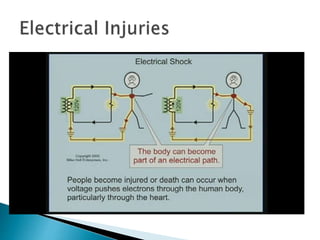
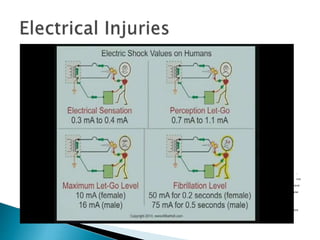
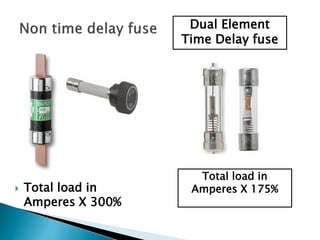
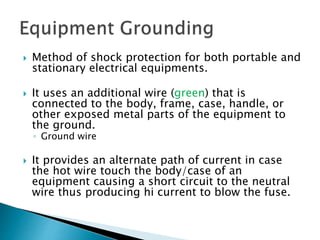
The document outlines essential information regarding electrical safety, including common voltage levels, the effects of electric current on the human body, and the proper measures for rescue and first aid. It describes the dangers of electrical shock, the importance of proper grounding, and the role of safety devices such as fuses and circuit breakers in preventing overcurrent situations. Additionally, it emphasizes safety precautions when working with electrical circuits and equipment, and the need for regular maintenance and inspections to ensure safe operation.