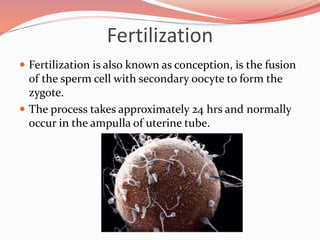
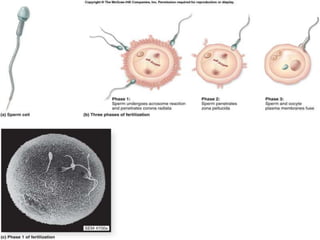
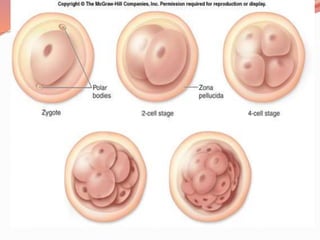
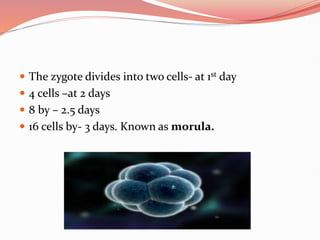
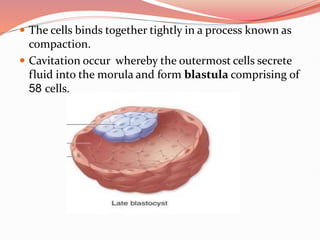
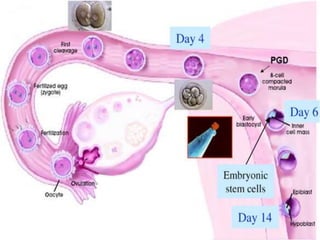
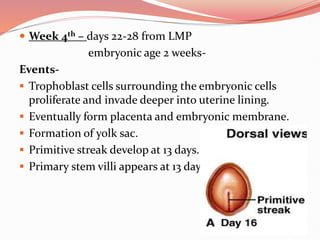
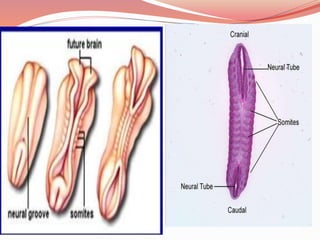
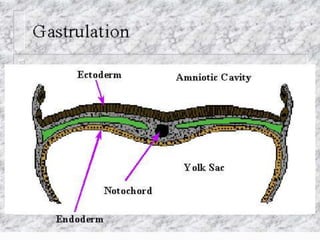
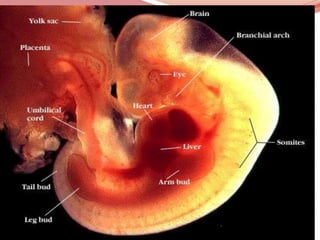
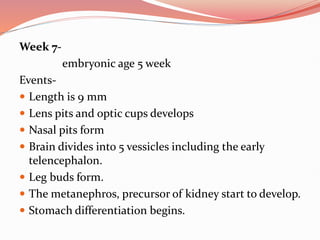
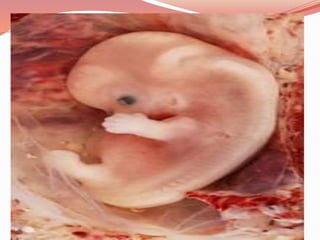
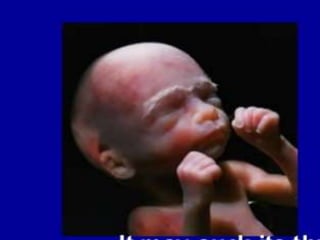
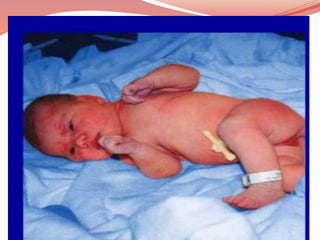
Prenatal or antenatal development refers to the process of development of an embryo or fetus during pregnancy from fertilization until birth. It involves three main periods - the pre-embryonic period from fertilization to implantation, the embryonic period of organ formation, and the fetal period of growth and development. During each week of gestation, specific developmental changes and events occur as the embryo and fetus grow and develop all major body structures and organs. By week 8, the basic body structures are established, and thereafter the fetus continues growing and maturing until birth.