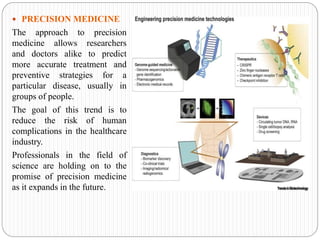
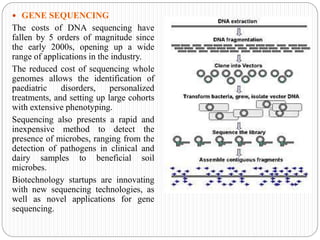
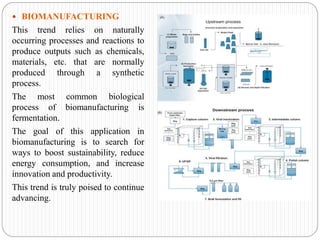
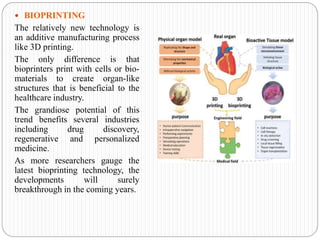
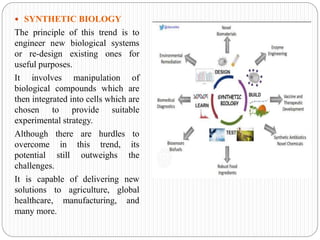
This document discusses emerging trends in biotechnology. It begins with an introduction to biotechnology and its history, including major discoveries from 1919 to 2020. It then outlines emerging trends like artificial intelligence, big data, gene editing, precision medicine, gene sequencing, biomanufacturing, bioprinting, and synthetic biology. Each trend is briefly described in 1-2 sentences. The document concludes by noting challenges in biotechnology like high costs, regulatory issues, talent shortages, and inadequate technology, but emphasizes that biotechnology advancement is crucial to address global issues in health, food, and the environment.