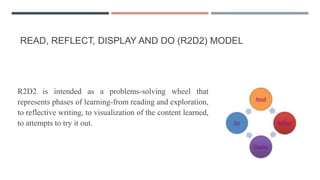
This document discusses e-learning and online tutoring. It describes four types of interaction in online learning: learner-interface, learner-content, learner-instructor, and learner-learner. It also discusses levels of interaction, functions of interaction, and strategies for assessment and supporting online learners. Additionally, it presents models for e-moderation and the R2D2 approach to learning, which involves reading, reflecting, displaying content learned, and doing activities.