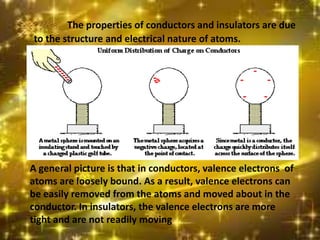
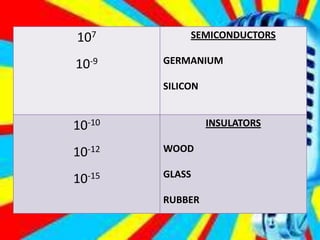
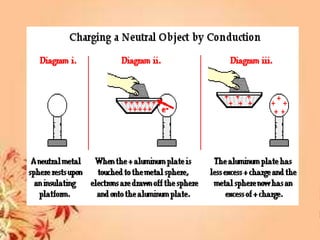
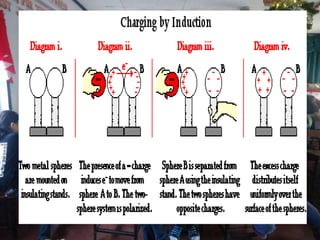
This document discusses electrostatic charging and the differences between conductors, insulators, and semiconductors. Electrostatic charging is the process by which an insulator or insulated conductor gains a net electric charge. Materials are charged through friction, contact/conduction, induction, or polarization. Conductors allow electric charge to move through them, insulators do not, and semiconductors fall in between. Charging can be demonstrated using an electroscope and is useful in applications like electrostatic precipitation to clean air.