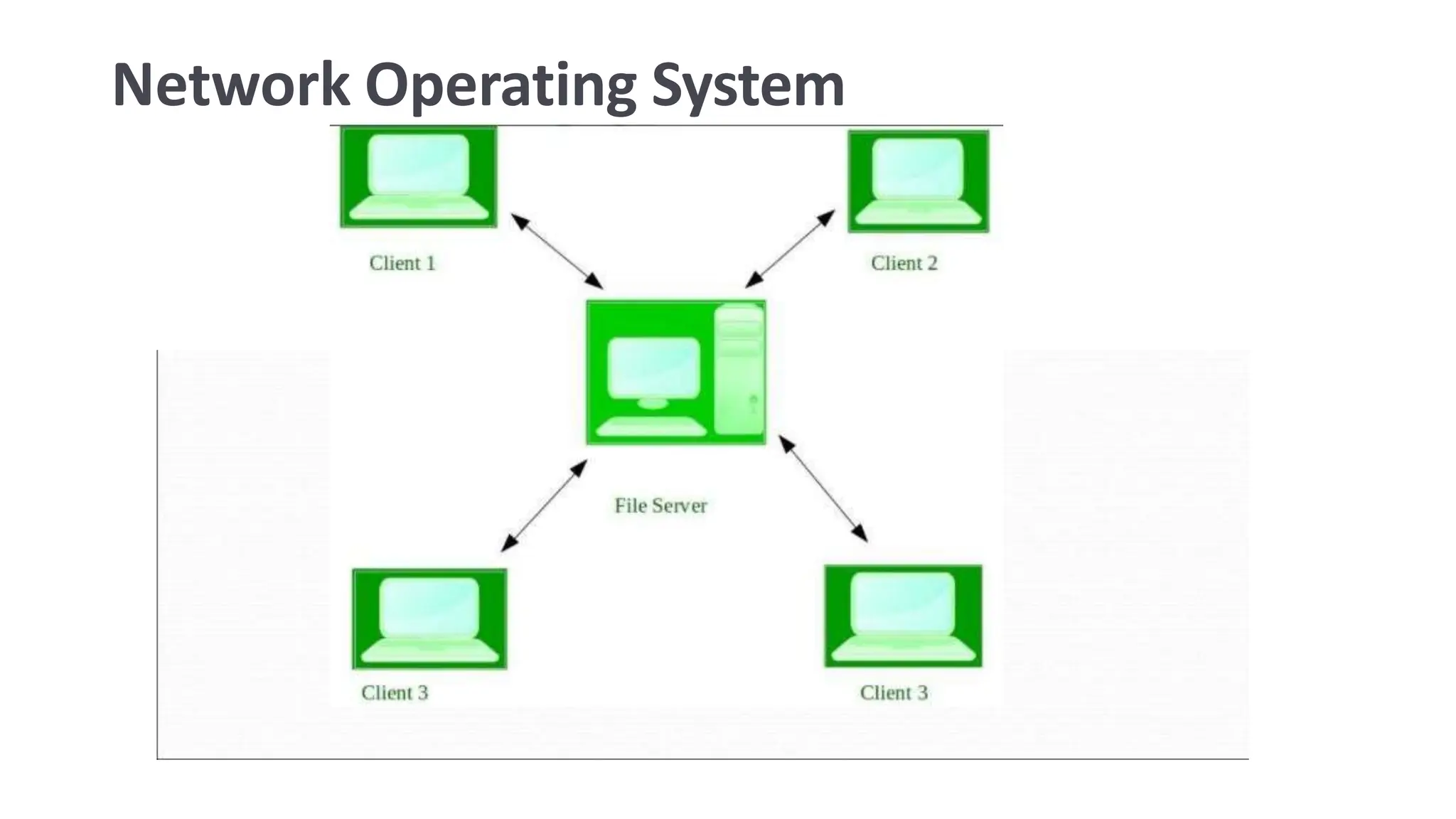
This document discusses real-time operating systems. It defines real-time systems as systems that require very small and strict time intervals to process inputs and provides examples like missile systems. It describes two types of real-time systems: hard real-time systems which have the strictest time constraints and soft real-time systems which have less strict constraints. The document covers key aspects of real-time systems like estimating program run times, task assignment and scheduling, and discusses techniques like precomputed and dynamic scheduling.