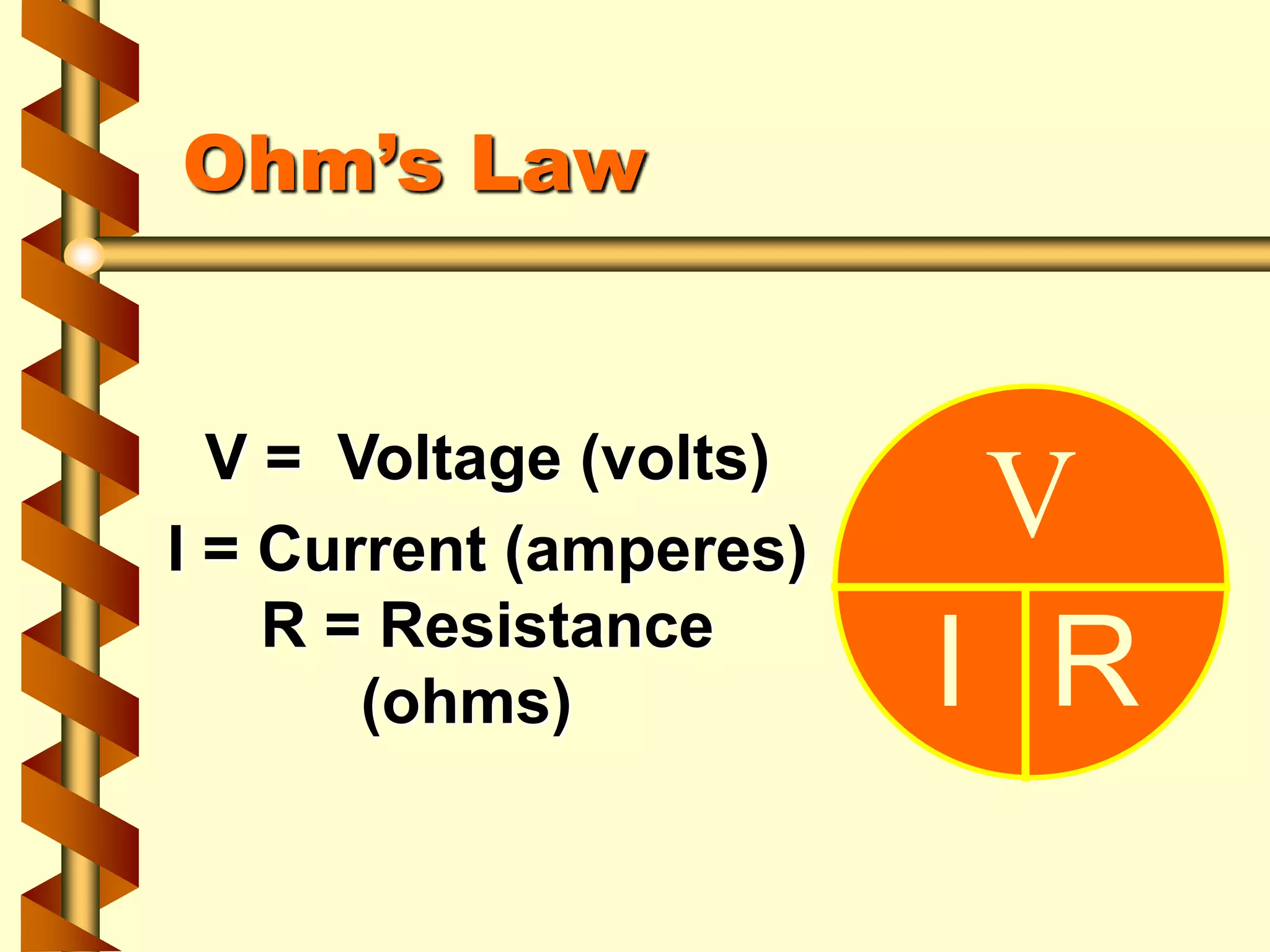
This document discusses various electrical safety topics for construction sites. It begins with an explanation of Ohm's Law and electrical current. It then covers electric shock and its severity, effects of current on the human body, and proper grounding and circuit protection devices like GFCIs. Additional sections provide guidance on lockout/tagout procedures, insulation, personal protective equipment, cable routing, and IP ratings for equipment protection from solids and liquids. The overall message is that electrical safety is everyone's responsibility to help achieve zero accidents.