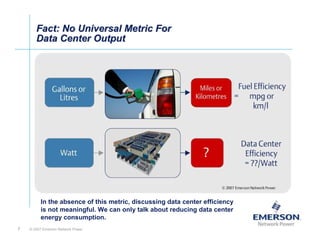
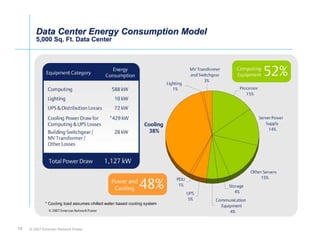
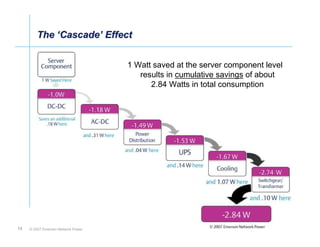
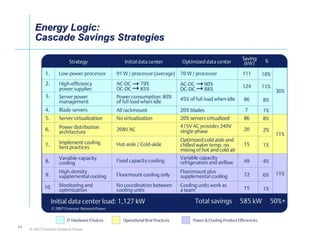
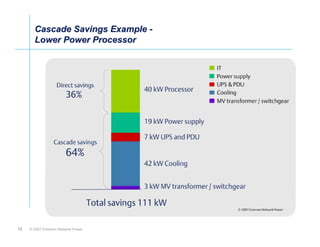
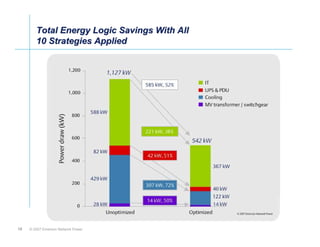
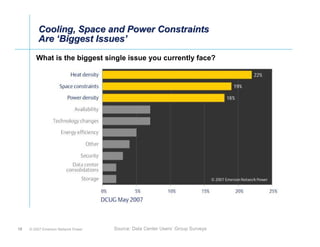
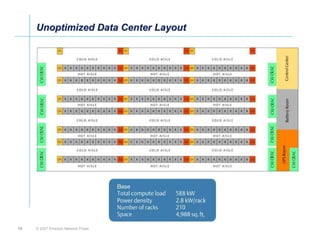
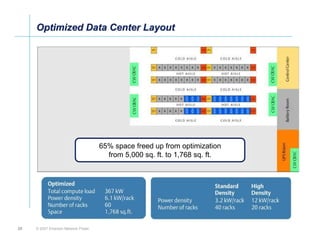
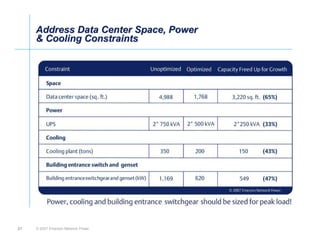
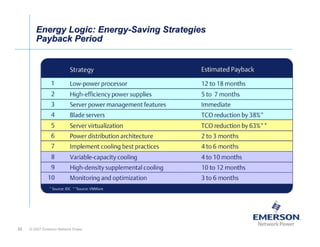
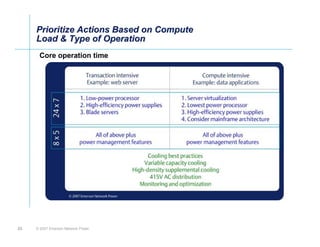
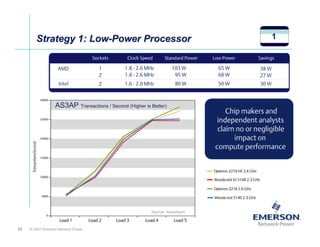
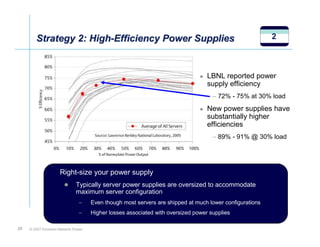
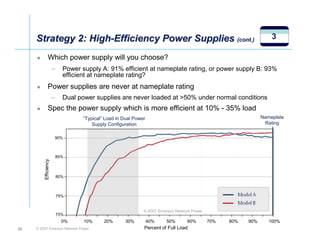
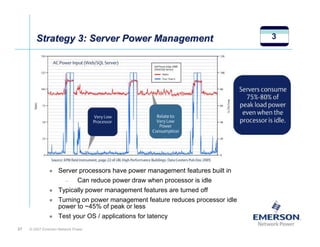
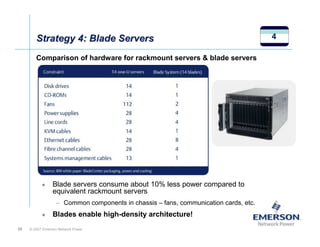
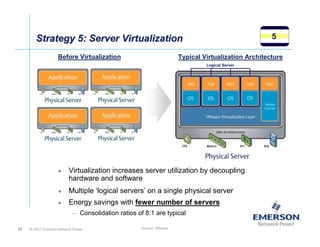
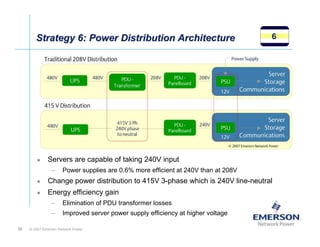
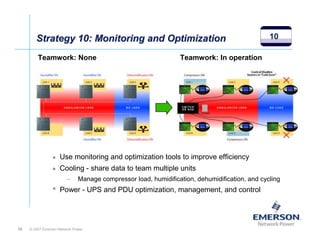
The document outlines a strategy called "Energy Logic" proposed by Emerson Network Power to reduce energy consumption in data centers. It identifies 10 strategies that can be implemented sequentially, starting at the IT equipment level and moving through supporting infrastructure. Implementing the strategies in order provides cascading energy savings without compromising availability or flexibility. The strategies include using more efficient processors, power supplies, server virtualization, optimized cooling practices, variable capacity cooling, and infrastructure monitoring. Applying all 10 strategies could potentially reduce total energy consumption in the modeled 5,000 square foot data center by over 50%.