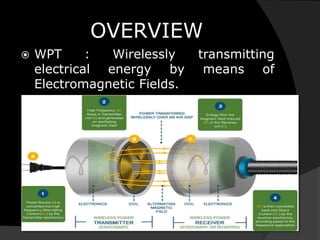
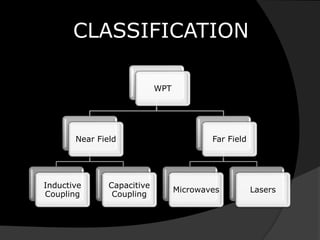
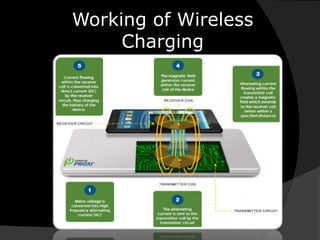
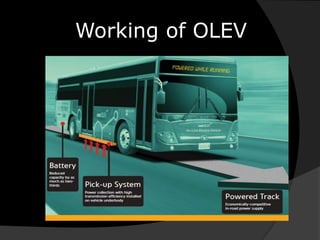
Wireless power transmission (WPT) allows for wirelessly transmitting electrical energy, reducing the reliance on disposable batteries and associated e-waste. The document highlights the application of WPT in wireless charging and the Online Electric Vehicle (OLEV) system, which offers benefits like zero emissions and lower operating costs but faces challenges such as high installation costs and limitations in power grid capabilities. Overall, WPT offers a promising solution for powering electronic devices and modern transport systems.