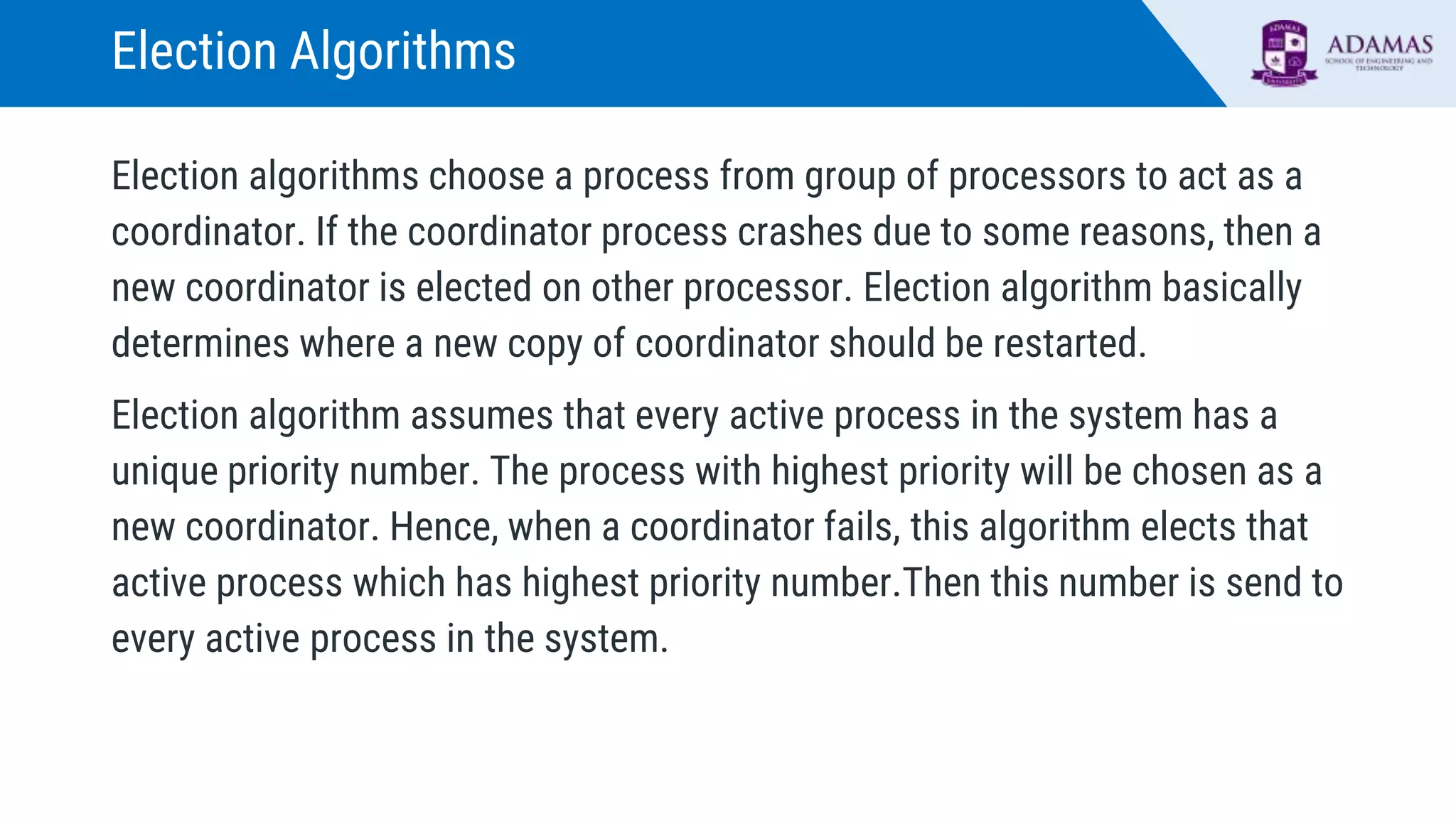
Election algorithms are used in distributed systems to choose a coordinator process in case the current coordinator fails. There are two main election algorithms: the Bully algorithm and the Ring algorithm. The Bully algorithm elects the process with the highest unique ID number as coordinator, while the Ring algorithm passes an election message around a logical ring of processes until it returns to the starter, at which point the process with the highest ID in the message is elected coordinator. Election algorithms ensure a distributed system can automatically select a new coordinator to take over tasks when the current one fails.





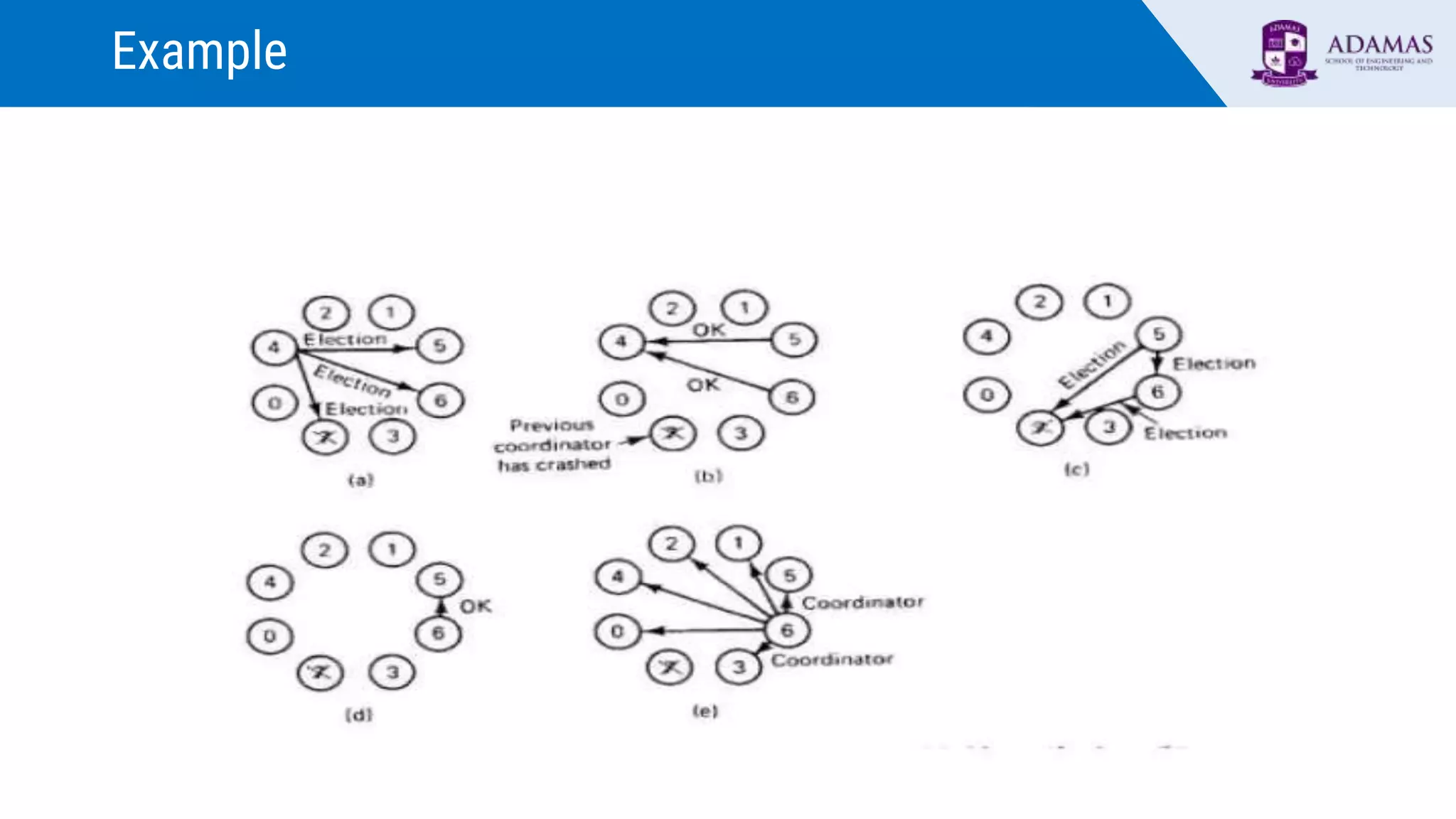



![Example
● When the message
returns to p, it sees its
own process ID in the list
and knows that the
circuit is complete.
● P circulates a
COORDINATOR message
with the new high
number. Here, both 2
and 5 elect 6:
[5,6,0,1,2,3,4]
[2,3,4,5,6,0,1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electionalgorithms-210722054222/75/Election-algorithms-13-2048.jpg)