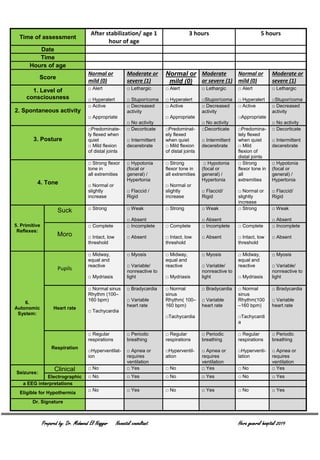
This document outlines the eligibility criteria for therapeutic hypothermia treatment in newborns. Babies must be greater than 36 weeks gestation and weigh over 2 kg to be eligible. Exclusion criteria include moribund infants, major abnormalities, coagulopathy or head trauma. To be eligible, infants must meet criteria A (such as low blood pH or Apgar score) and criteria B (clinical seizures or moderate-severe encephalopathy signs). Encephalopathy is assessed using a scale that evaluates consciousness, tone, reflexes and more. If criteria A and B are met, hypothermia treatment may begin after ensuring no brain abnormalities via ultrasound. The infant's temperature and neurological status are then monitored every 15 minutes and 1