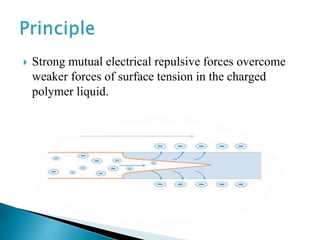
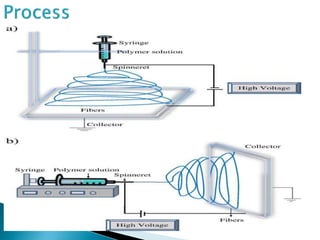
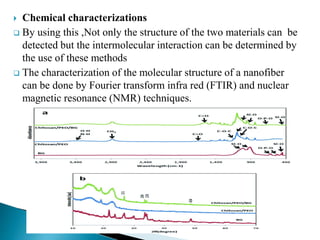
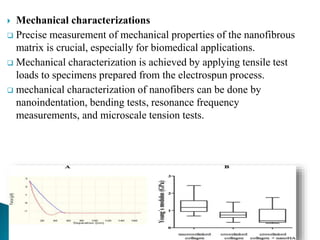
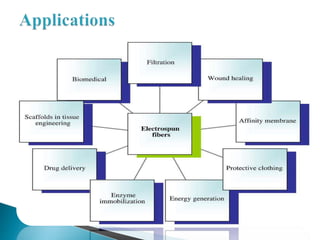
Electrospinning is a technique that utilizes an electrical charge to produce ultra-fine fibers from polymer solutions, enabling the creation of nanofibers with controllable properties like high surface area and porosity. This process is versatile, allowing for the use of both synthetic and natural polymers and is conducted at room temperature using a high voltage power supply. Despite its advantages in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, electrospinning faces limitations such as small pore sizes and challenges with cellular infiltration.