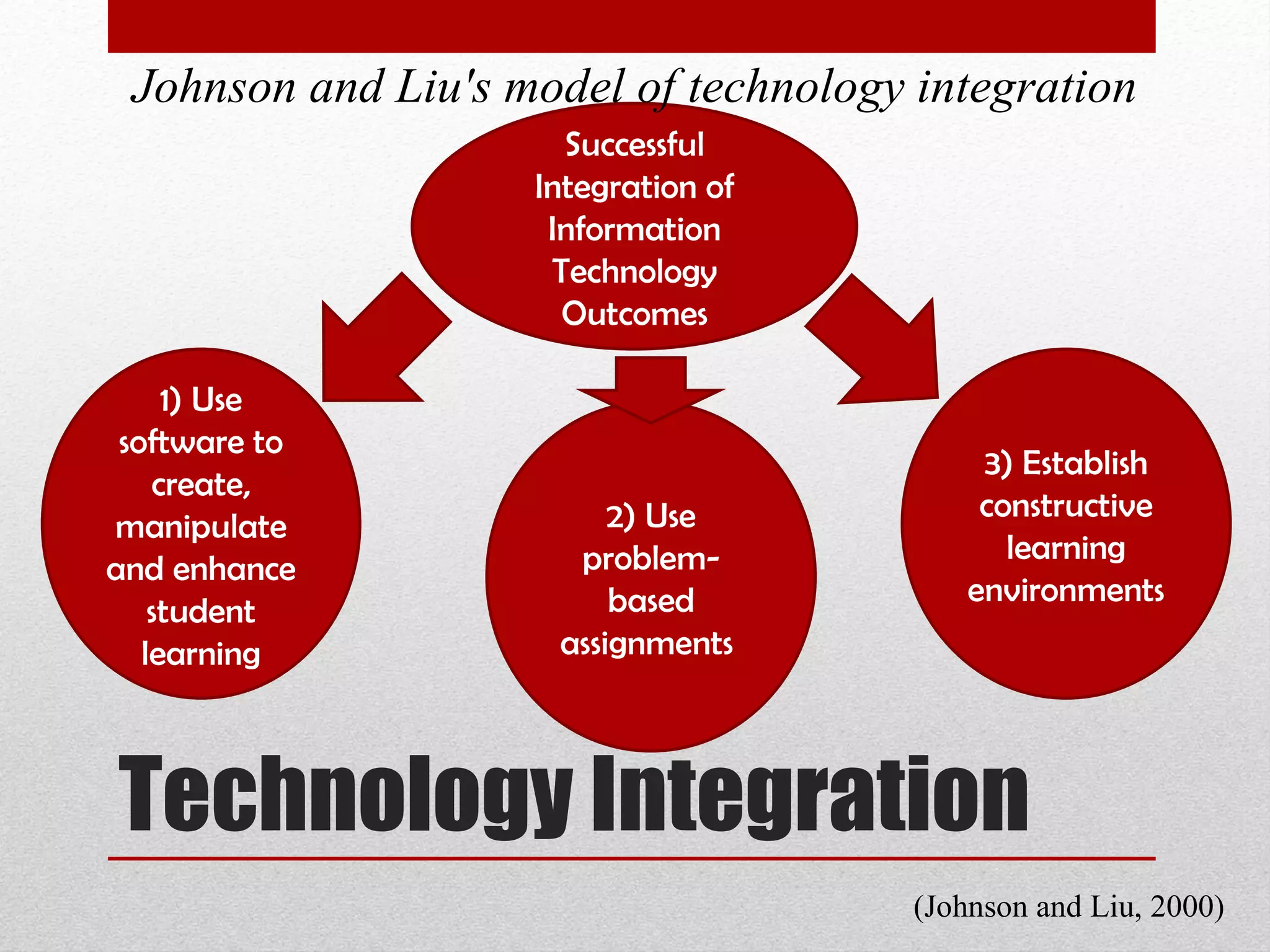
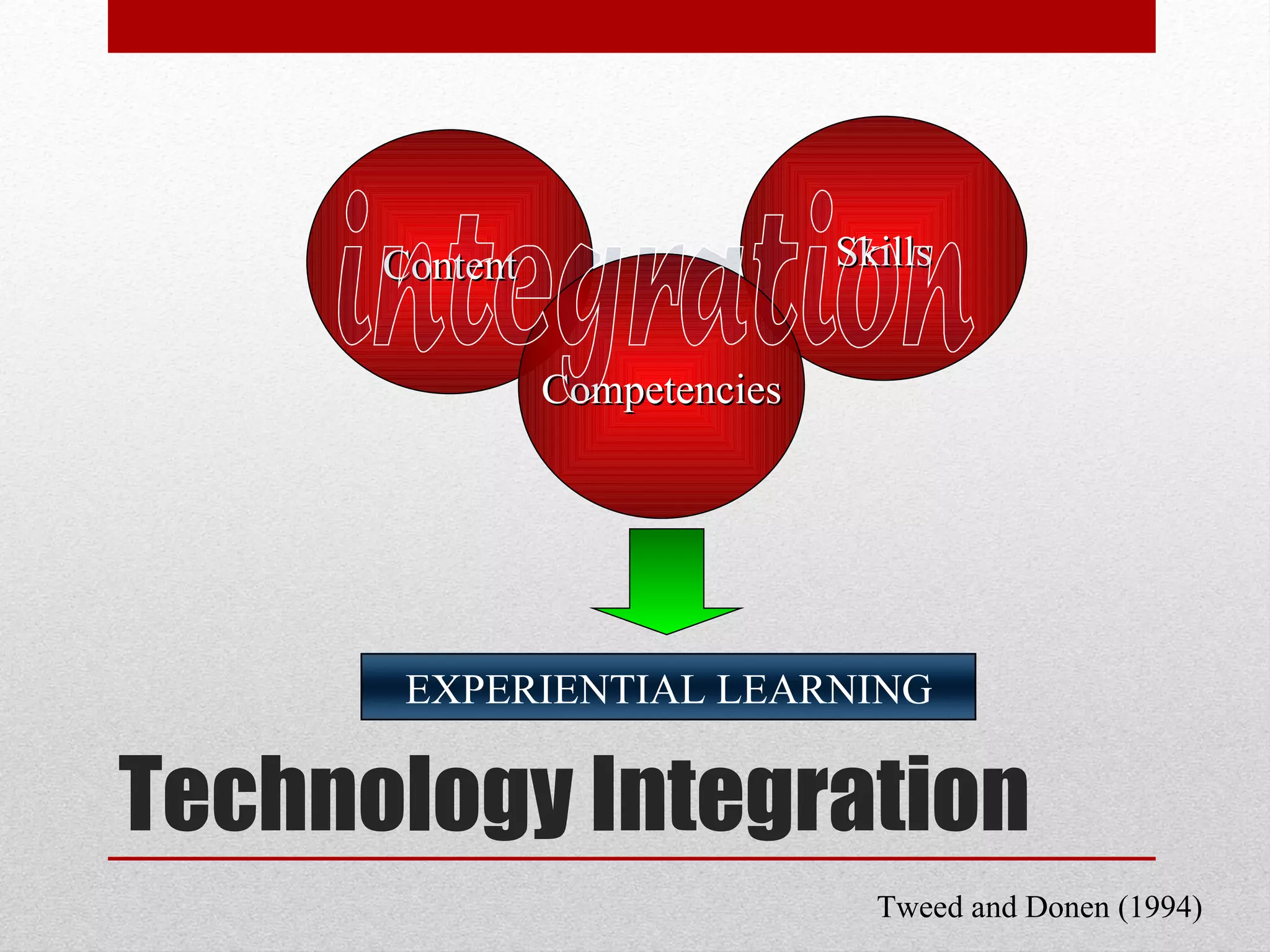
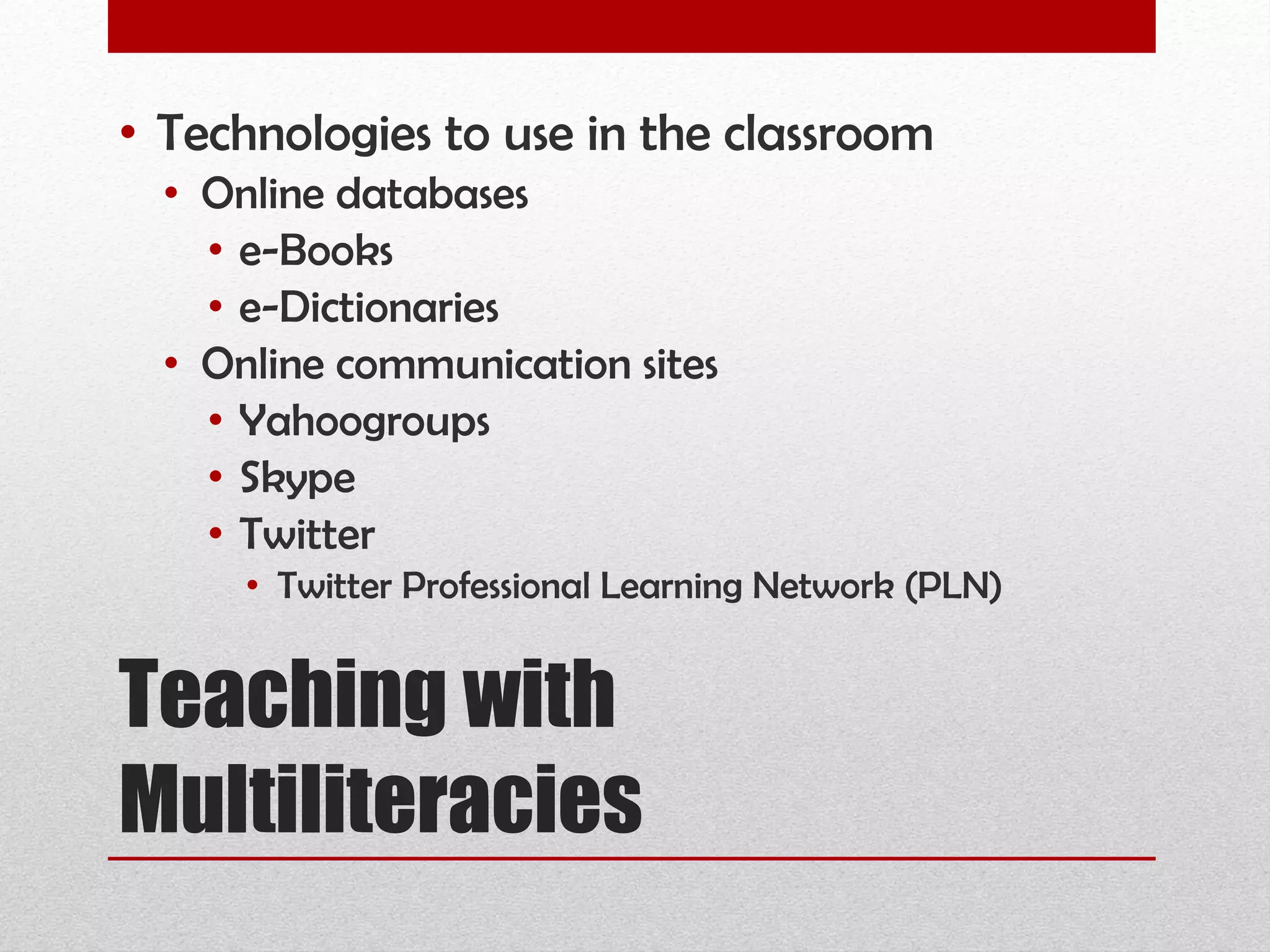
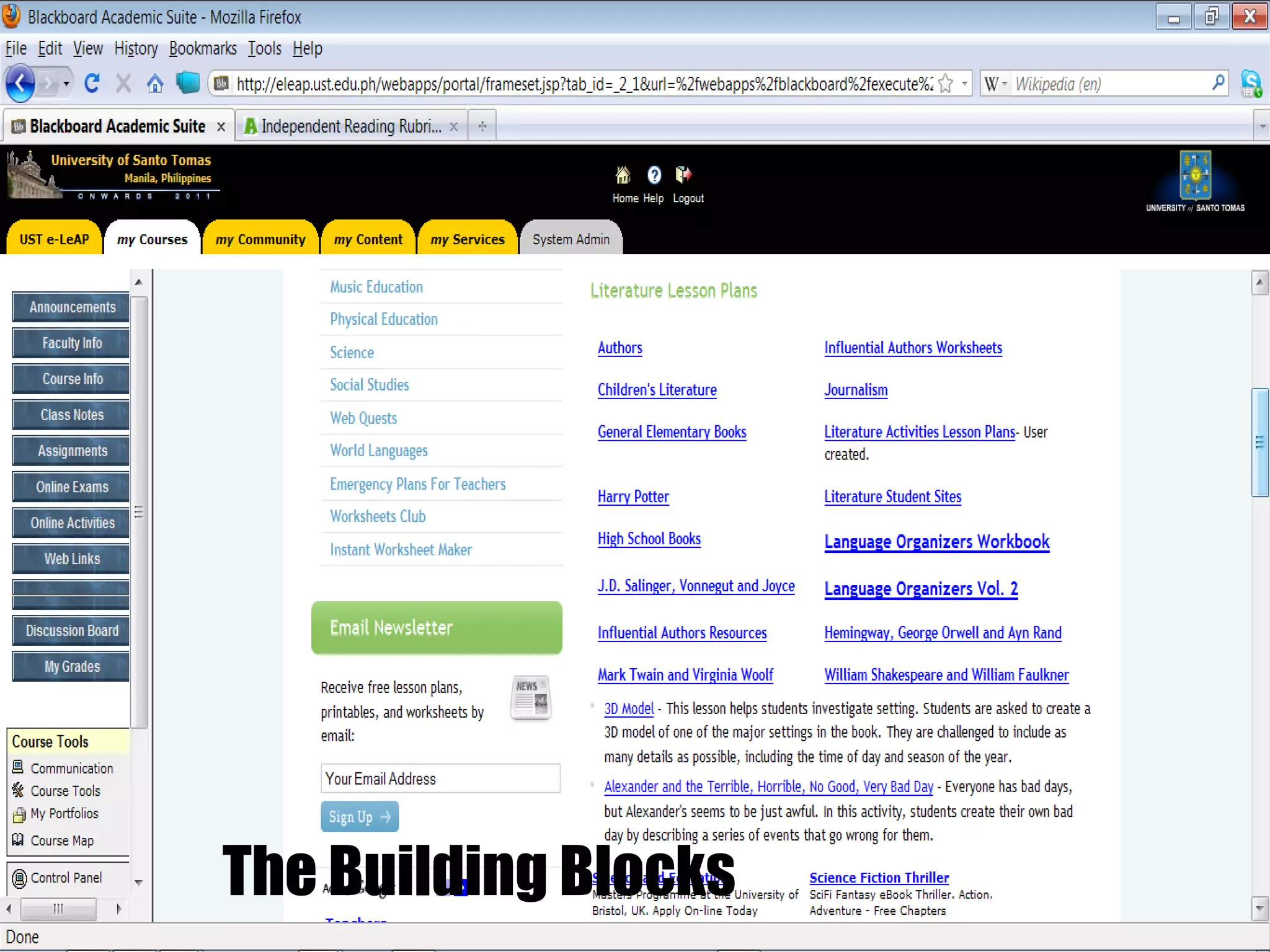
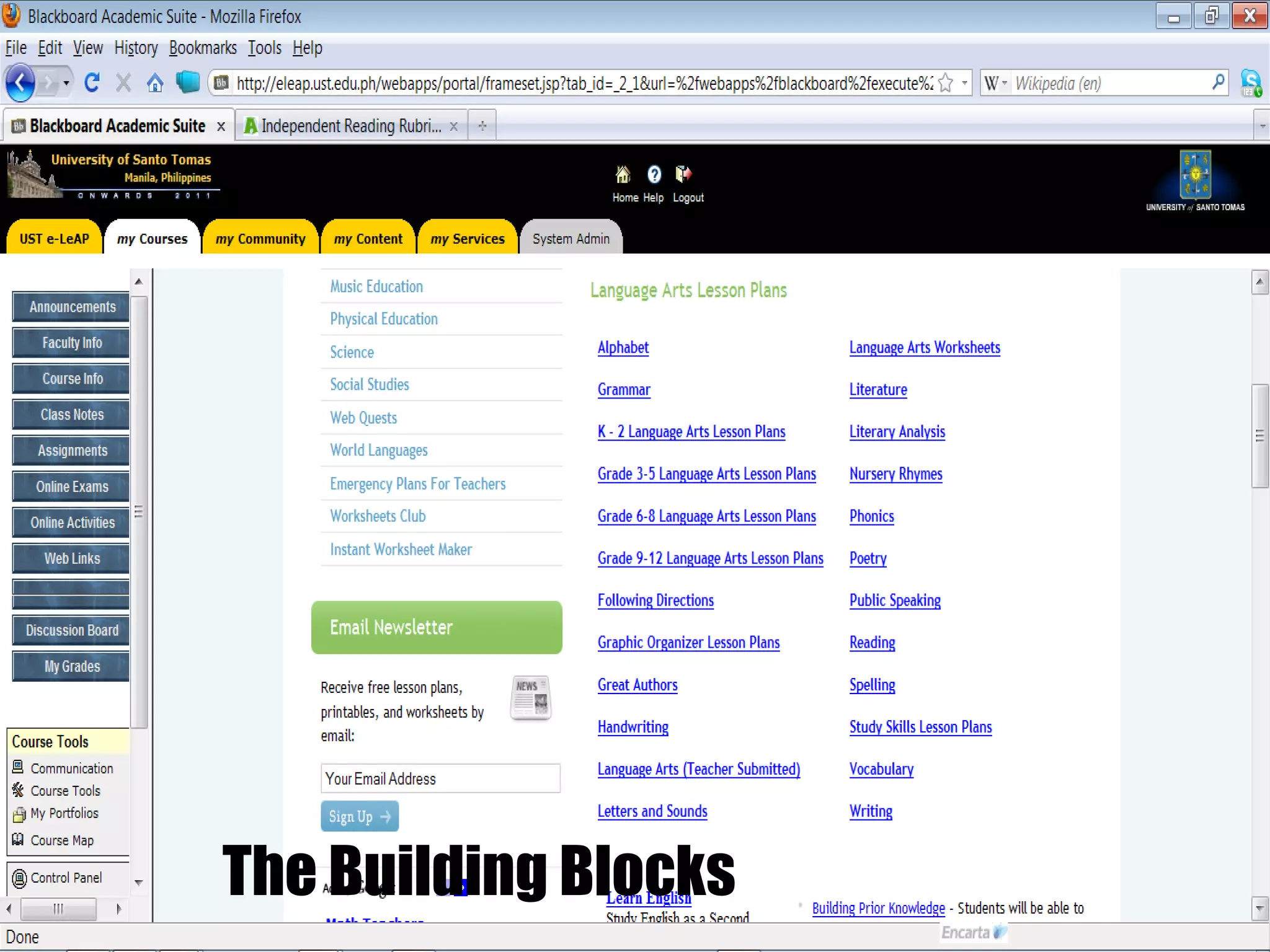
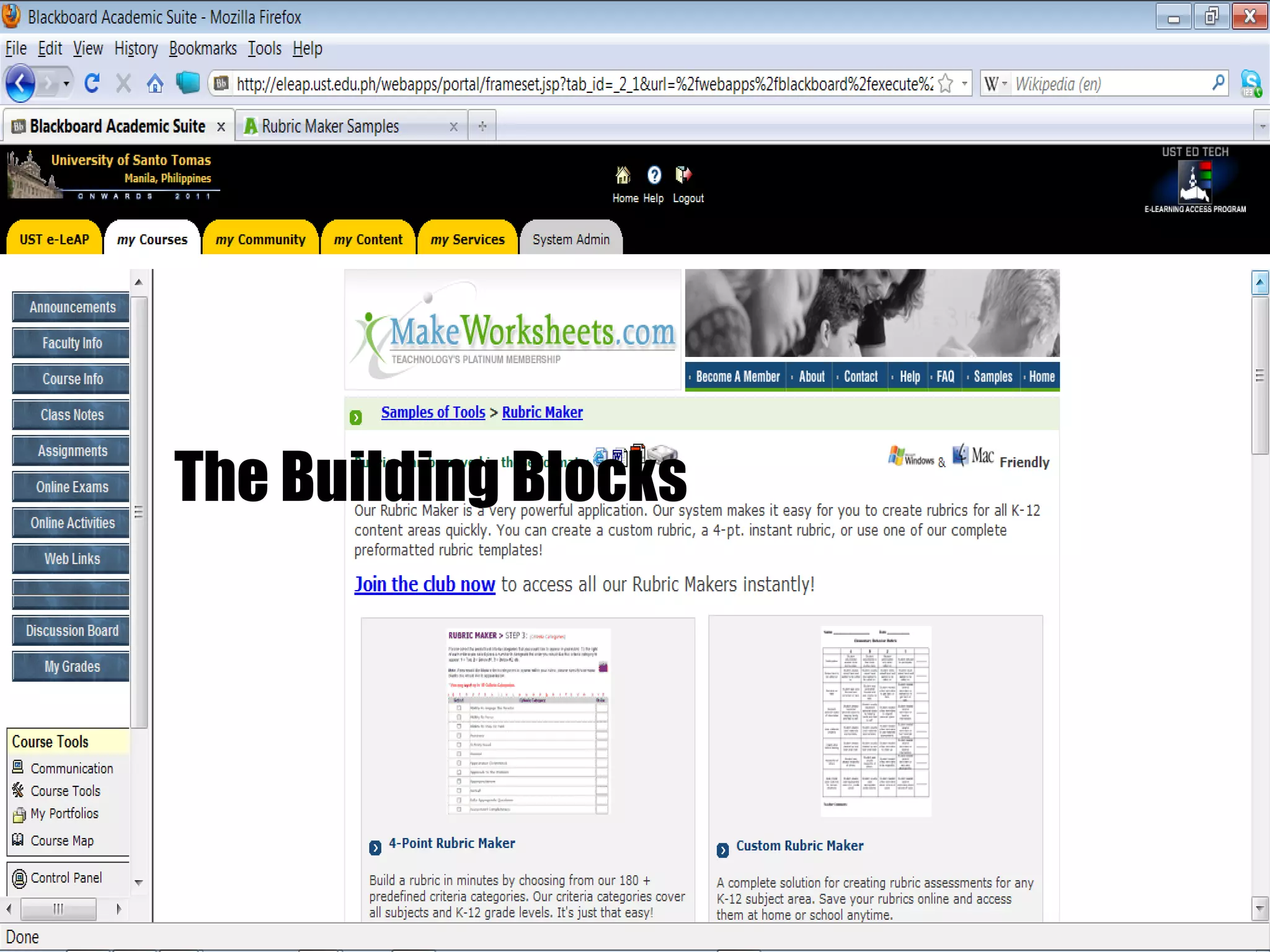
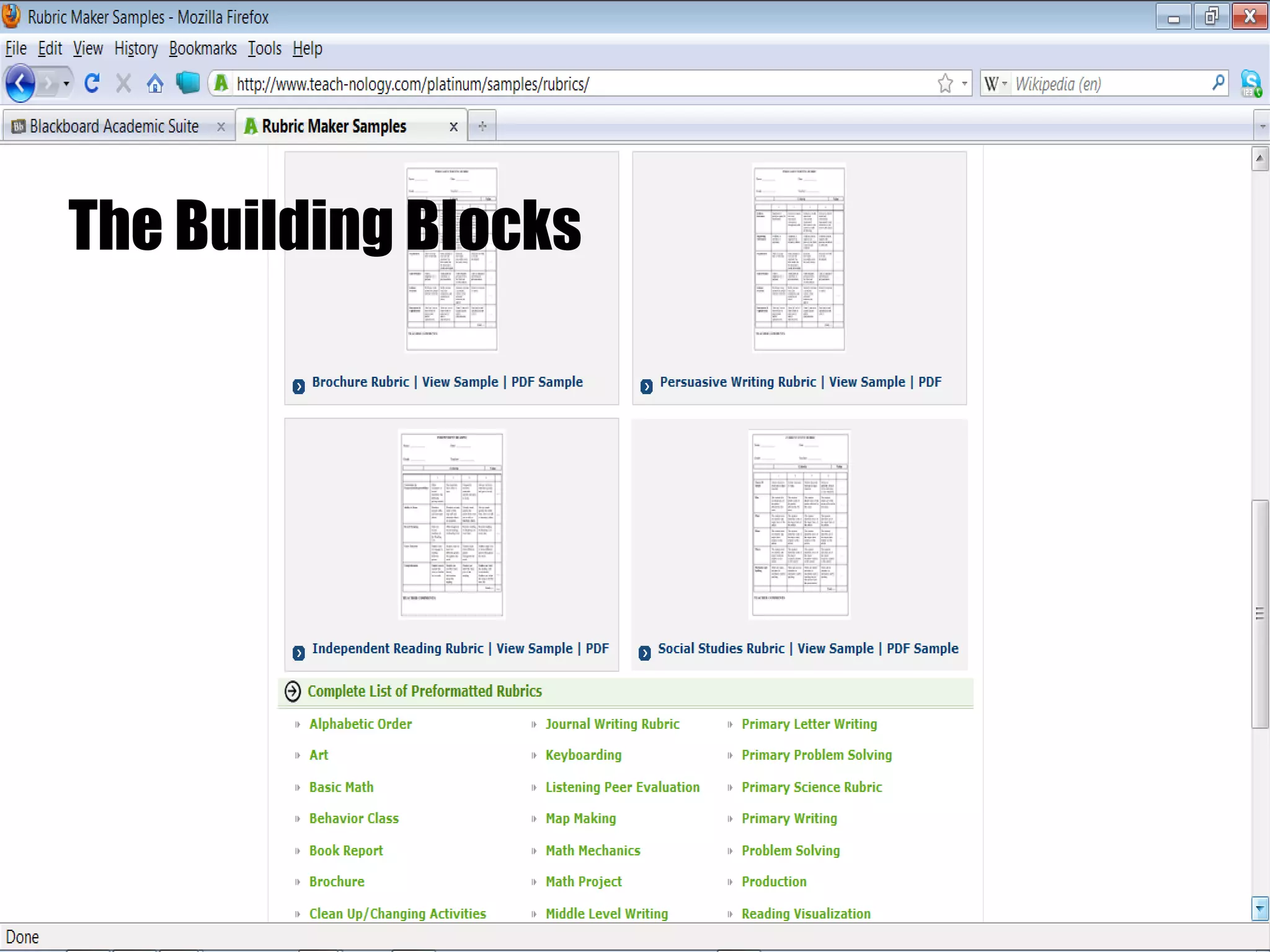
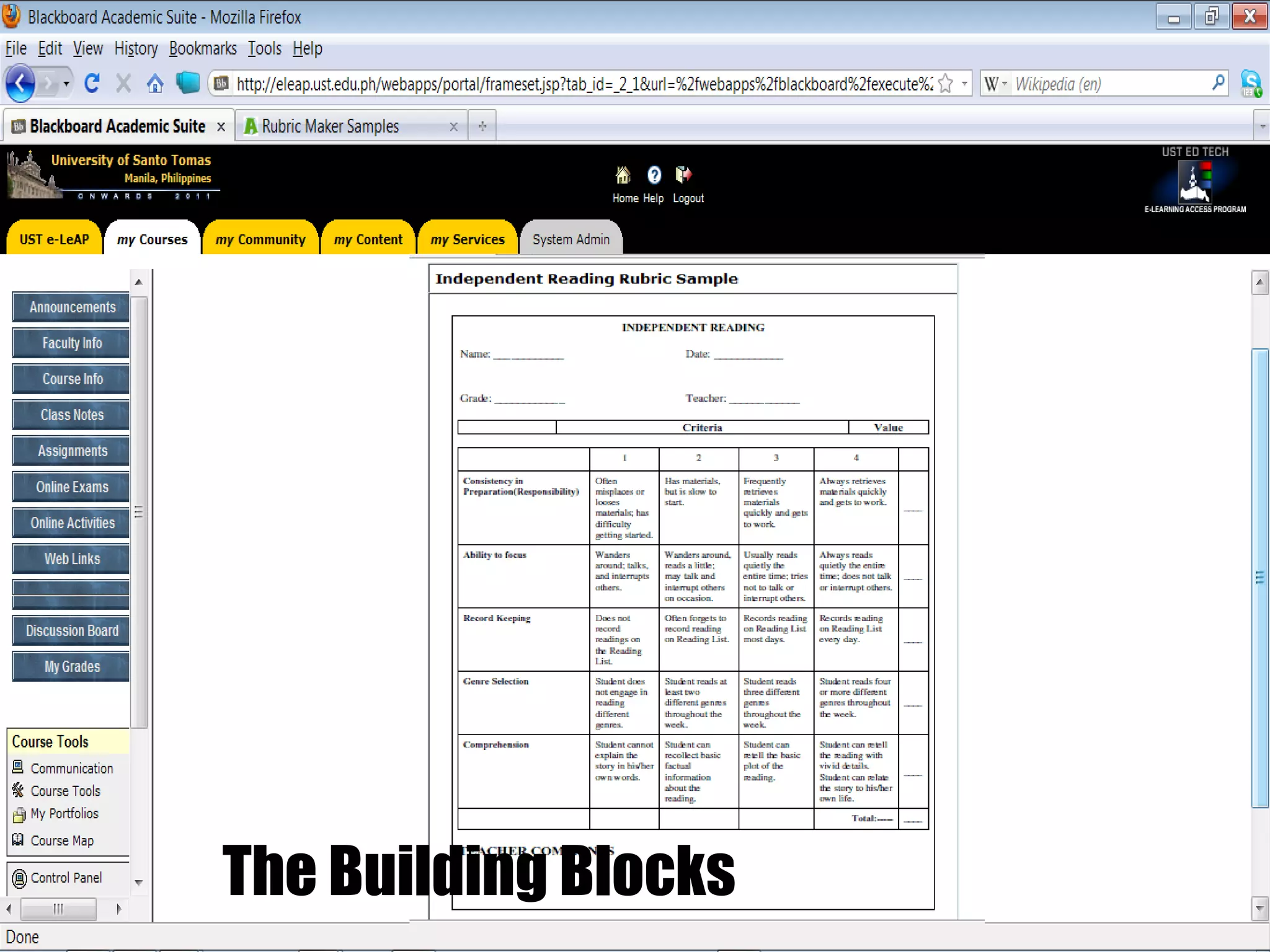
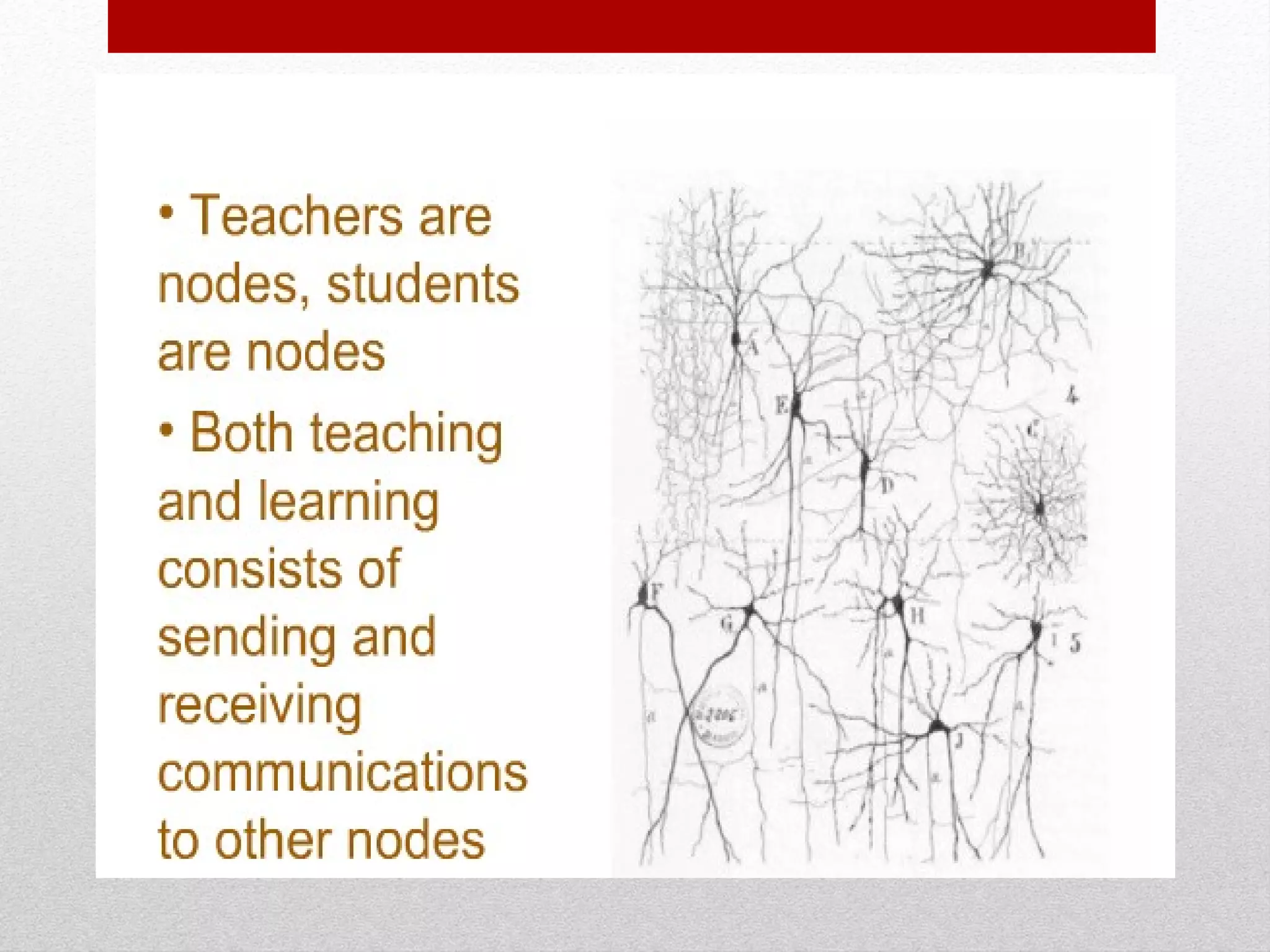
The document discusses strategies for integrating technology into English education classrooms. It defines technology integration as using technology as an instructional tool to deliver curriculum content. It provides several models for technology integration and discusses barriers that teachers face in integrating technology. It also provides examples of technologies that can be used in the classroom and strategies to encourage higher levels of teacher technology integration, such as developing a clear vision, building professional learning networks, investing in professional development, and developing a reflective practice.