1. The document discusses the design of converting a gasoline-powered scooter into an electric vehicle. It aims to address issues with existing electric vehicles like high costs, low speeds and mileage, and long battery charging times.
2. The proposed methodology includes fitting a hub motor to the front wheel of a conventional scooter and experimenting with battery packs to determine the optimal energy and power requirements. A cost-benefit analysis will also be conducted.
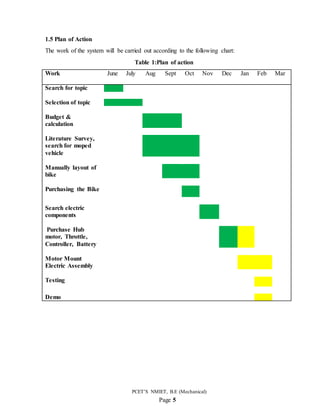
3. The plan of action outlines converting and testing the scooter from June to March, including purchasing electric components, assembling the motor and batteries, and demoing the electric vehicle. Literature on electric vehicles and their benefits is also reviewed.









![PCET’S NMIET, B.E (Mechanical)
Page 12
3.3 Components Description
The components used in this project are BLDC hub motor, motor controller, sealed
batteries, charging circuit, ignition switch, Display unit, Throttle.
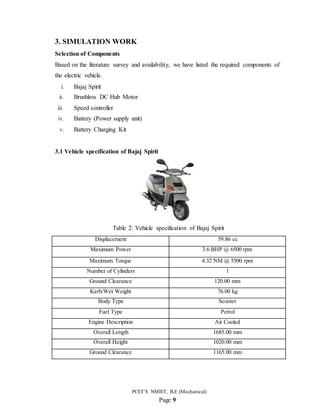
3.3.1 I C Engine
It had a 59.86cc Engine with a single cylinder, 2-stroke, forced air cooled, which gave
maximum power of 3.6bhp@6500rpm and maximum torque of about 4.32Nm
@5500rpm. It had 2-speed automatic transmission and drum brakes at front and at rear
end, which made it suitable to drive on busy roads.
Figure 1: Bajaj Spirit of IC Engine [7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electricscooterreport-210518152329/85/Electric-scooter-report-12-320.jpg)
![PCET’S NMIET, B.E (Mechanical)
Page 14
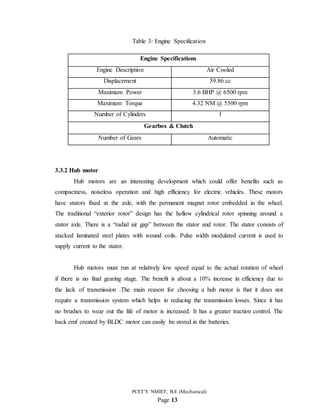
Figure 2: Hub motor [8]
Brushless Direct Current (BLDC) motor is a type of synchronous motor, where magnetic
fields generated by both stator and rotate have the same frequency. The BLDC motor has
a longer life because no brushes are needed. Apart from that, it has a high starting torque,
high no-load speed and small energy losses. The BLDC motor can be configured in 1-
phase, 2-phase, and 3-phase. Three-phase motors are the most popular among all the
configurations and are widely used in e-bikes.
We have selected hub motor because the motor replaces the hub of wheel.
Coupling loss is reduced and mounting can be made easy without the use of chains or
belts, and that reduces size and weight of the scooter.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electricscooterreport-210518152329/85/Electric-scooter-report-14-320.jpg)
![PCET’S NMIET, B.E (Mechanical)
Page 16
off determining the average voltage. Chopping is performed by power electronic circuitry
such as diodes and thrusters and silicon control rectifiers (SCR). Controllers also effect
regenerative braking, by which the motor is acted as a generator to recharge the batteries.
The controller for the motor is being interfaced with the motor speed regulation.
The speed controlling throttle is being interfaced through the motor controller circuit. The
motor used here is 48V, 250W, Ampere made hub motor.
The controller for the motor is also Ampere made suitable for controlling the
specified motor. The throttle is an ampere made throttle for speed regulation of the
specified motor. The input to the motor is supplied by four Exide made Electra lead-acid
batteries each of 12V, 26Ah through controller for testing purpose. Two independent
propelling sources are being employed for obtaining total propulsion of the vehicle.
Figure 3: DC Controller [9]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electricscooterreport-210518152329/85/Electric-scooter-report-16-320.jpg)

![PCET’S NMIET, B.E (Mechanical)
Page 18
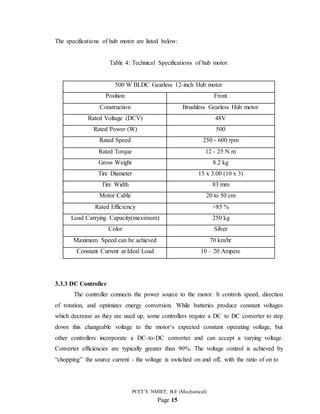
3.3.4 Batteries
Figure 4: Lithium ion Battery pack [10]
Lithium-ion batteries are the most suitable in existing technology for electric vehicles
because they can deliver high output because of having capability to store high power per
unit of battery mass, allowing them to be lighter and smaller than other rechargeable
batteries. These features also explain why lithium-ion batteries are already widely used for
consumer electronics such as cell phones, laptop computers, digital cameras/video
cameras, and portable audio/game players. Other advantages of lithium-ion batteries
compared to lead acid and nickel metal hydride batteries include high-energy efficiency,
no memory effects, no self discharging and a relatively long cycle life. The electric
scooter uses battery having capacity of 48V 20Ah capacity.
Table no 6: Battery Specification
Battery Type Li ion
Battery Capacity 20
Capacity (ampere hour) 20Ah
Model 48Volts 20Ah
Warranty 1 Years/2 Years
Product Type Li ion battery
Voltage (V) 48
Weight (g) 6000
Condition New
Weight (kg) 6
Current 30 Amps
Use E bikes
Charge Current 10
Max Pulse Discharge Rate 40 Amps
Charging Current 10
Battery Dimensions 265mm x 175mm x 68mm
Cycles 1000 cycles @ 80% DOD
Voltage 48
Amperage 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electricscooterreport-210518152329/85/Electric-scooter-report-18-320.jpg)
![PCET’S NMIET, B.E (Mechanical)
Page 19
3.3.5 Battery Charging Kit
Figure 5: Battery Charging Kit [11]
Lithium ion (Li-ion) batteries’ advantages have cemented their position as the primary
power source for portable electronics, despite the one downside where designers have to
limit the charging rate to avoid damaging the cell and creating a hazard. Fortunately,
today’s Li-ion batteries are more robust and can be charged far more rapidly using “fast
charging” techniques.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electricscooterreport-210518152329/85/Electric-scooter-report-19-320.jpg)

