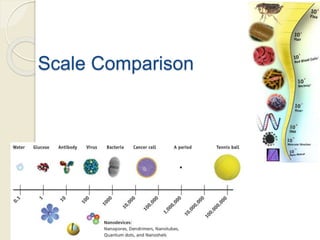
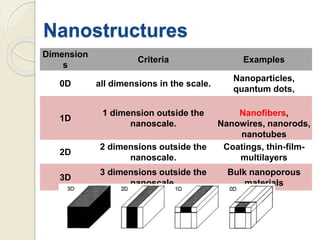
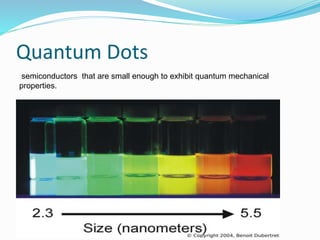
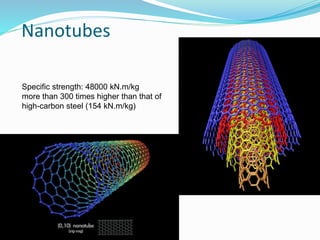
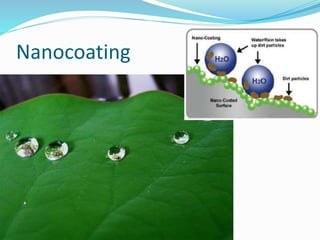
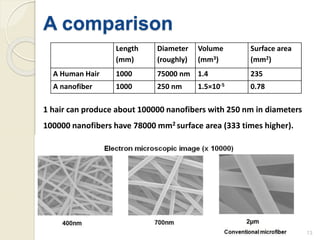
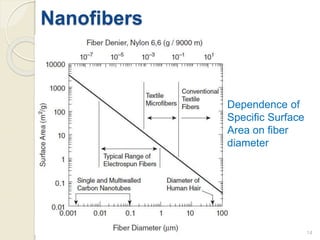
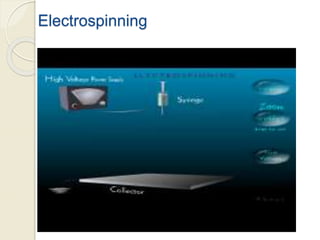
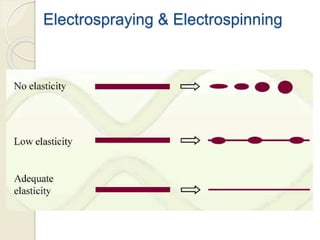
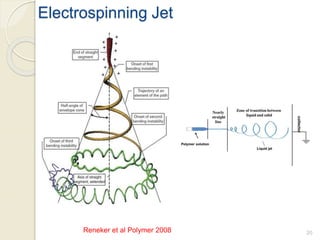
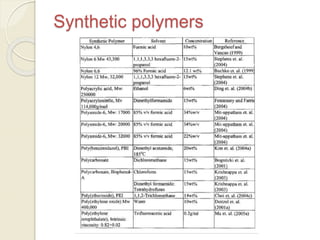
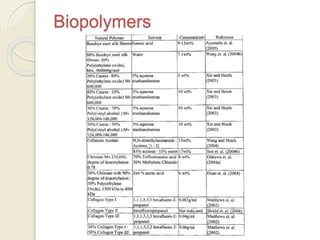
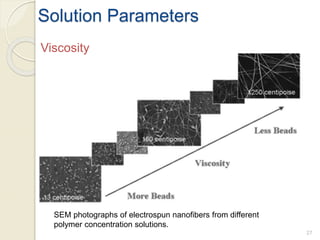
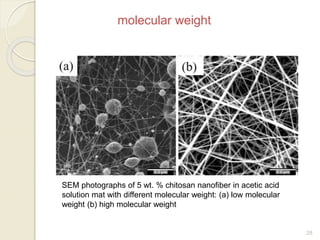
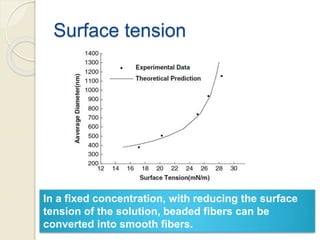
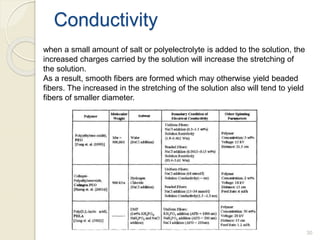
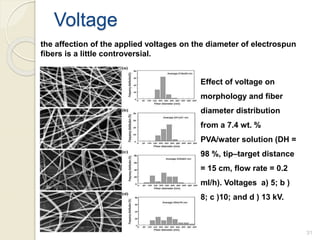
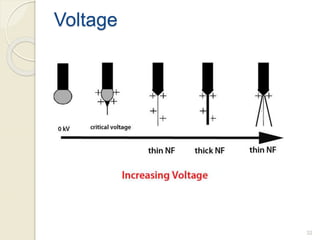
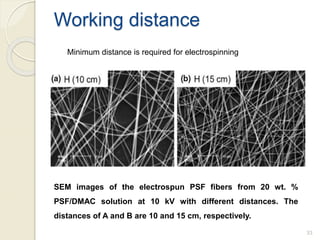
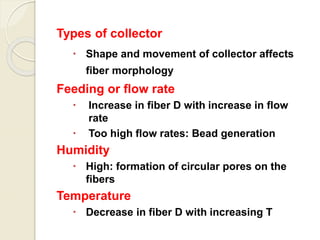
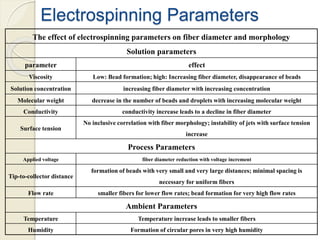
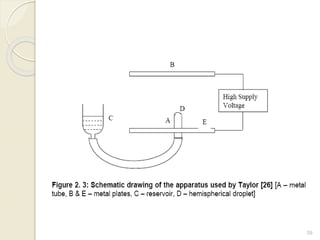
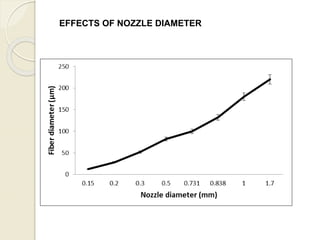
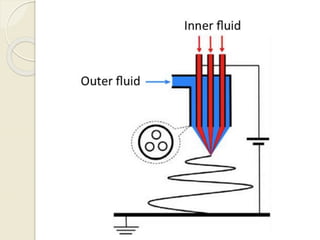
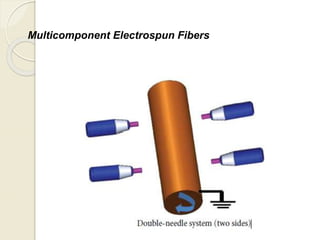
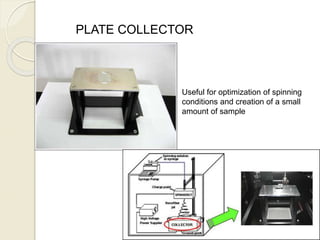
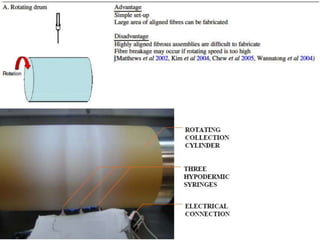
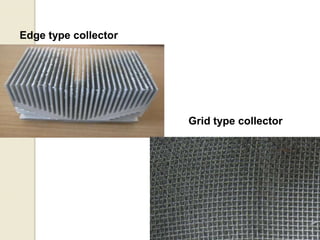
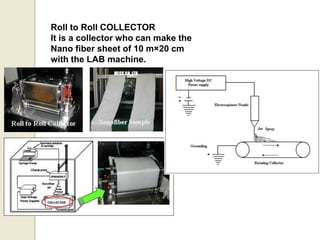
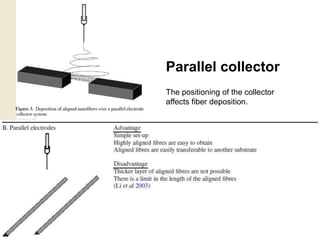
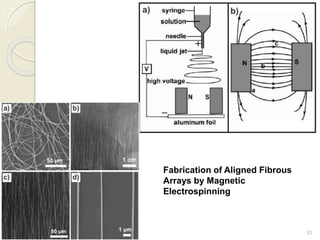
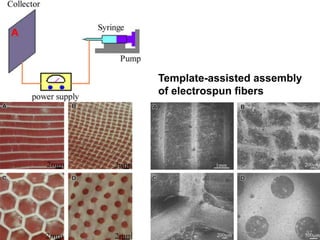
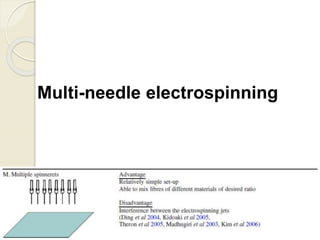
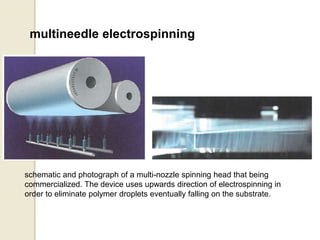
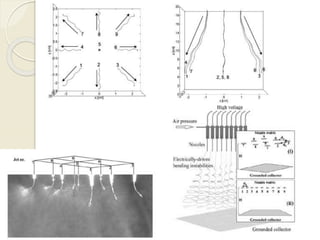
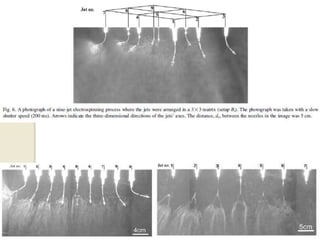
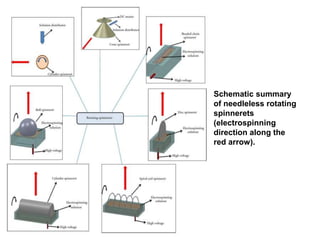
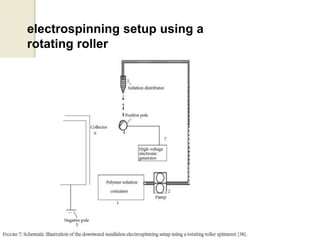
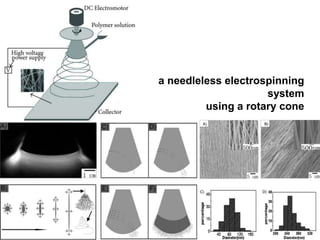
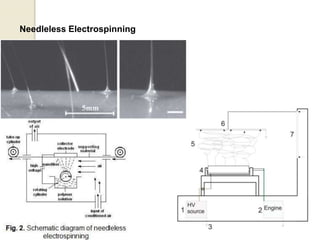
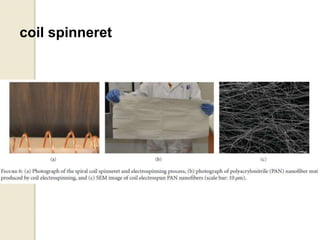
Electrospinning is a nanofiber fabrication technique that uses electrostatic forces to produce fibers with diameters as small as 1 nanometer. The process involves applying a high voltage to a polymer solution or melt, which is extruded through a spinneret to form fibers that are deposited onto a grounded collector. Key parameters that affect fiber morphology include solution properties like concentration and viscosity, as well as process parameters like voltage, flow rate, and working distance. Electrospinning can be used to produce a variety of nanofibers from polymers, ceramics, and composites for applications like filtration, energy storage, and tissue engineering. Scale-up methods involve using multiple spinnerets or continuous systems like rotating drums to produce