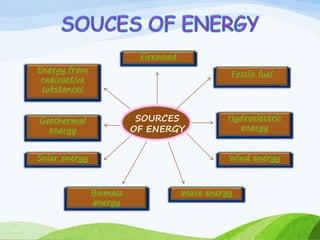
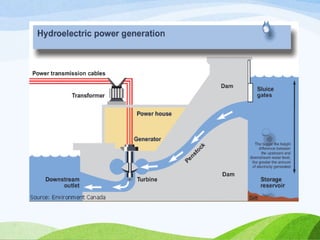
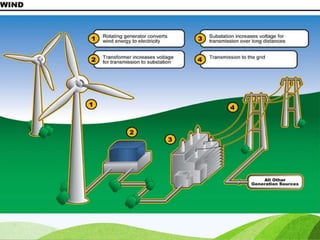
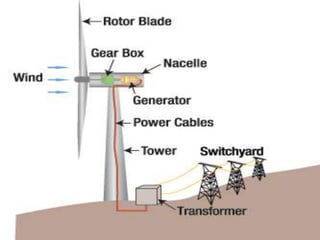
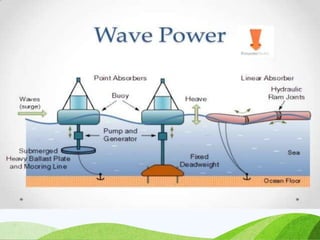
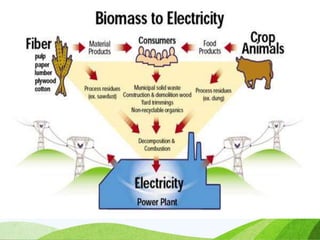
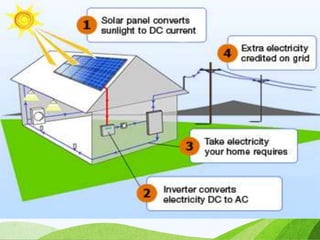
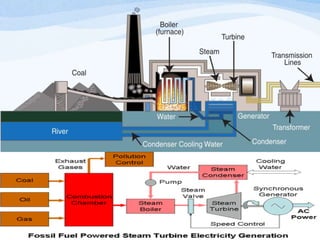
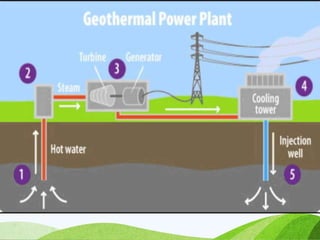
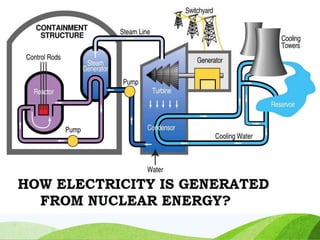
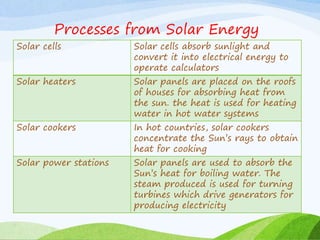
The document discusses various sources of energy including renewable sources like hydroelectric, wind, wave, solar, geothermal, biomass energy and non-renewable sources like fossil fuels, firewood and radioactive substances. It provides details on each source such as the process of generating energy, advantages and disadvantages. It emphasizes the importance of conserving non-renewable sources as supplies are limited and promoting greater use of renewable sources to reduce environmental pollution and damage from energy production and use.