This document discusses diffusion, including:
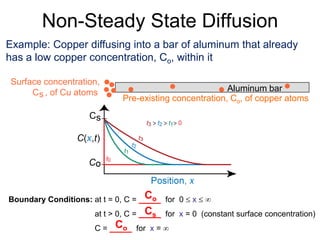
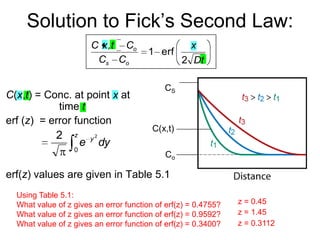
1) Steady-state diffusion is when the rate of diffusion is independent of time and follows Fick's first law. Non-steady state diffusion follows Fick's second law, where concentration depends on both position and time.
2) The diffusion coefficient D increases exponentially with temperature and can be calculated from an Arrhenius equation.
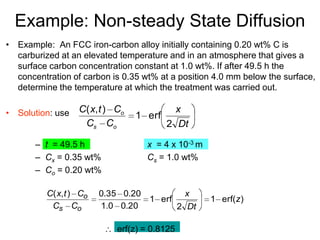
3) Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating D at different temperatures and solving diffusion problems involving concentration gradients over time.





![Diffusion and Temperatureæ ö ç =DDoexpè ø QdD= diffusion coefficient [m2/s]-DoRT= pre-exponential [m2/s]Qd= activation energy [J/mol or eV/atom] R= gas constant [8.314 J/mol-K]T= absolute temperature [K]Diffusion Coefficient, D, increases with increasing T.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/em321lesson08asolutions-ch5-diffusion-100907092225-phpapp02/85/Em321-lesson-08a-solutions-ch5-diffusion-6-320.jpg)