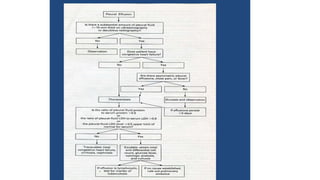
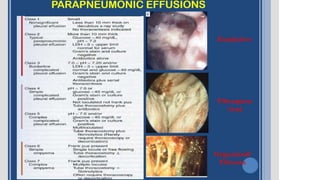
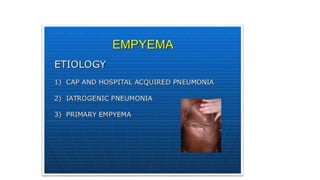
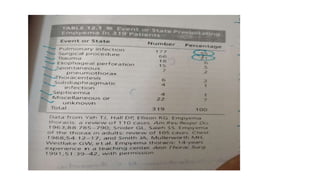
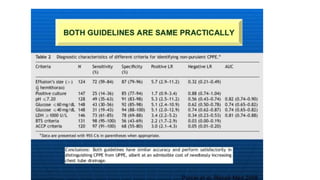
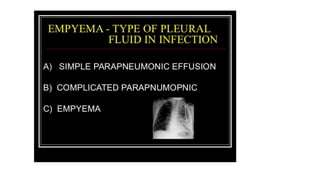
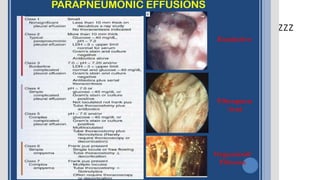
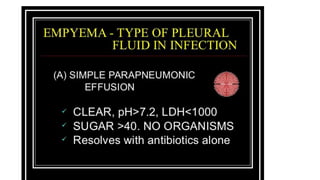
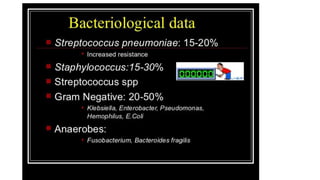
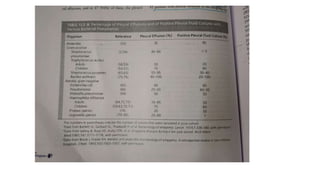
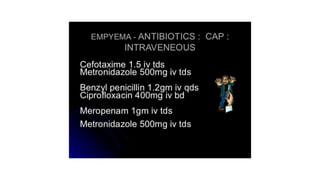
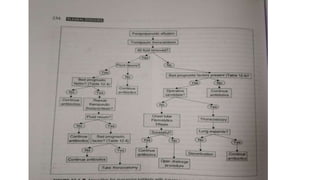
This document discusses parapneumonic effusion and empyema. It defines a parapneumonic effusion as any pleural effusion associated with bacterial pneumonia, lung abscess, or bronchiectasis. Empyema is specifically defined as pus in the pleural space. It then outlines various treatment options for pleural fluid including observation, therapeutic thoracentesis, tube thoracostomy, intrapleural fibrinolytics, VATS with lysis of adhesions and/or decortication, decortication, and open drainage. It provides details on studies investigating the effectiveness of intrapleural fibrinolytics.