Support Vector Machines (SVM) are a type of supervised learning algorithm introduced by Vapnik in 1995, widely used for classification and regression tasks including object detection and text recognition. SVM works by finding the hyperplane that maximizes the margin between different classes, with two types being hard margin and soft margin SVMs. The algorithm uses support vectors, which are the closest data points to the hyperplane, to define the decision boundary.























![Solving the Optimization Problem
0]1)([ by iii wx
only SVs will have non-zero ai
24
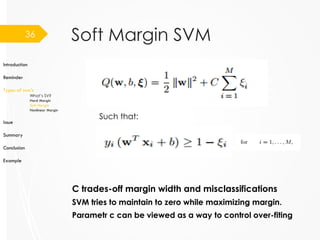
Introduction
Reminder
Types of svm’s
What’s SV?
Hard Margin
Soft Margin
Nonlinear Margin
Issue
Summary
Conclusion
Example
Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) conditions:
𝑎𝑖 ≥0
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rir1d4lsak5wsutz9jew-signature-abad3706aee97642cc94b2f587c1d0df8aa09670e0ed0061be7a72daa380a363-poli-150103151014-conversion-gate01/85/End1-24-320.jpg)
![0]1)([: bycondKKT iii wx
6=1.4
Class 1
Class 2
1=0.8
2=0
3=0
4=0
5=0
7=0
8=0.6
9=0
10=0
25
Introduction
Reminder
Types of svm’s
What’s SV?
Hard Margin
Soft Margin
Nonlinear Margin
Issue
Summary
Conclusion
Example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rir1d4lsak5wsutz9jew-signature-abad3706aee97642cc94b2f587c1d0df8aa09670e0ed0061be7a72daa380a363-poli-150103151014-conversion-gate01/85/End1-25-320.jpg)



![Hard Margin SVM29
Introduction
Reminder
Types of svm’s
What’s SV?
Hard Margin
Soft Margin
Nonlinear Margin
Issue
Summary
Conclusion
Example
0]1)([ by iii wxKKT cond: or
01)( by ii wx
0i NSV
iiyb wx
SVs
only SVs will have non-zero ai](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rir1d4lsak5wsutz9jew-signature-abad3706aee97642cc94b2f587c1d0df8aa09670e0ed0061be7a72daa380a363-poli-150103151014-conversion-gate01/85/End1-29-320.jpg)
![0]1)([: bycondKKT iii wx
6=1.4
Class 1
Class 2
1=0.8
2=0
3=0
4=0
5=0
7=0
8=0.6
9=0
10=0
30
Introduction
Reminder
Types of svm’s
What’s SV?
Hard Margin
Soft Margin
Nonlinear Margin
Issue
Summary
Conclusion
Example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rir1d4lsak5wsutz9jew-signature-abad3706aee97642cc94b2f587c1d0df8aa09670e0ed0061be7a72daa380a363-poli-150103151014-conversion-gate01/85/End1-30-320.jpg)
![Summary Solving the Optimization Problem
گام1:دیتاست{X 𝑖, Y𝑖}مقدار که است این هدف گیریم می را اولیهw,b
بیاوریم بدست را
گام2:ماتریسH ,fتابع از و سازیم می رامتلبa = quadprog(H,f)
کنیم می استفادهمقدار تاaآید بدست
h𝑖𝑗=𝑦𝑖 𝑦𝑗 𝑥𝑖
𝑇
𝑥𝑗 , f=-1 , H=[h𝑖𝑗]
گام3:مقدارw ,bآوریم می بدست زیر فرمول از را
گام4:شود می زیر رابطه ما خطی ساز جدا:
31
Introduction
Reminder
Types of svm’s
What’s SV?
Hard Margin
Soft Margin
Nonlinear Margin
Issue
Summary
Conclusion
Example
خروجی = 𝑠𝑖𝑔𝑛(𝑊 𝑇 𝑋𝑖 + b)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rir1d4lsak5wsutz9jew-signature-abad3706aee97642cc94b2f587c1d0df8aa09670e0ed0061be7a72daa380a363-poli-150103151014-conversion-gate01/85/End1-31-320.jpg)








































![matlab
svmtrain(Training,Group, 'kernel_function',Value)
Value:
'linear' — Linear kernel, meaning dot product.
'quadratic' — Quadratic kernel.
'polynomial' — Polynomial kernel (default order 3). Specify
another order with the polyorder name-value pair.
'rbf' — Gaussian Radial Basis Function kernel with a default
scaling factor, sigma, of 1. Specify another value for sigma
with the rbf_sigma name-value pair.
'mlp' — Multilayer Perceptron kernel with default scale [1 –1].
Specify another scale with the mlp_params name-value pair.
Default: 'linear
73
Introduction
Reminder
Types of svm’s
Issue
Summary
Conclusion
Example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rir1d4lsak5wsutz9jew-signature-abad3706aee97642cc94b2f587c1d0df8aa09670e0ed0061be7a72daa380a363-poli-150103151014-conversion-gate01/85/End1-73-320.jpg)

![مثال1:نمونه یک تست
species = svmclassify(svmStruct,[5 2],'ShowPlot',true)
hold on;
plot(5,2,'ro','MarkerSize',12);
hold off
75
Introduction
Reminder
Types of svm’s
Issue
Summary
Conclusion
Example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rir1d4lsak5wsutz9jew-signature-abad3706aee97642cc94b2f587c1d0df8aa09670e0ed0061be7a72daa380a363-poli-150103151014-conversion-gate01/85/End1-75-320.jpg)

