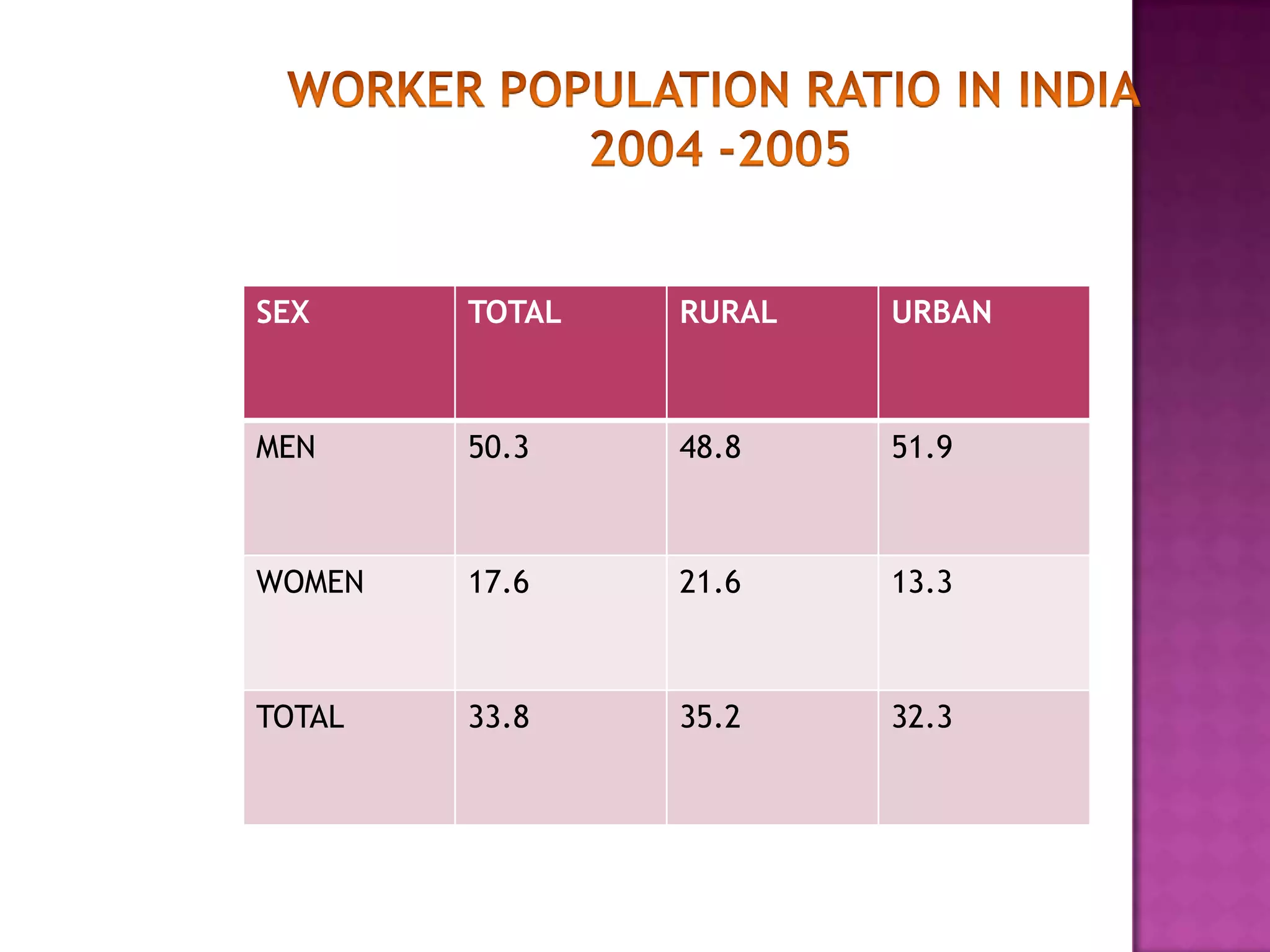
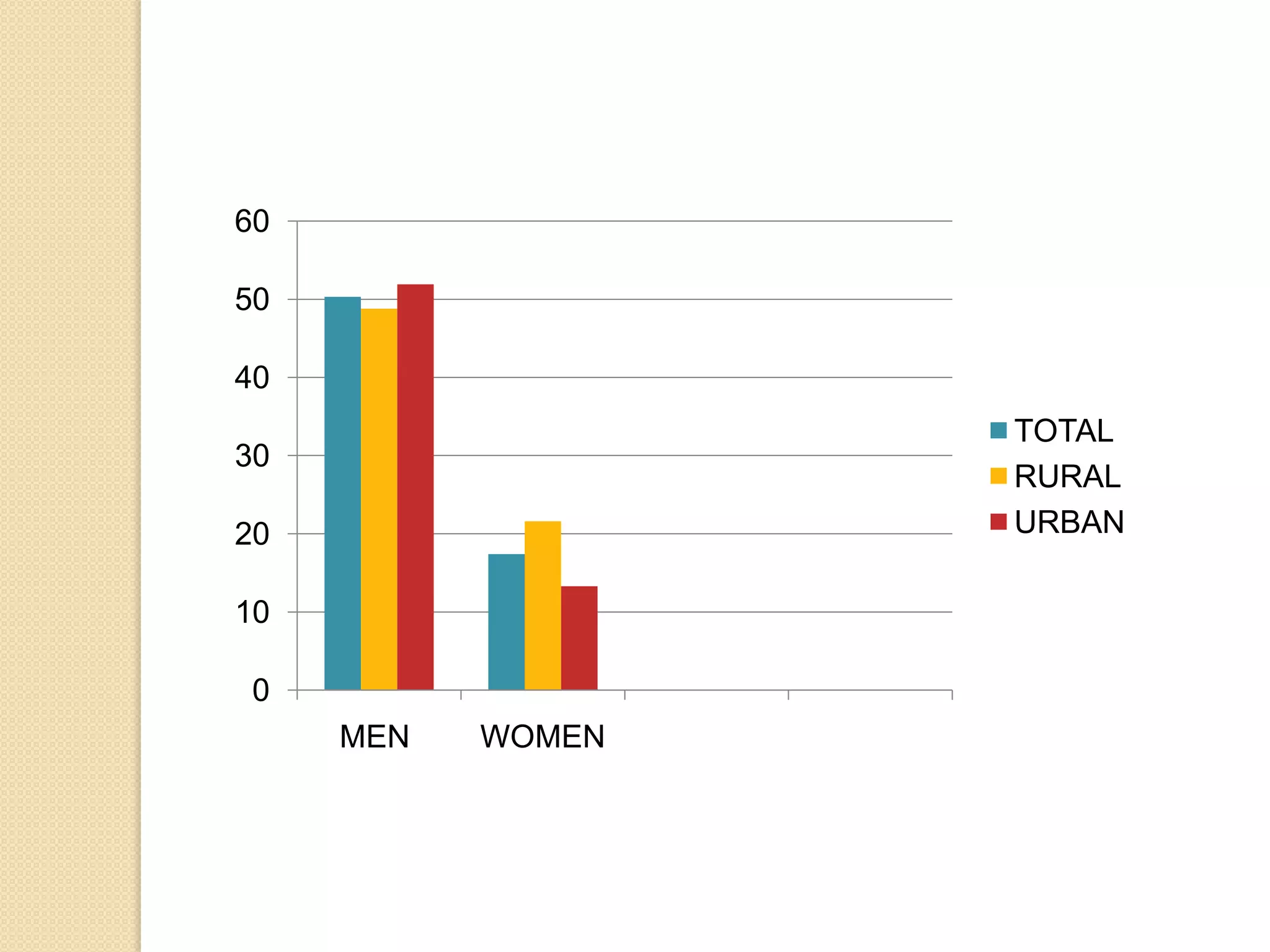
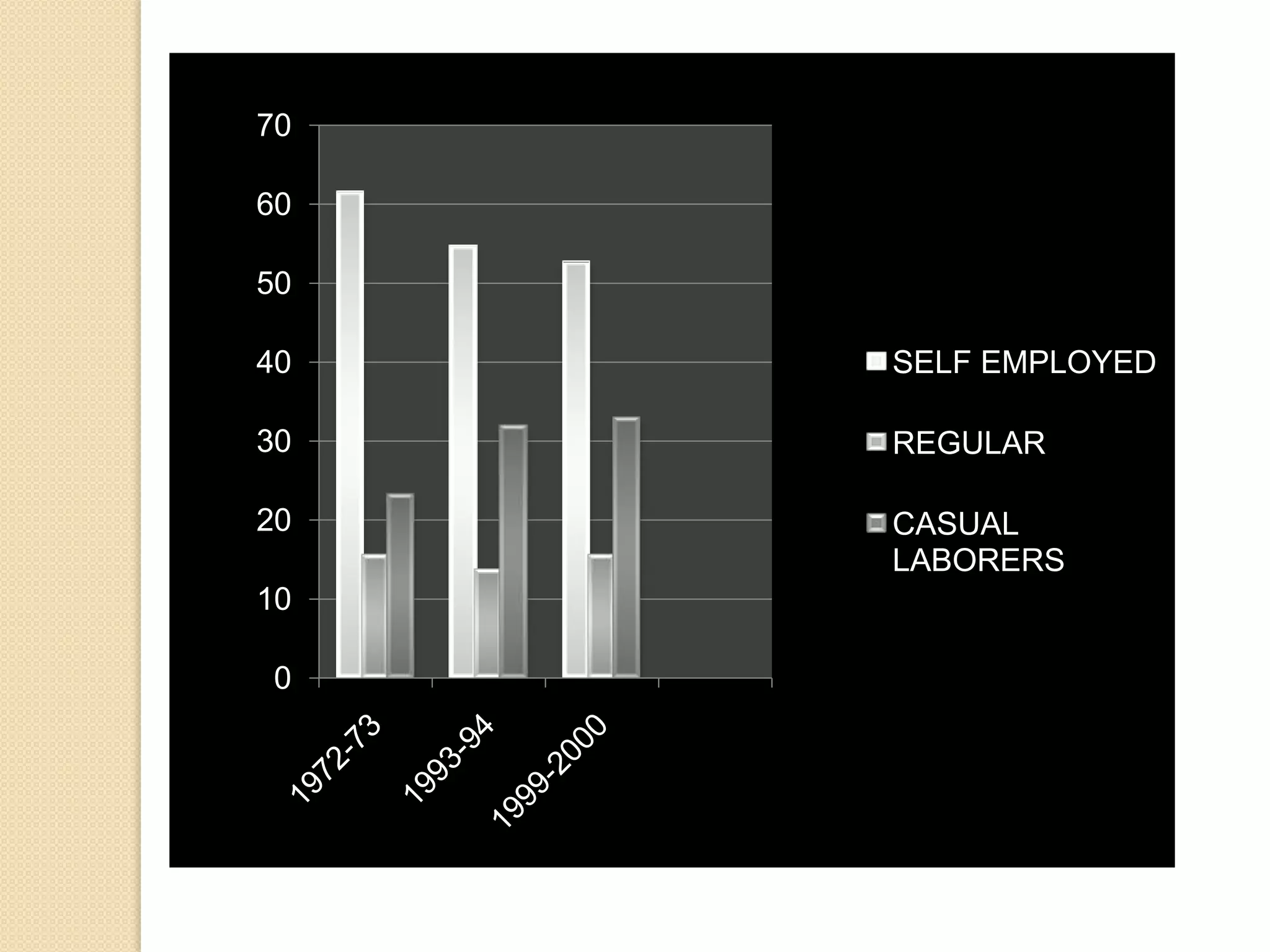
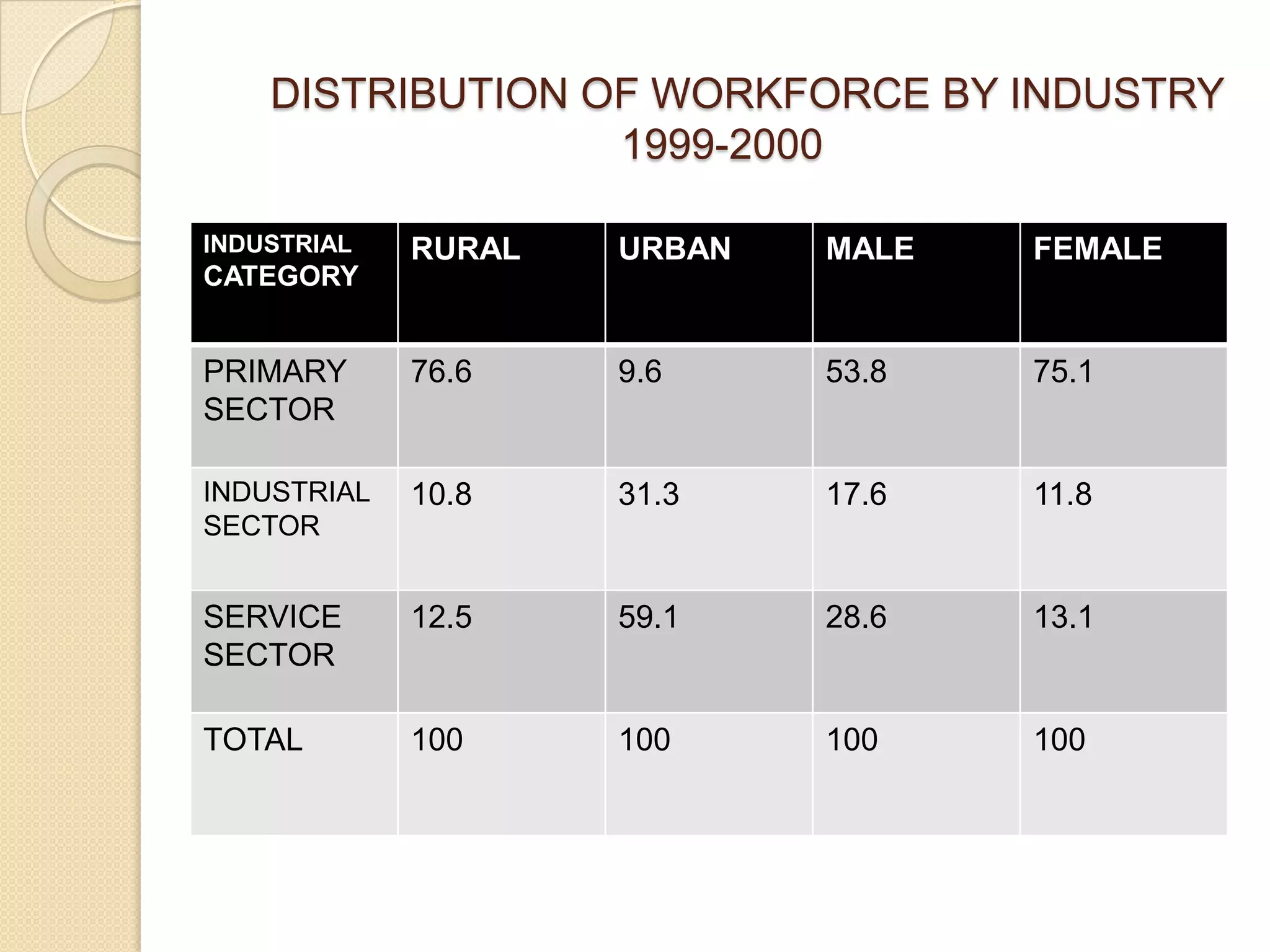
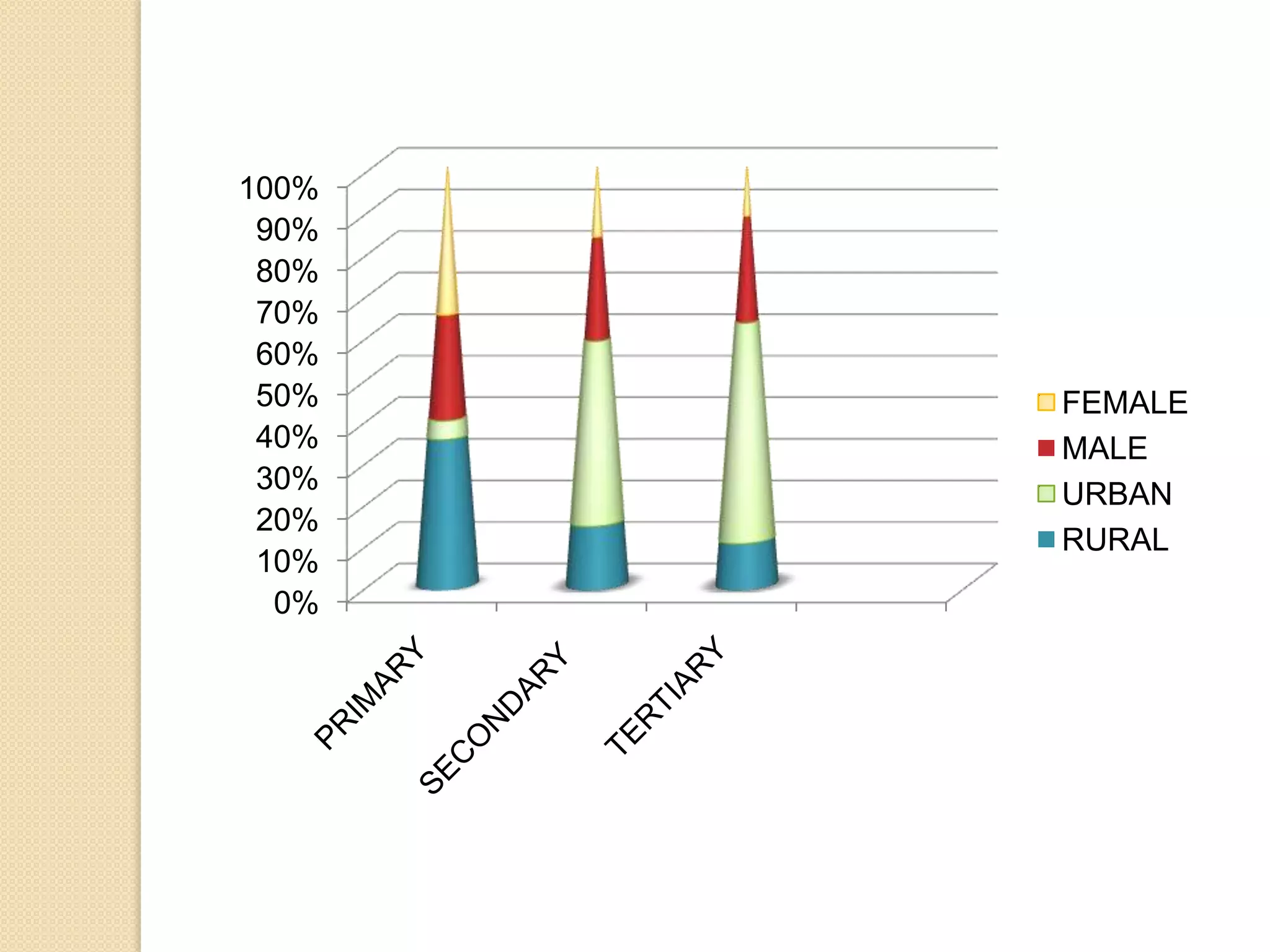
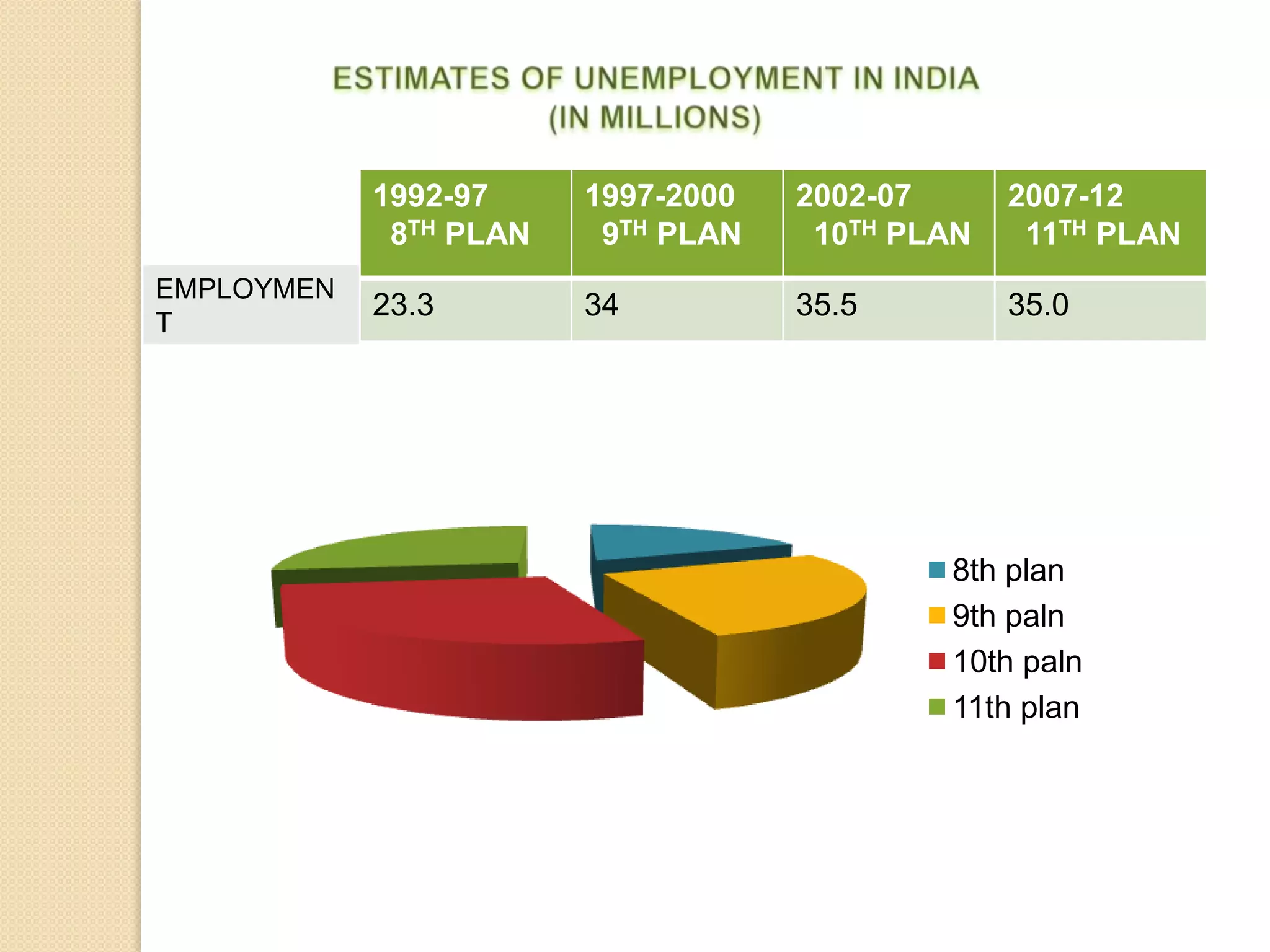
This document discusses employment, unemployment, and government measures related to employment in India. It defines formal and informal employment sectors and notes that India has experienced rising informalization and casualization of labor. Unemployment rates are estimated for different time periods. Causes of unemployment include faulty employment planning, population growth outpacing job growth, and an emphasis on capital-intensive projects. The government has implemented measures like NREGA to promote rural employment and alleviate poverty.