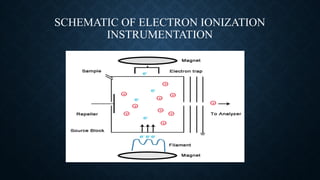
Electron ionization (EI) is an effective mass spectrometry technique for identifying organic compounds by using high-energy electrons to produce ions through a process that often leads to extensive fragmentation. While EI offers advantages such as high ionization efficiency and a wealth of structural information, it is unsuitable for volatile, thermally unstable samples and can only detect positive ions. This method finds application in fields like environmental analysis, pharmaceuticals, and petrochemicals for identifying and quantifying compounds.