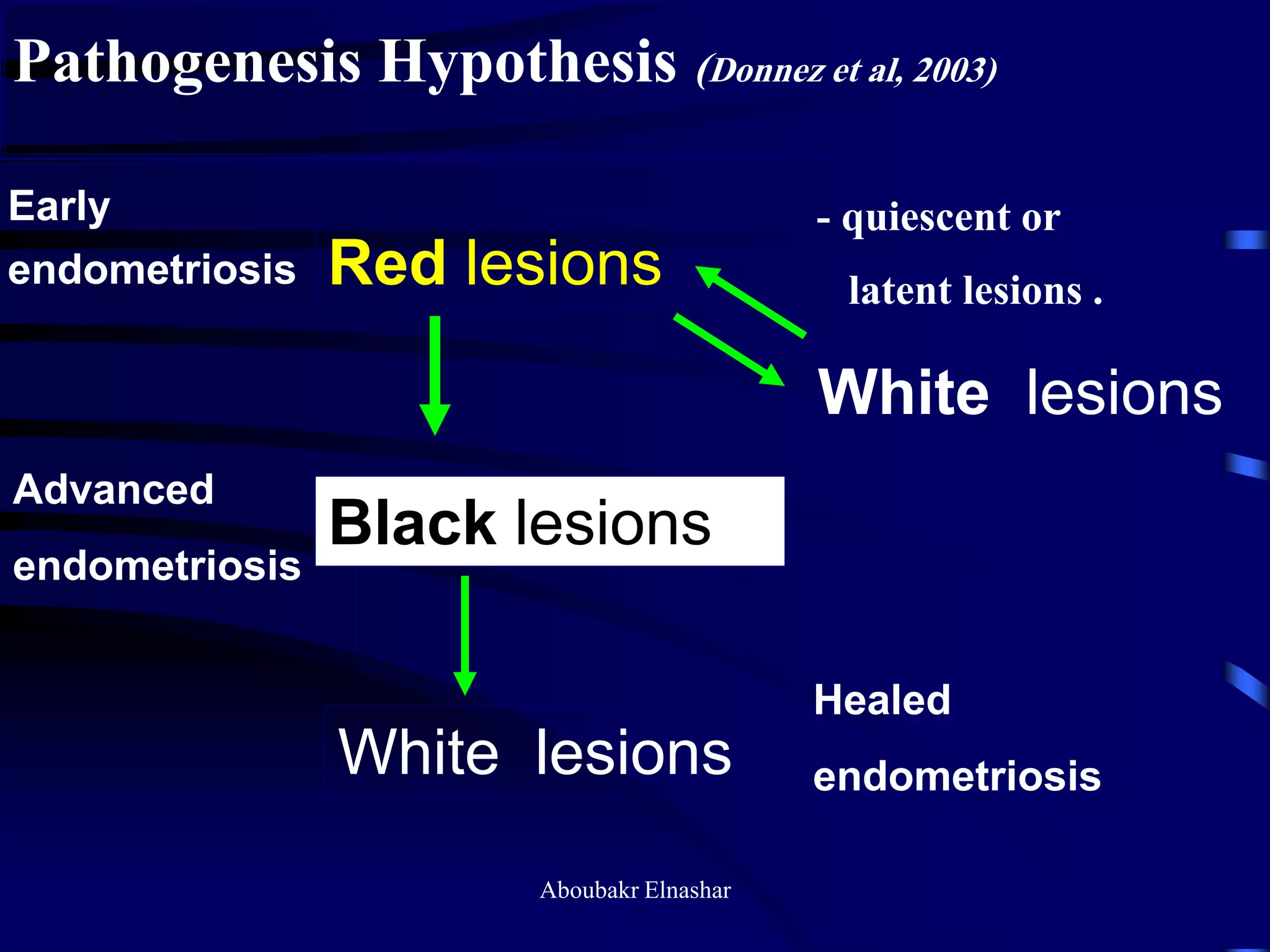
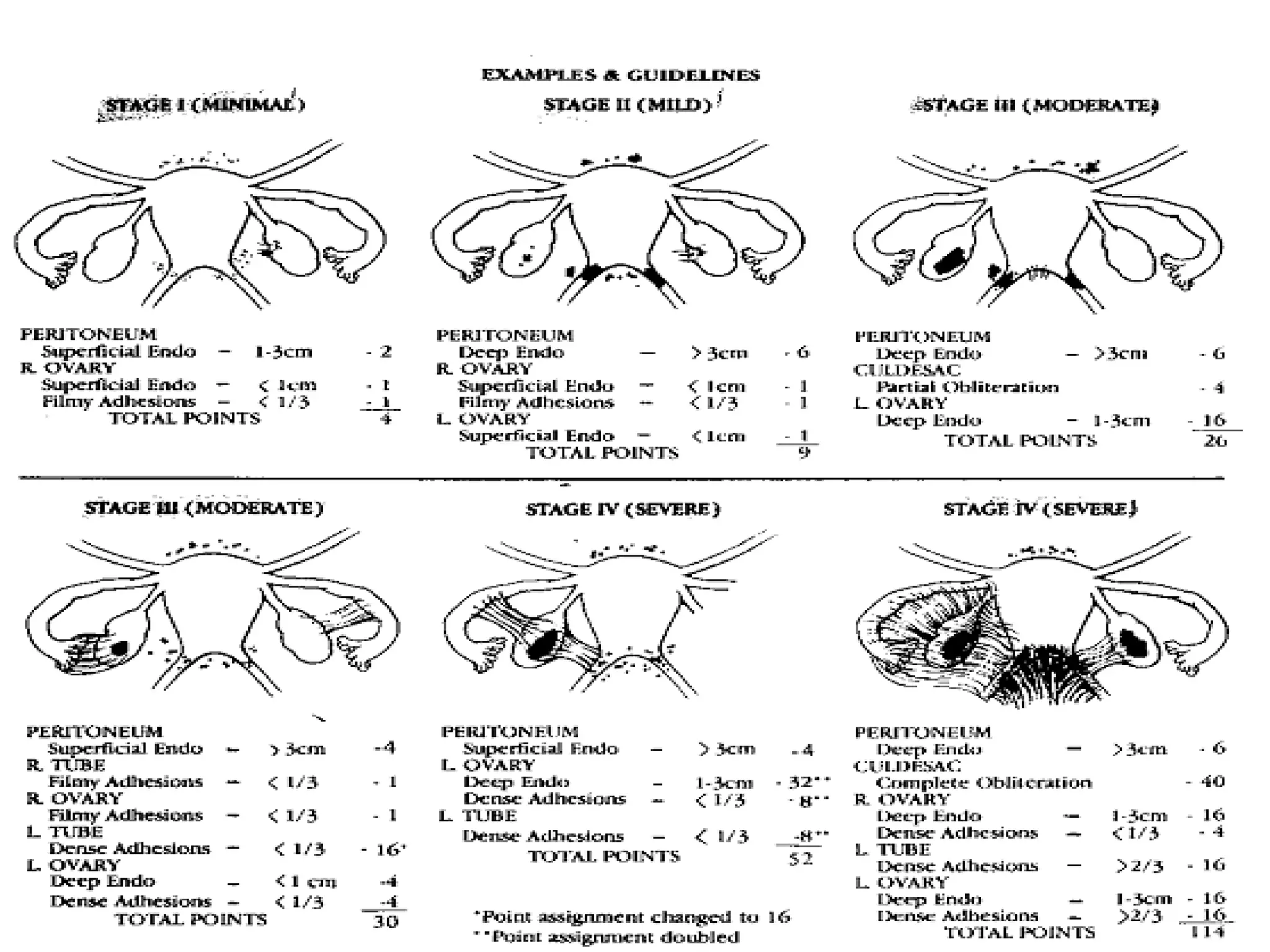
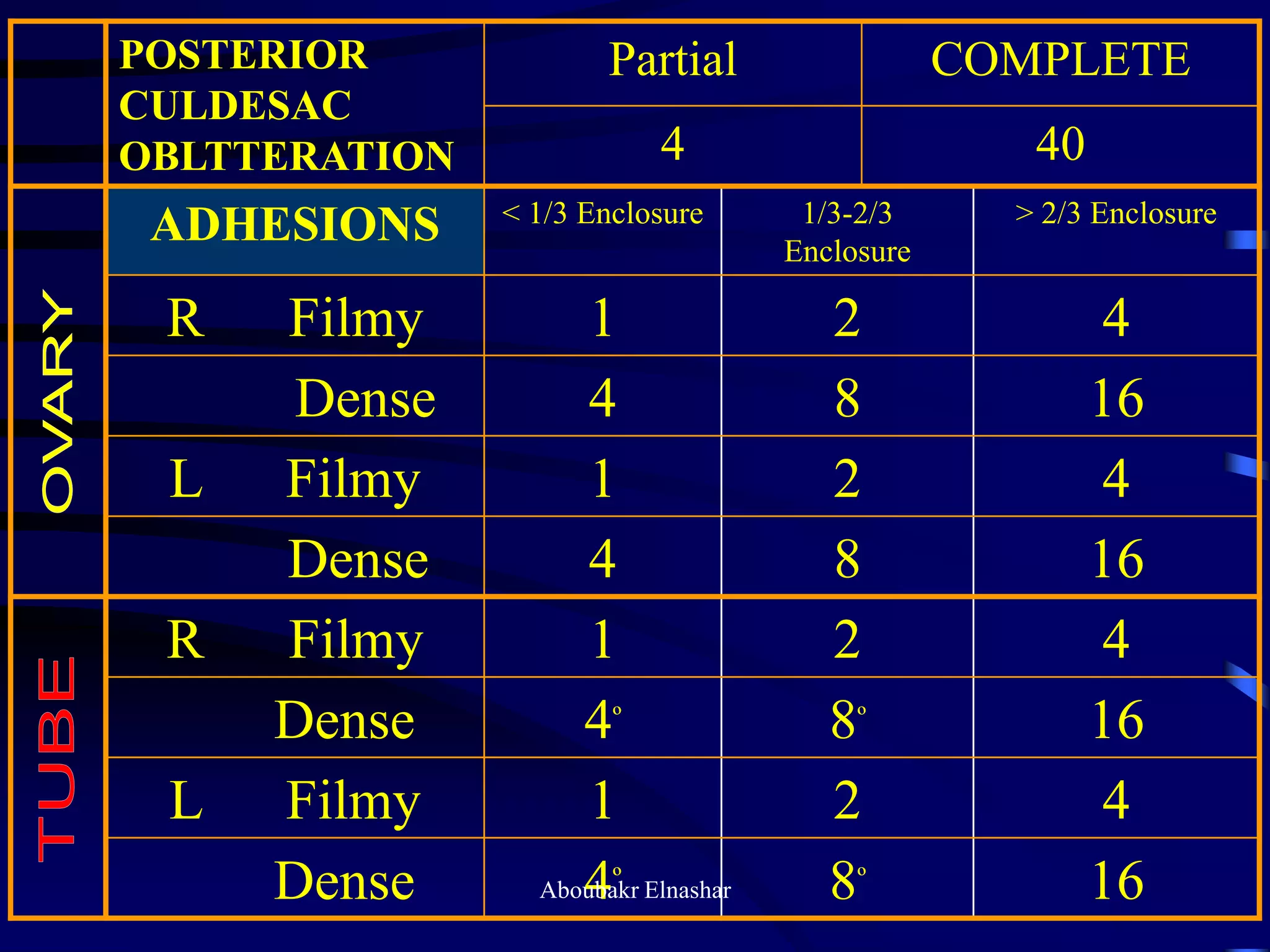
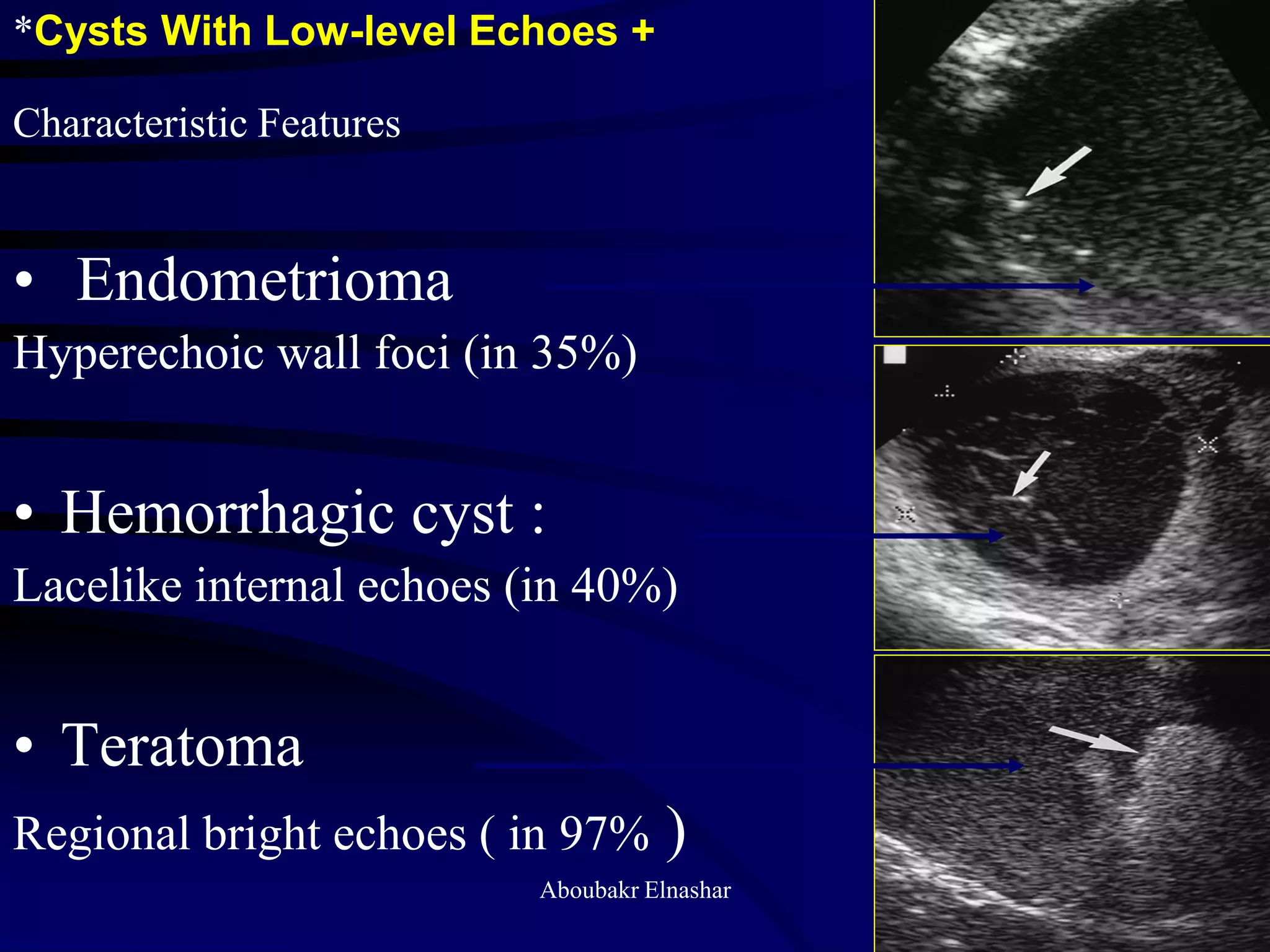
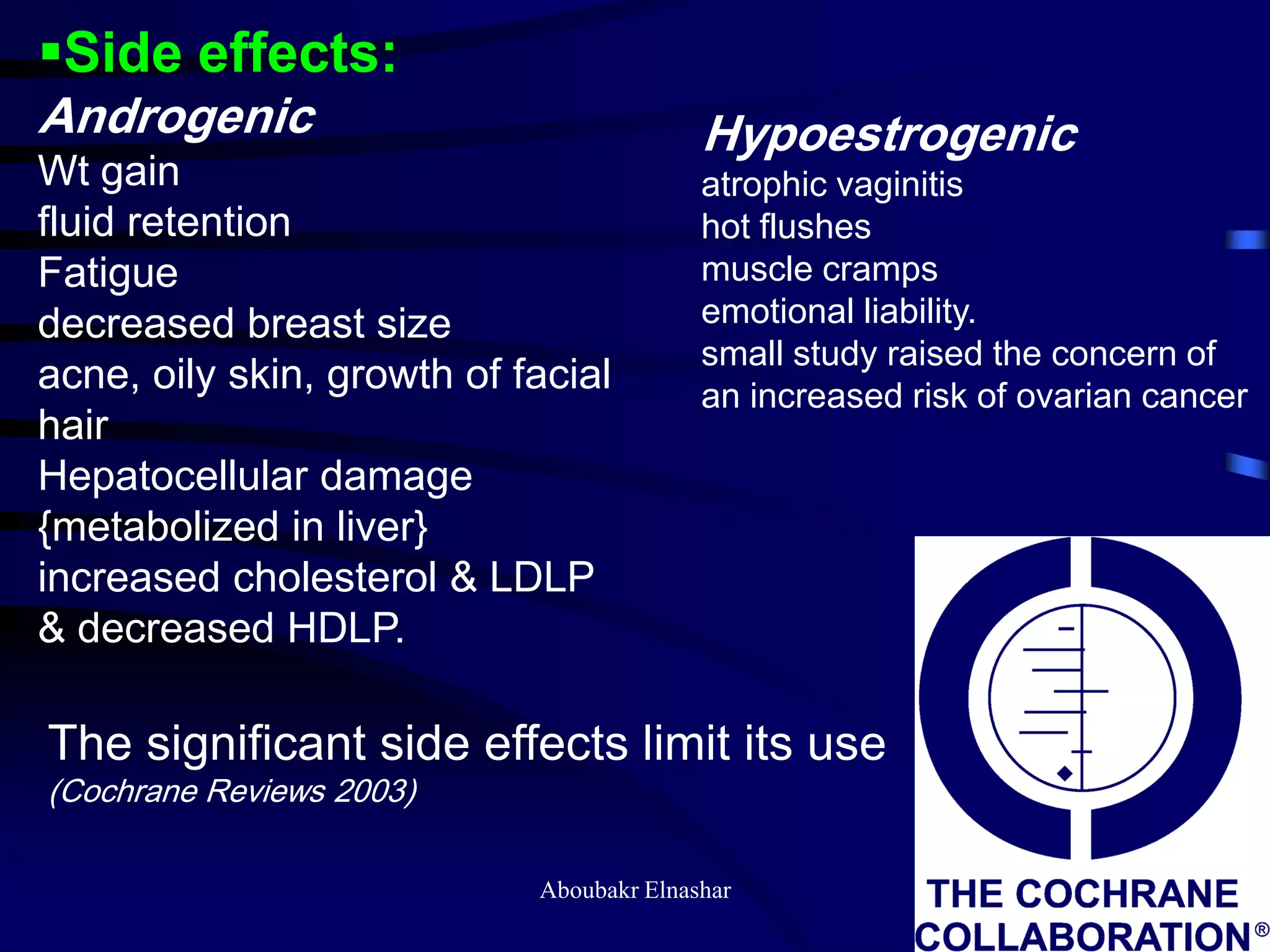
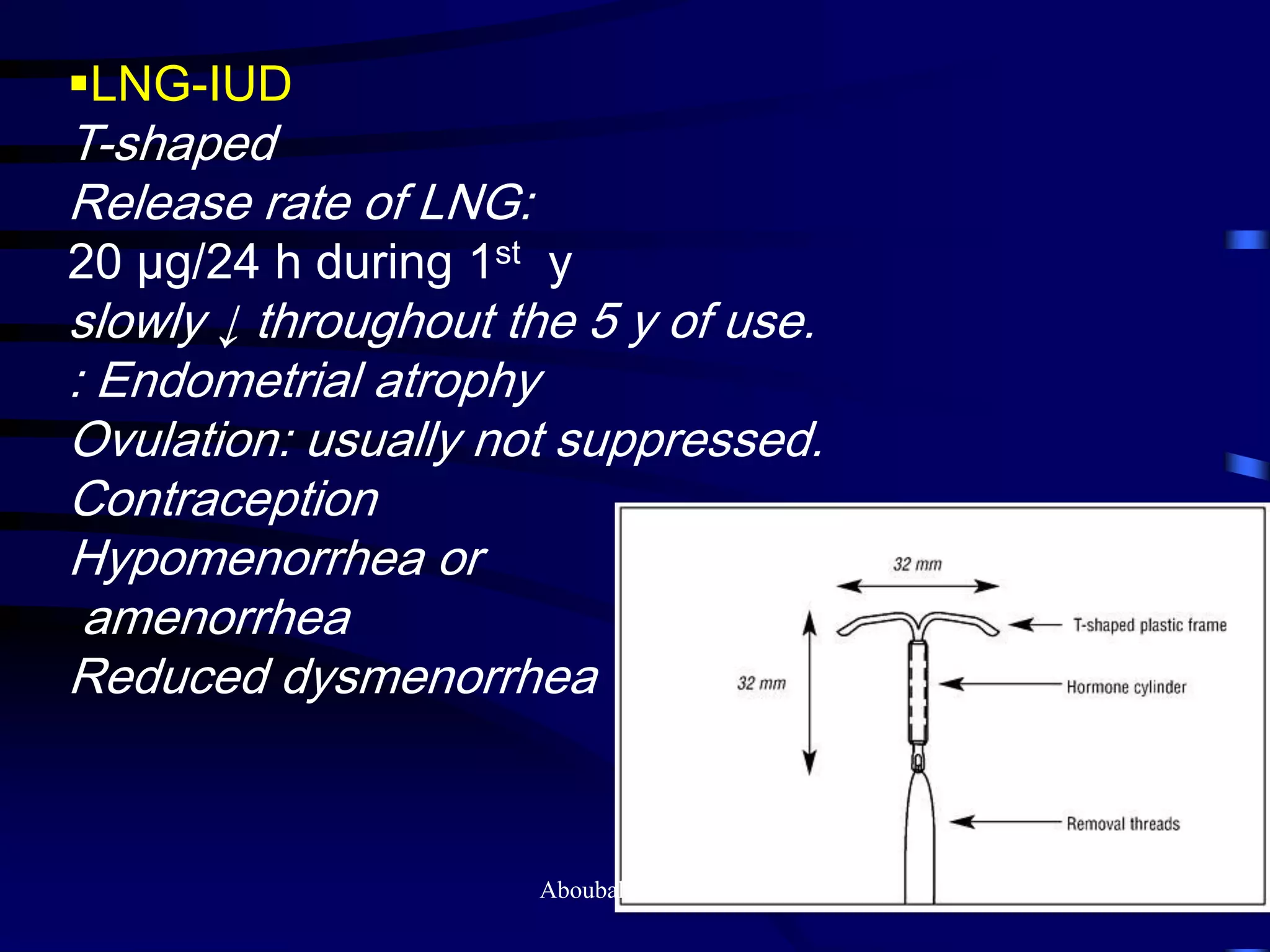
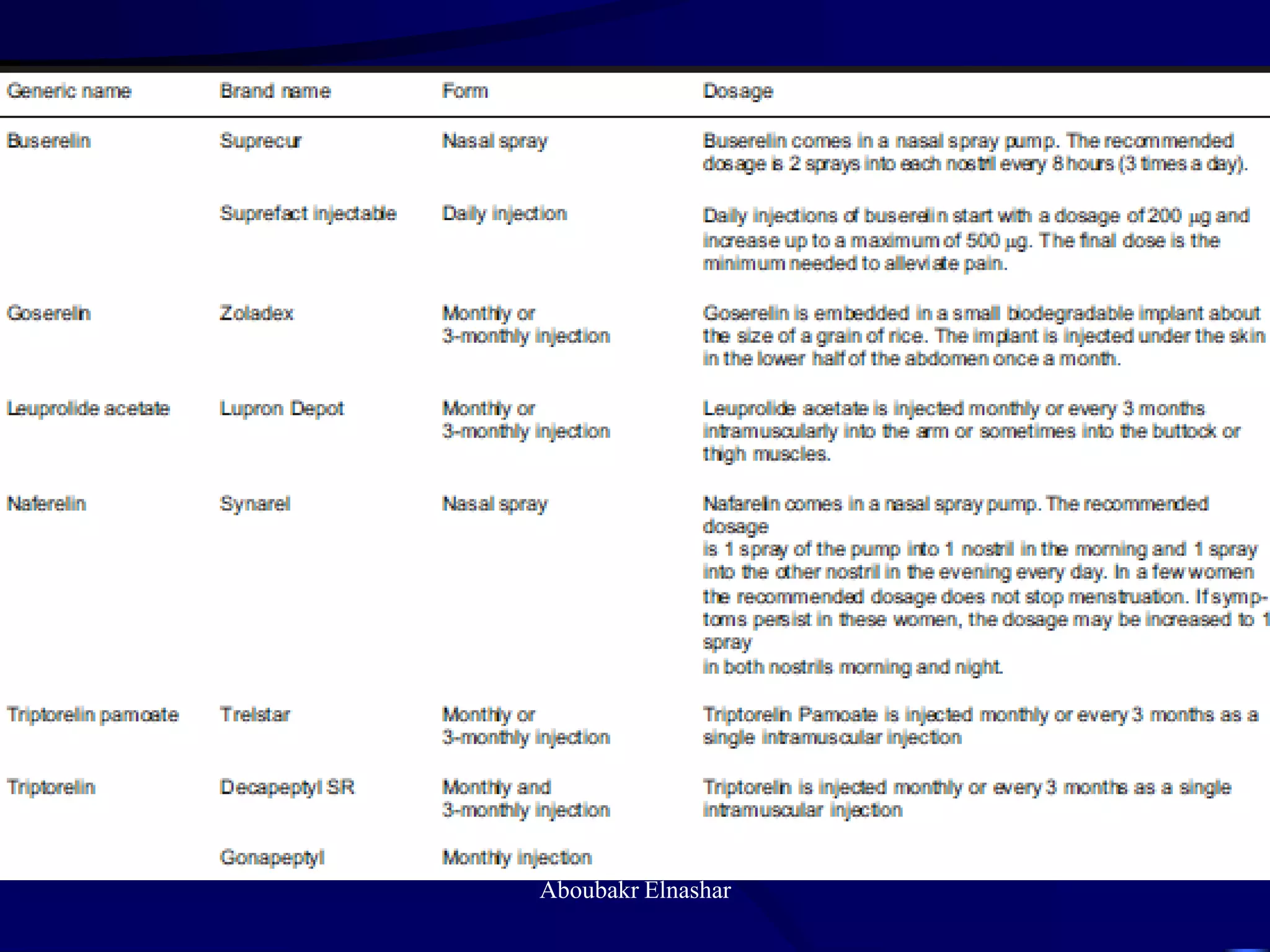
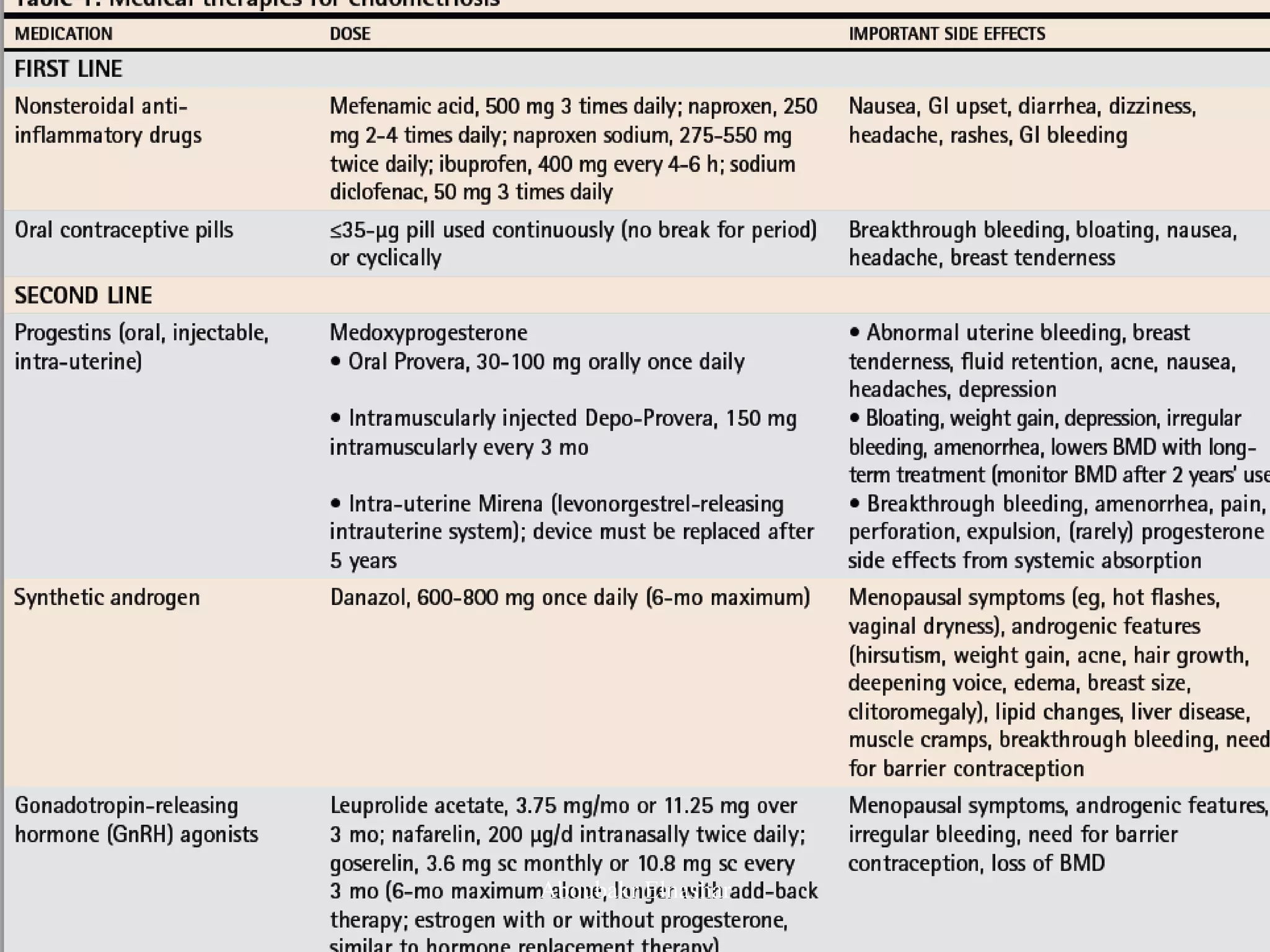
This document discusses endometriosis, including its definition, prevalence, age at diagnosis, sites, types, pathogenesis, risk factors, classification systems, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and laparoscopic findings. Some key points include:
- Endometriosis is defined as endometrial glands and stroma outside the uterus, and is prevalent in 5% of women of reproductive age.
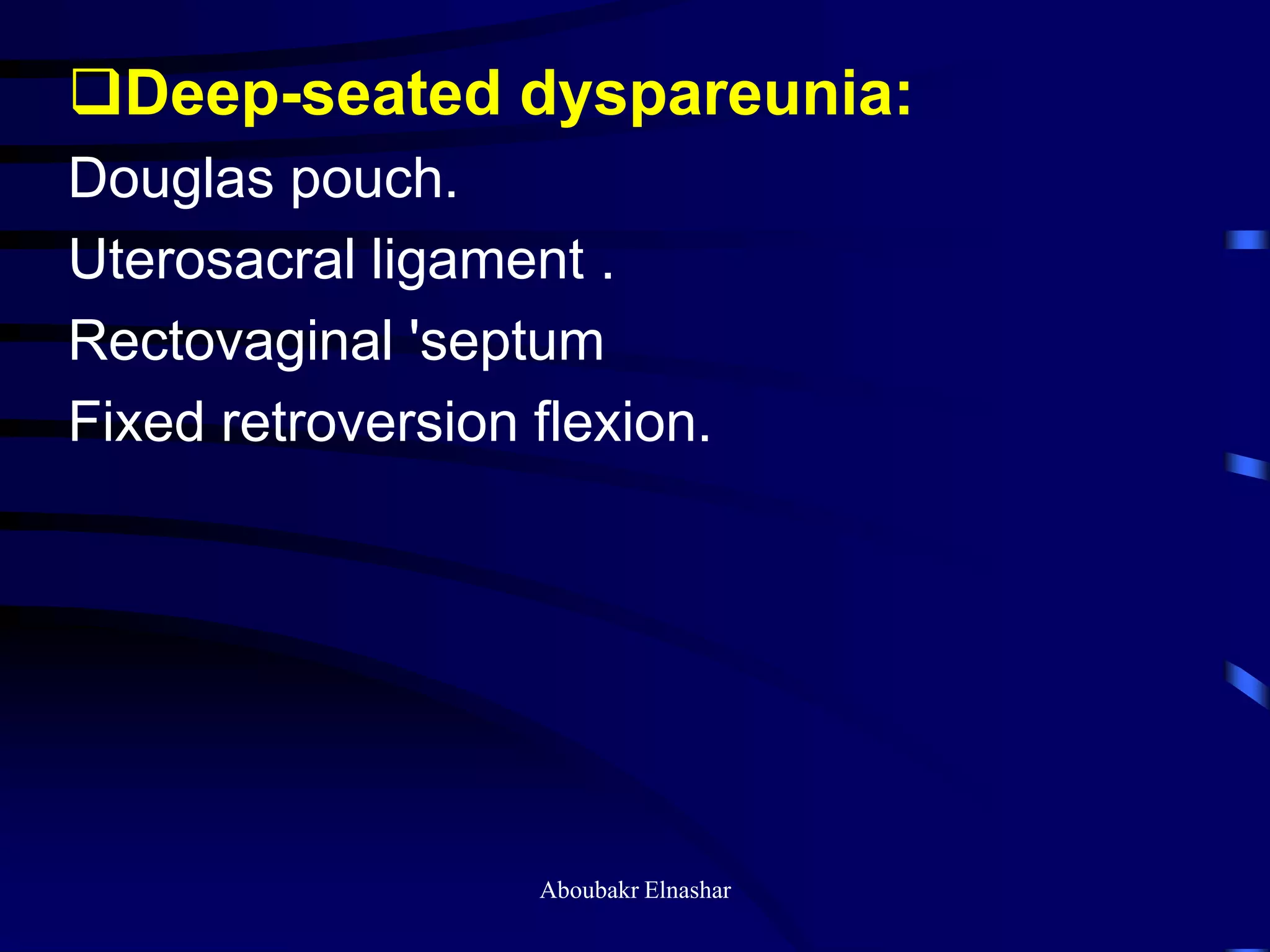
- It is most commonly diagnosed between ages 26-35 and presents with symptoms like infertility, pelvic pain, dysmenorrhea, and dyspareunia.
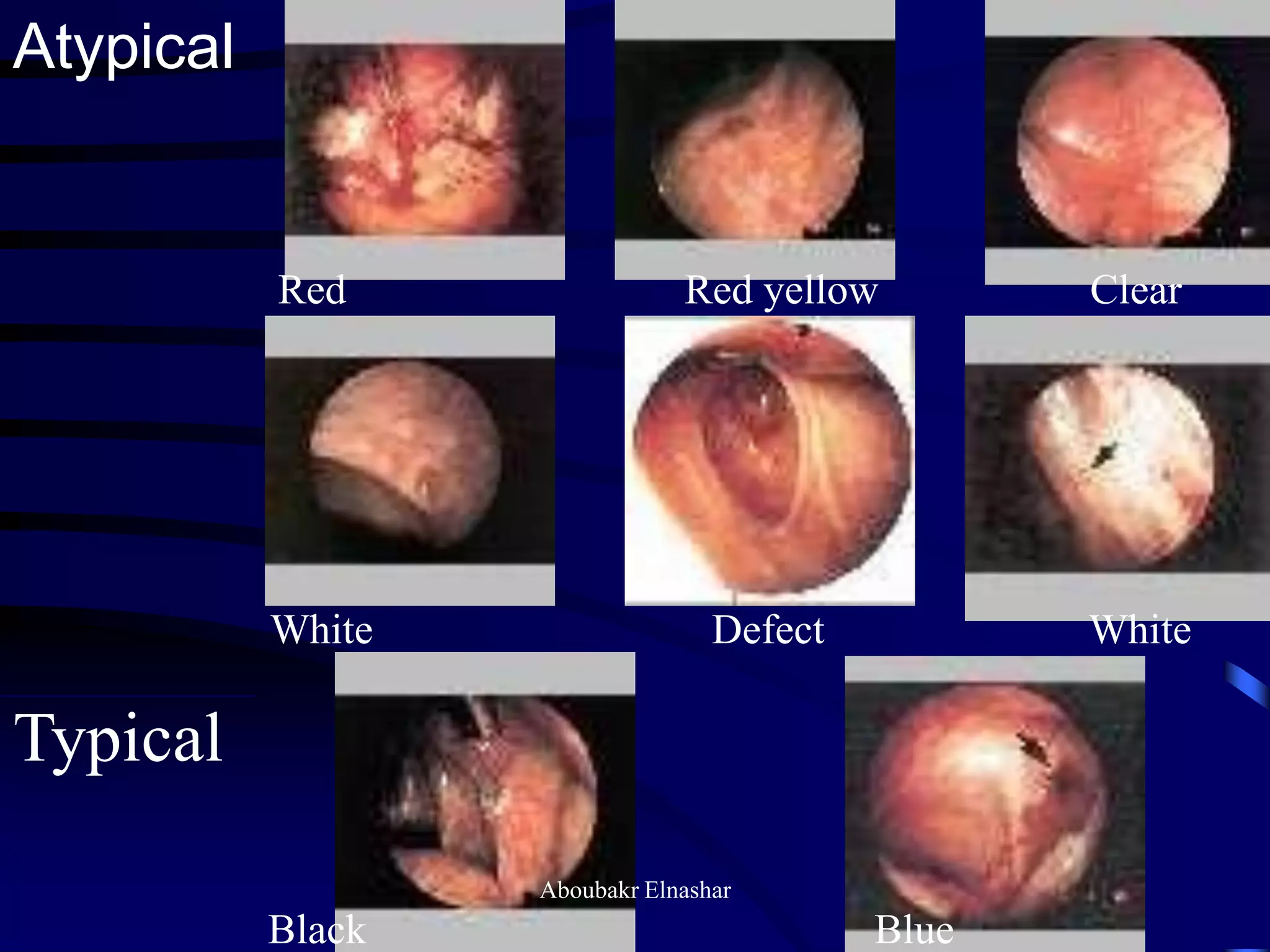
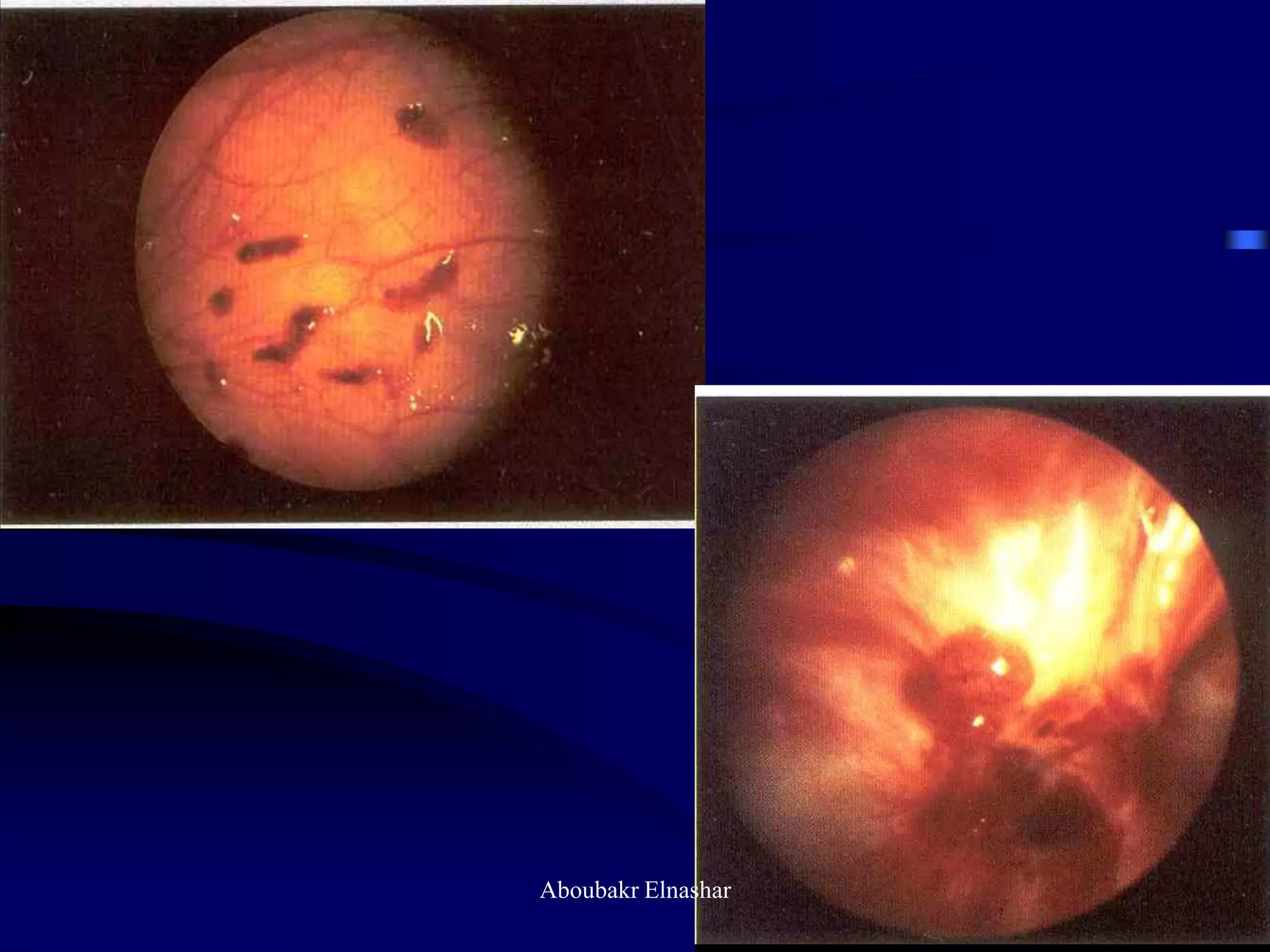
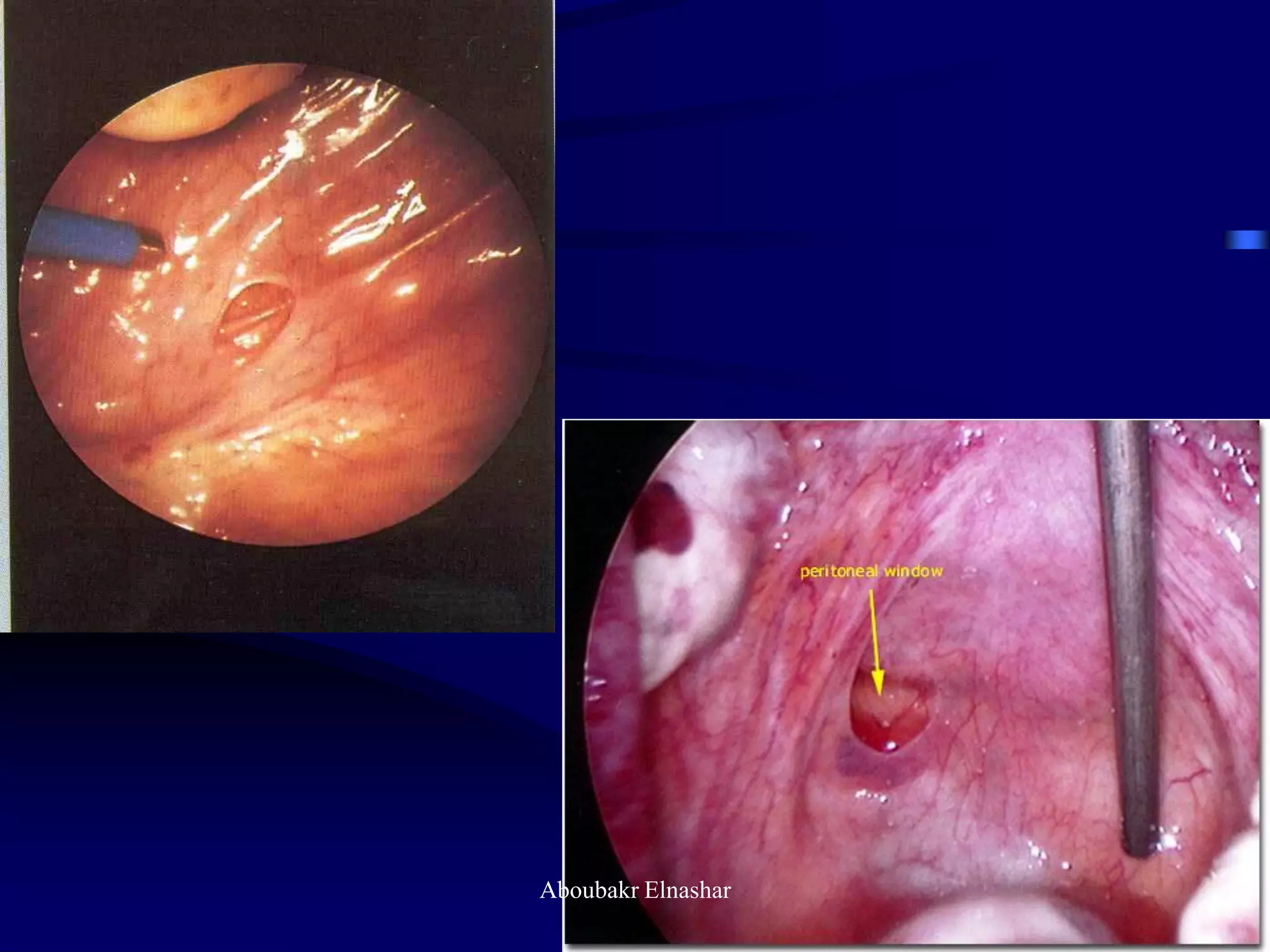
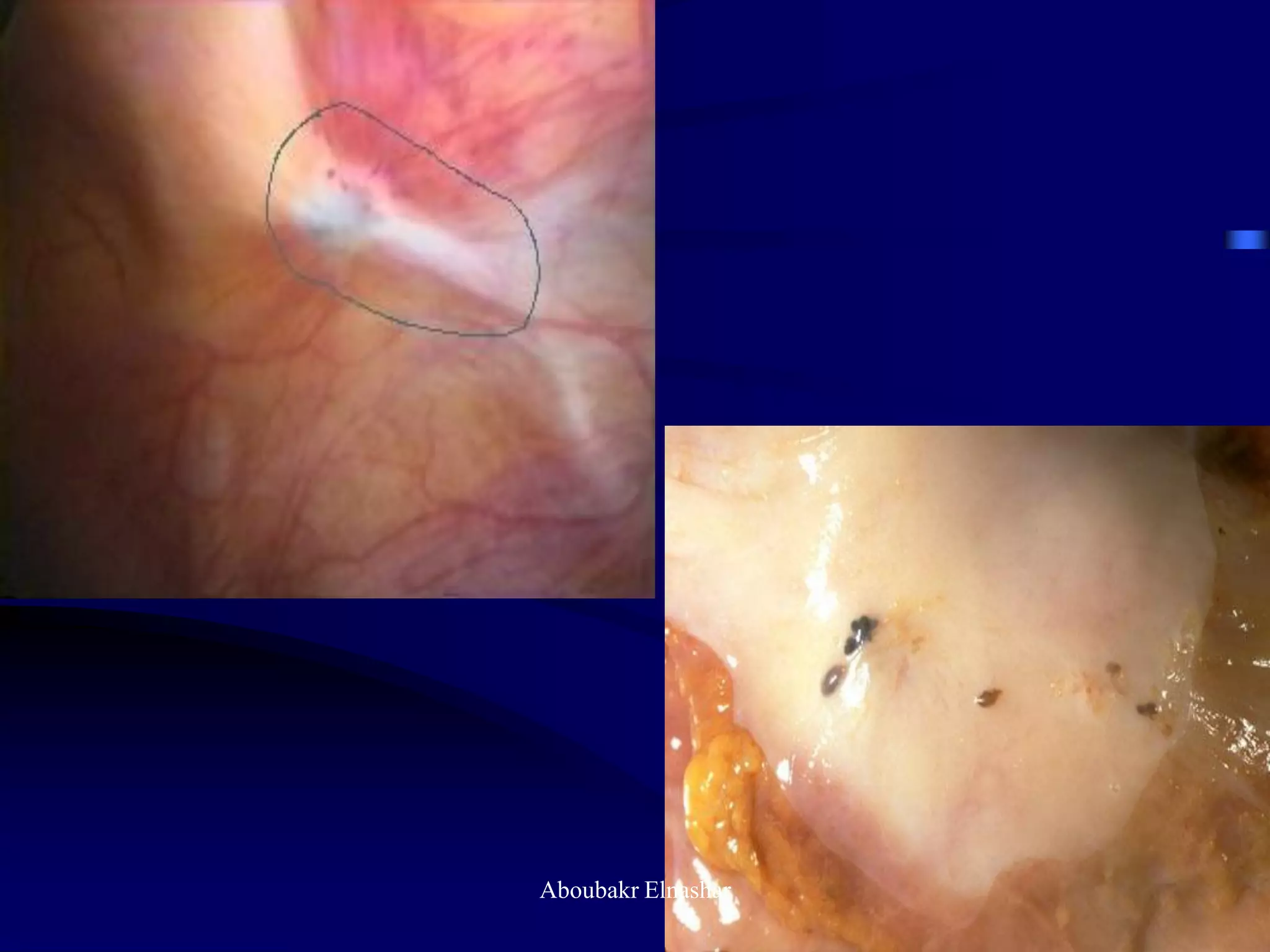
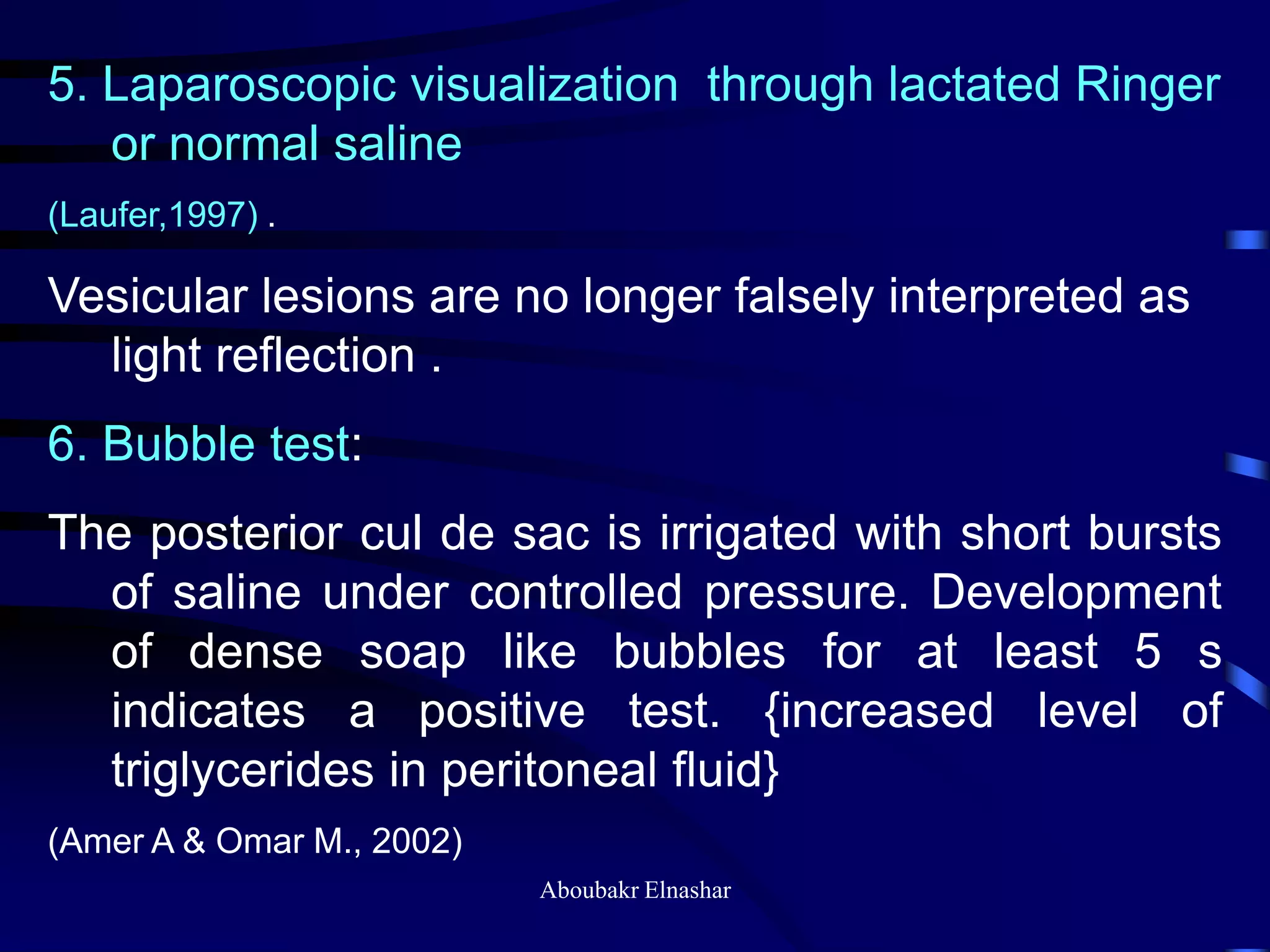
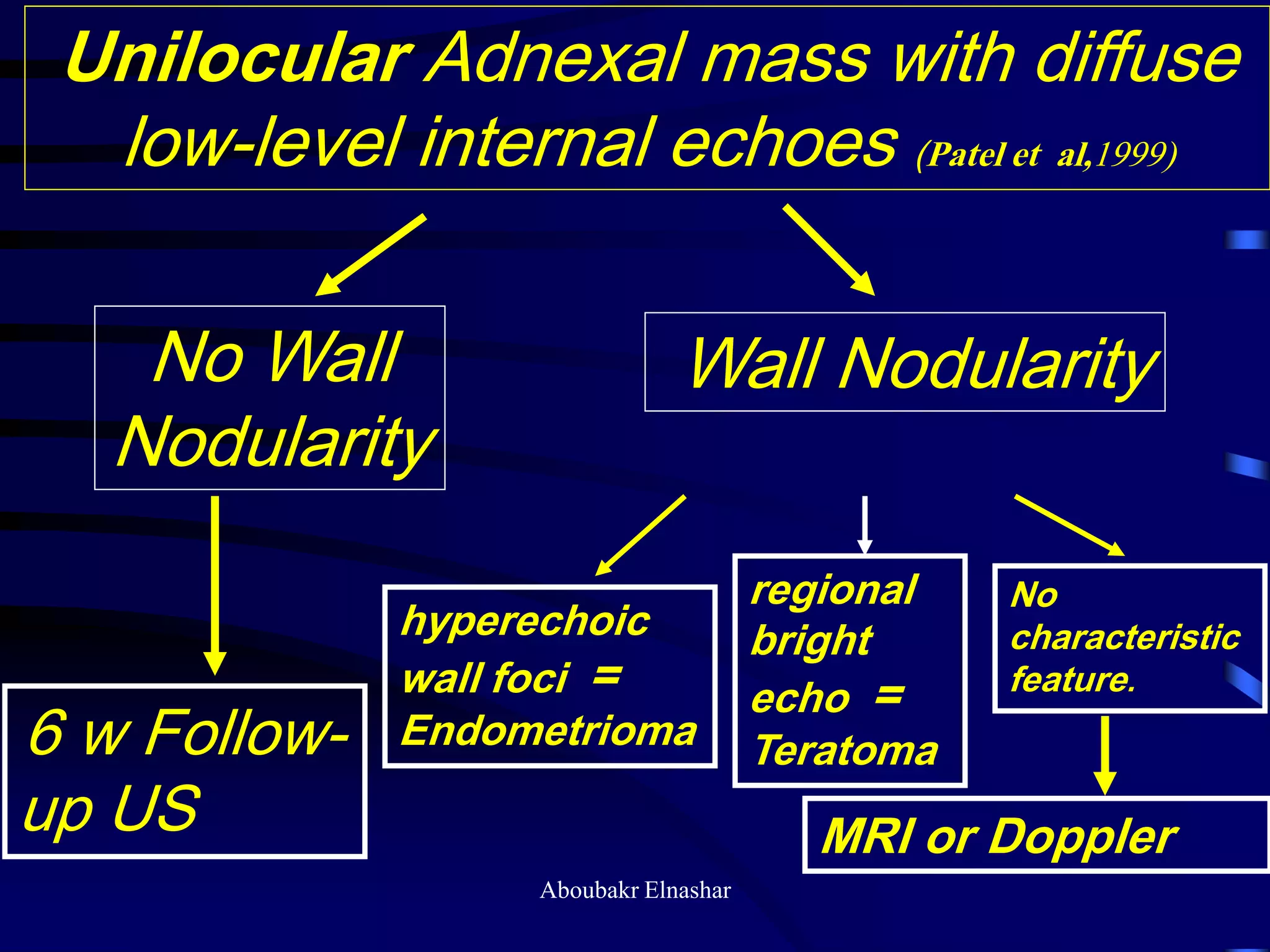
- Diagnosis is usually confirmed via laparoscopy, though atypical lesions can be difficult to identify visually and may require biopsy. Laparoscopy allows visualization






![II. Endometrioma (Endometriotic Cyst)
>90% are pseudocysts [formed by invagination of the ovarian
cortex, which is sealed off by adhesions]
(Brosens et al, 2003).
• Characterized by:
fibrosis
retraction of the cortex,
islands of glandular endometrial tissue
organized blood clots.
• The remainder of the cyst wall:
Smooth
lined by a thin endometrial-like tissue that consists of surface
epithelium and highly microvascularized stroma.
• There is no evidence that endometriotic tissue invades the
ovarian stroma; however, large multilocular cysts frequently
combine endometriomas with a hemorrhagic corpus luteum
or lutein cyst.
Aboubakr Elnashar](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/endometriosis-140727182255-phpapp01/75/Endometriosis-7-2048.jpg)