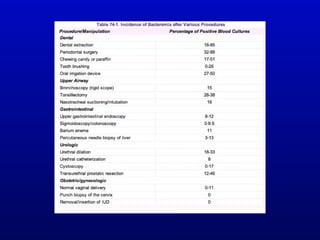
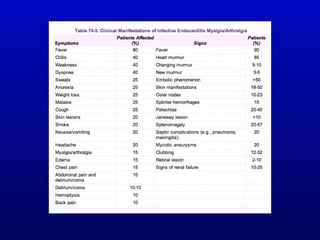
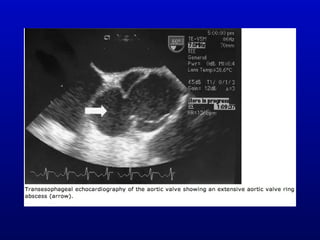
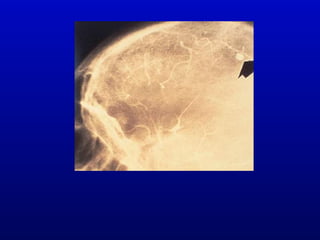
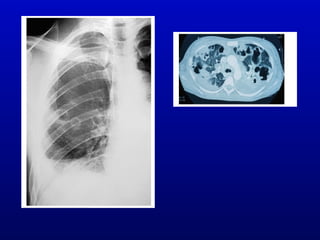
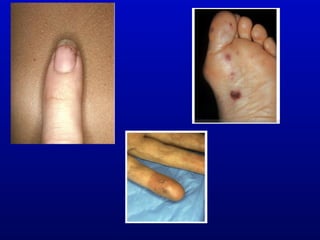
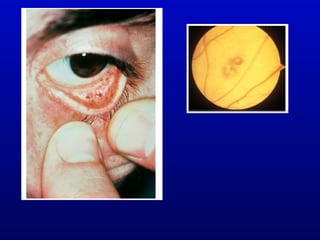
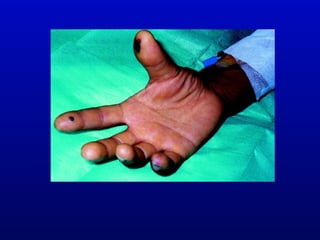
Infective endocarditis is an infection of the heart valves or endocardium. It occurs at a rate of 10,000-20,000 cases per year in the US. Staphylococcus aureus is the most common cause. Diagnosis is made using the Modified Duke Criteria which considers blood culture results, echocardiogram findings, and clinical features. Treatment involves prolonged antibiotic therapy for 4-6 weeks depending on the causative organism. Surgery may be required for complications or refractory infection. Prophylaxis with antibiotics is recommended for certain high risk dental and surgical procedures to prevent bacteremia and seeding of valves.