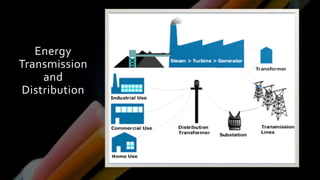
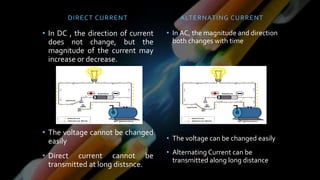
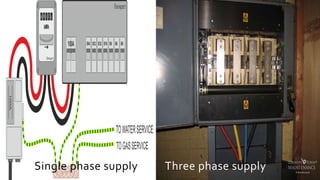
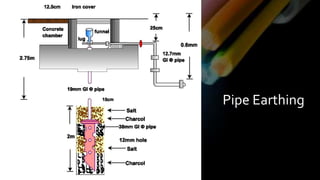
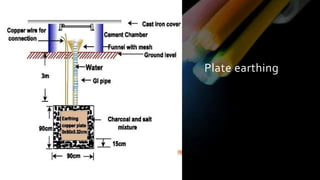
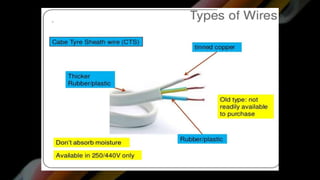
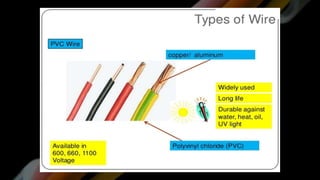
This document provides definitions and information about various electrical concepts and components. It defines electrical services and discusses their uses in residential, industrial, and commercial buildings. It also defines key electrical terms like current, potential difference, conductors, insulators, and discusses direct and alternating current. The document then covers domestic electric supply systems, wiring components like fuses and circuit breakers, and different types of earthing systems. It concludes by describing various wiring methods and types of wires.