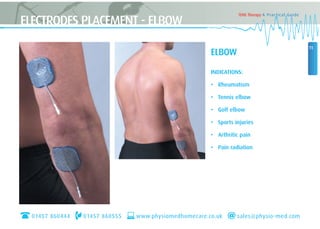
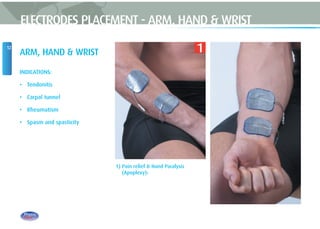
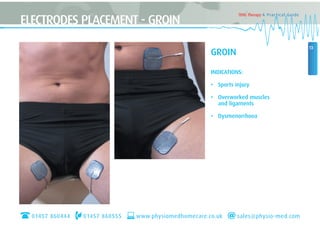
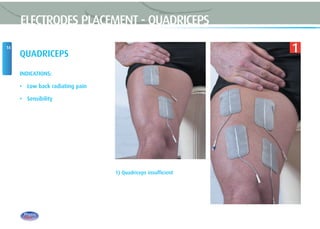
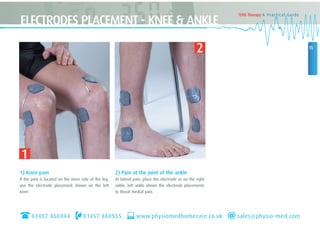
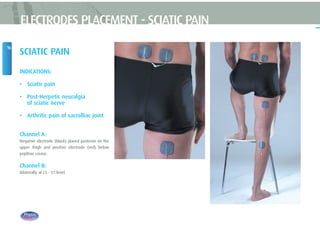
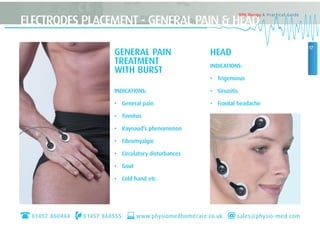
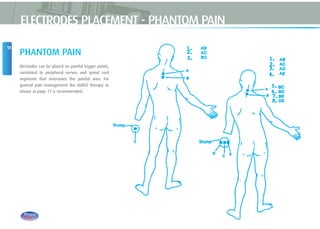
This document provides instructions for using TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) therapy. It explains that TENS works by using electrical pulses from electrodes placed on the skin to block pain signals to the brain. It can be used to treat many types of pain and has few side effects. The document provides guidance on electrode placement, settings for different modes of TENS treatment, and cautions for safe usage.