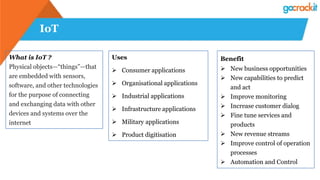
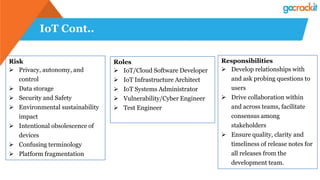
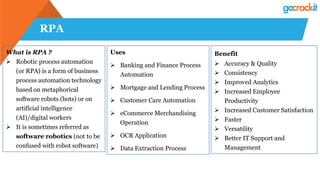
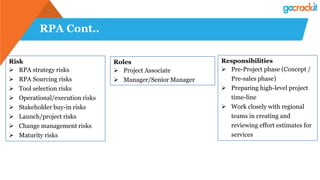
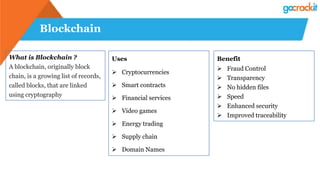
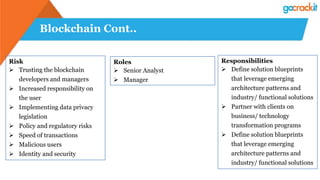
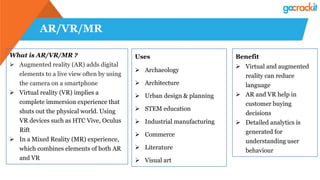
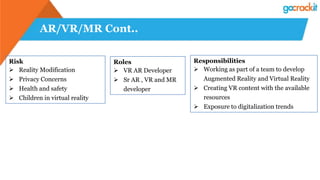
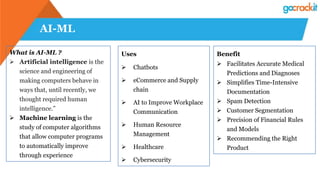
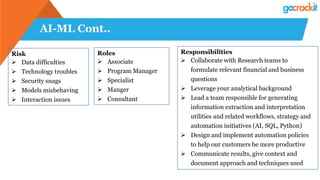
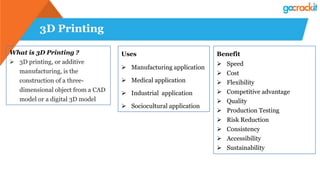
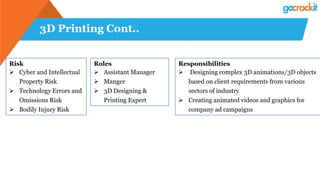
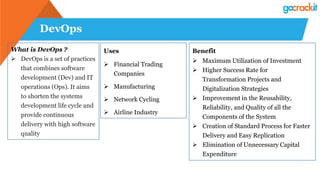
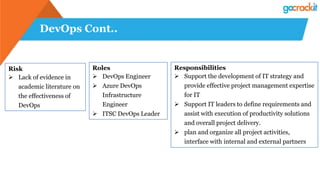
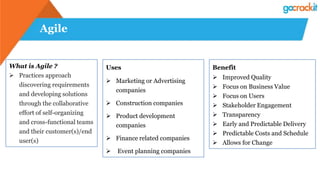
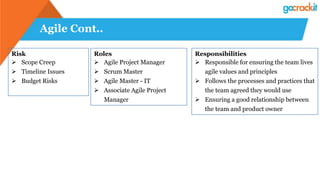
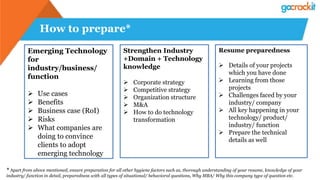
The document discusses various emerging technologies such as IoT, RPA, blockchain, AR/VR, AI-ML, 3D printing, DevOps, and Agile. It provides overviews and definitions of each technology, common uses, benefits, risks, and typical roles and responsibilities. It also discusses how to build a profile in emerging technologies through projects, skills development, certifications, competitions, research, and thought leadership.