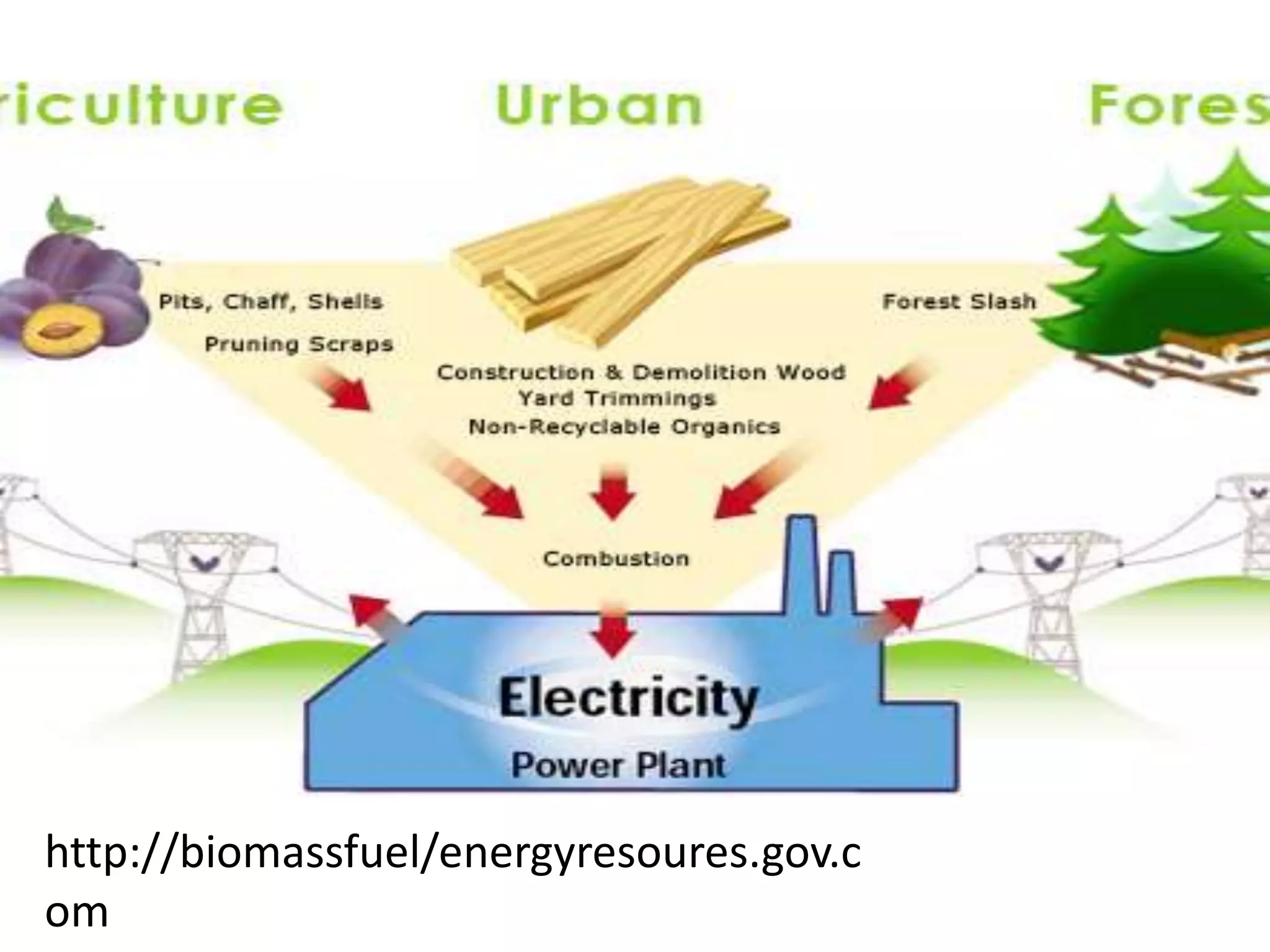
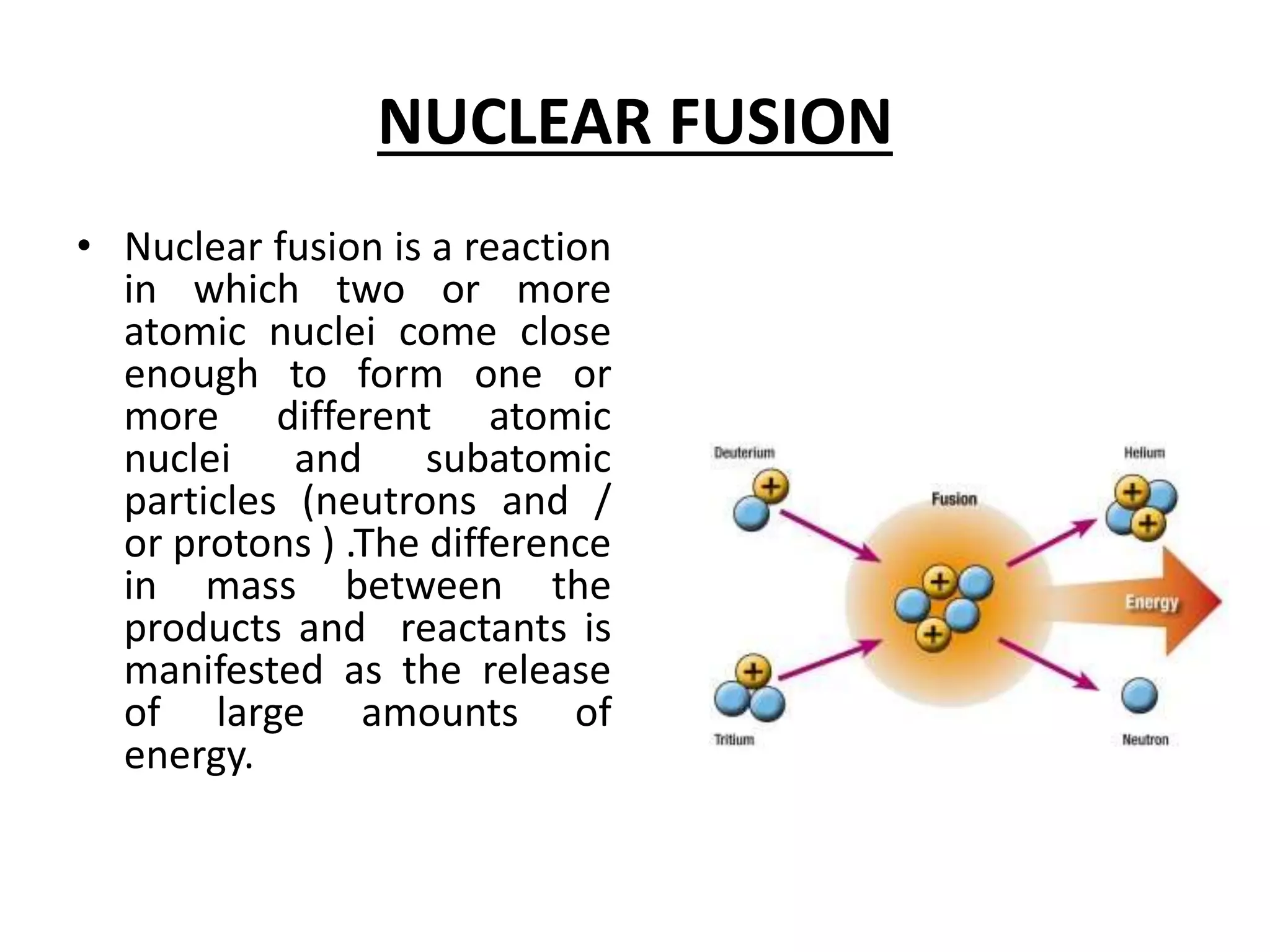
This document contains a presentation by Neha Singh on energy resources. It begins with an introduction defining energy and energy resources. It then classifies energy resources as renewable and non-renewable. Renewable resources discussed include solar, wind, hydro, and biomass energy. Non-renewable resources discussed are fossil fuels like coal, petroleum, and natural gas, as well as nuclear energy obtained from fission and fusion. The presentation emphasizes the importance of energy resources in India and their various applications. It concludes with the presenter's views and references.