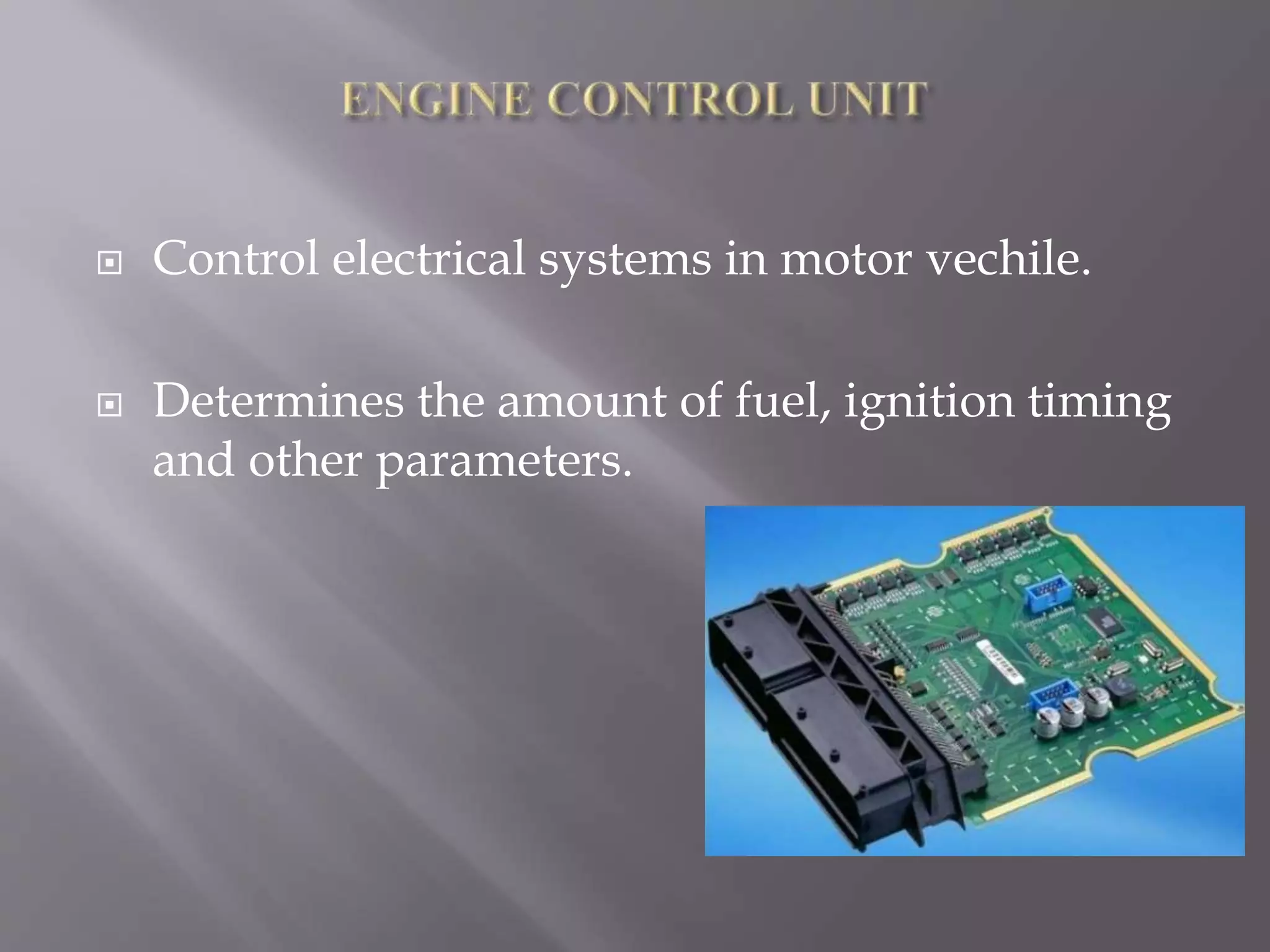
This document discusses electronic fuel injection (EFI) systems. It explains that EFI systems are more precise, reliable, and cost-effective than carburetor systems. EFI provides the correct air-fuel ratio, reduces exhaust pollution, and increases engine power. It then describes different types of fuel injection systems, including single-point and multi-point as well as indirect and direct injection. Various sensors that provide input to the engine control unit (ECU) are also outlined, such as oxygen, throttle position, engine temperature, inlet air temperature, and crankshaft position sensors.