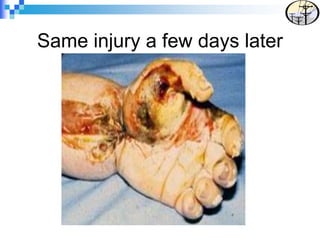
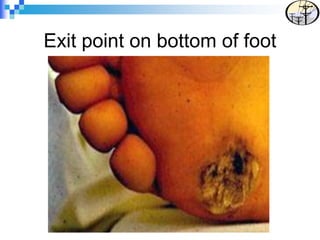
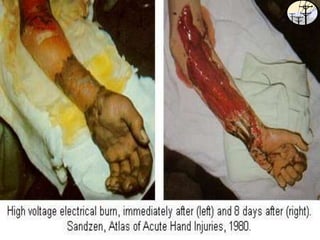
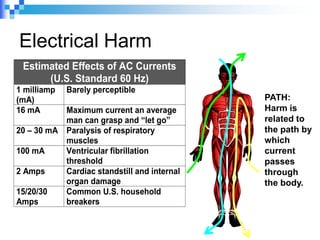
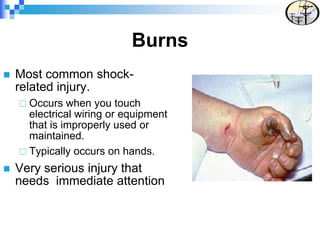
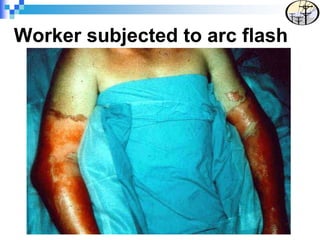
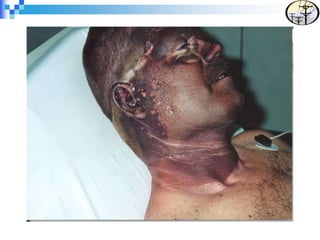
Electrical safety is an important issue that can prevent fatalities and injuries. Each year, contact with overhead power lines results in deaths and property damage. Working near electricity puts many workers at risk, including equipment operators, emergency responders, and those on ladders or scaffolds. Even small amounts of electricity can cause harm, with just 75mA potentially causing death. Proper safety training and coordinating work with utilities can help prevent electrical accidents.