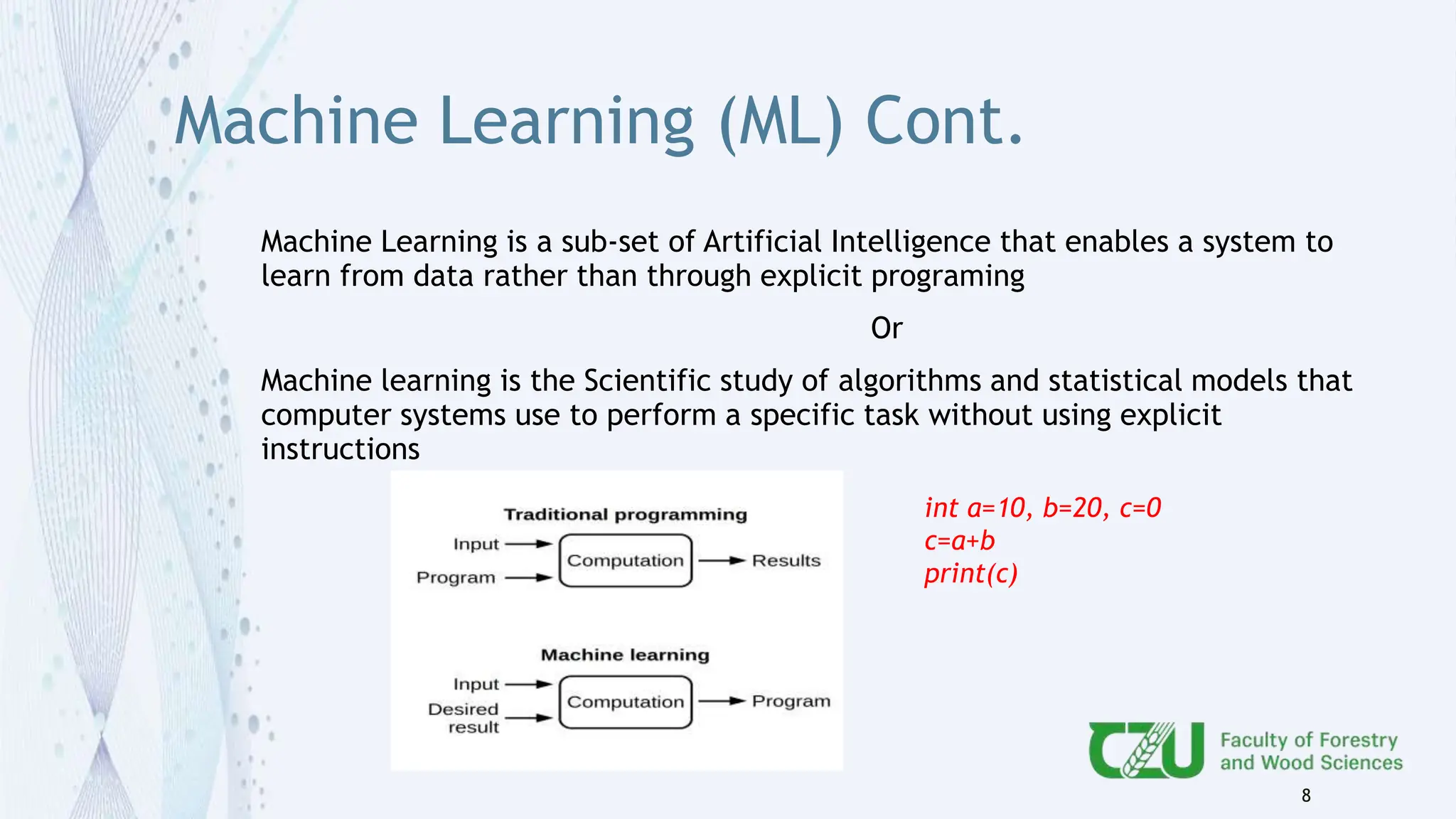
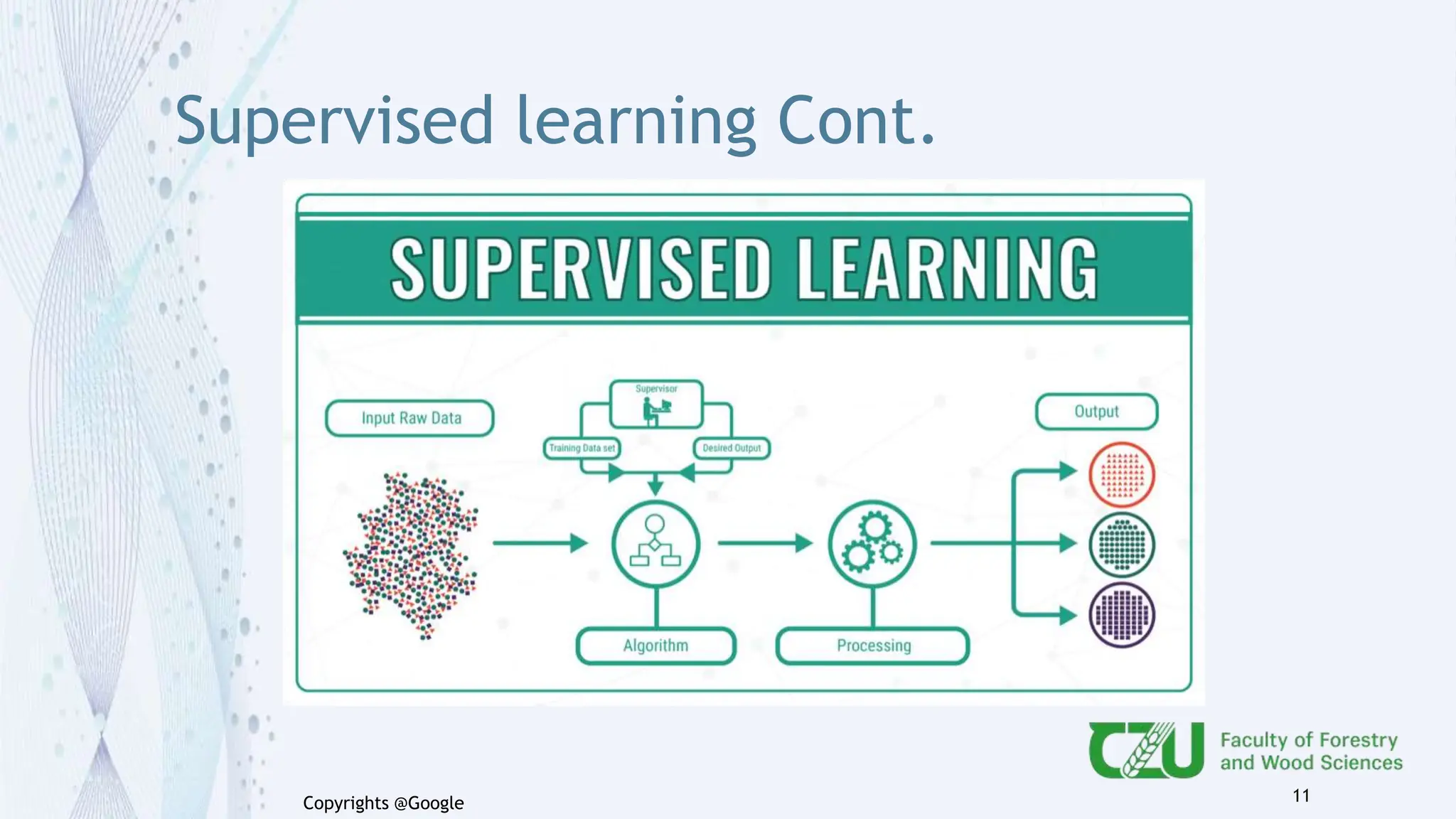
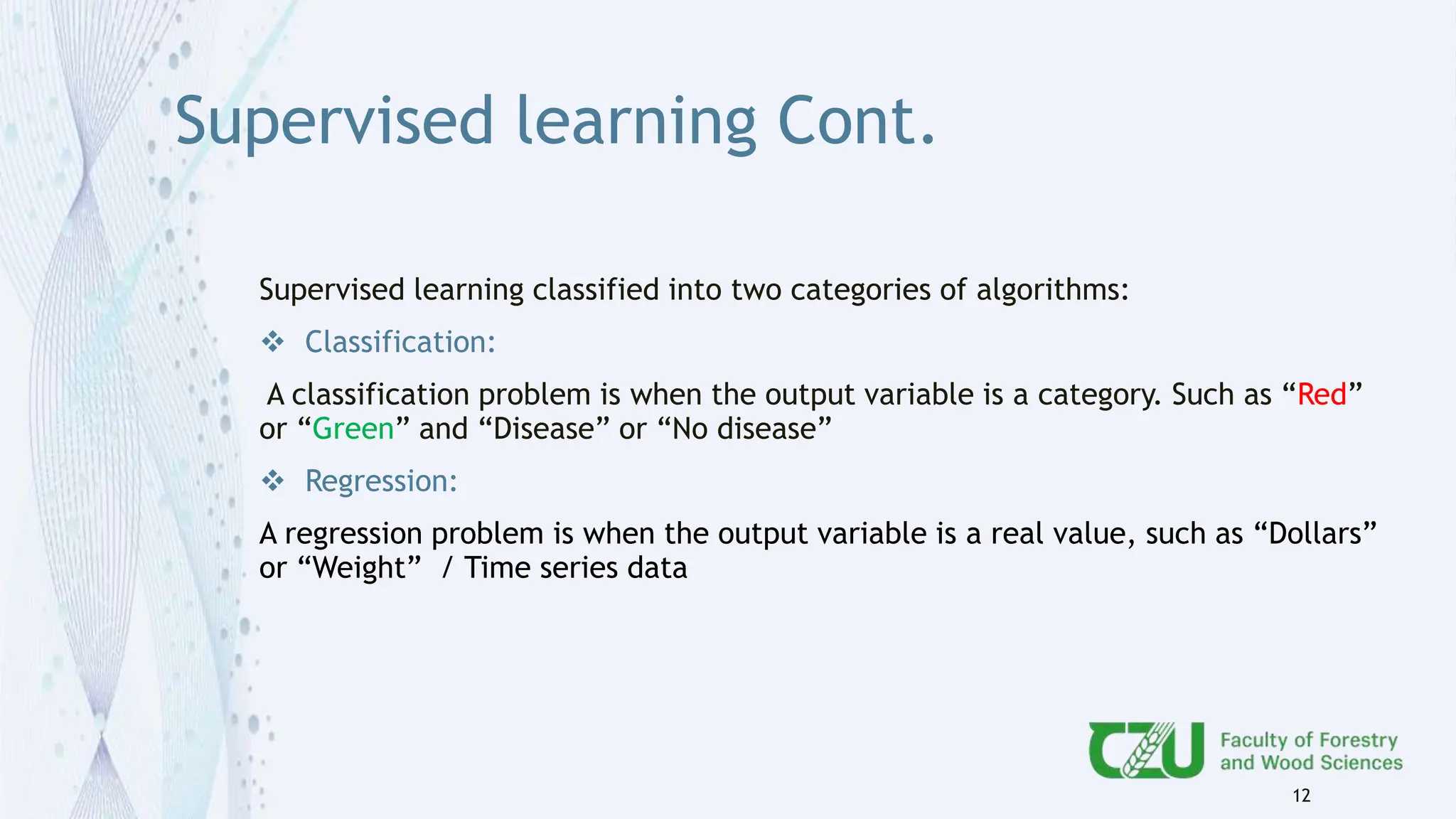
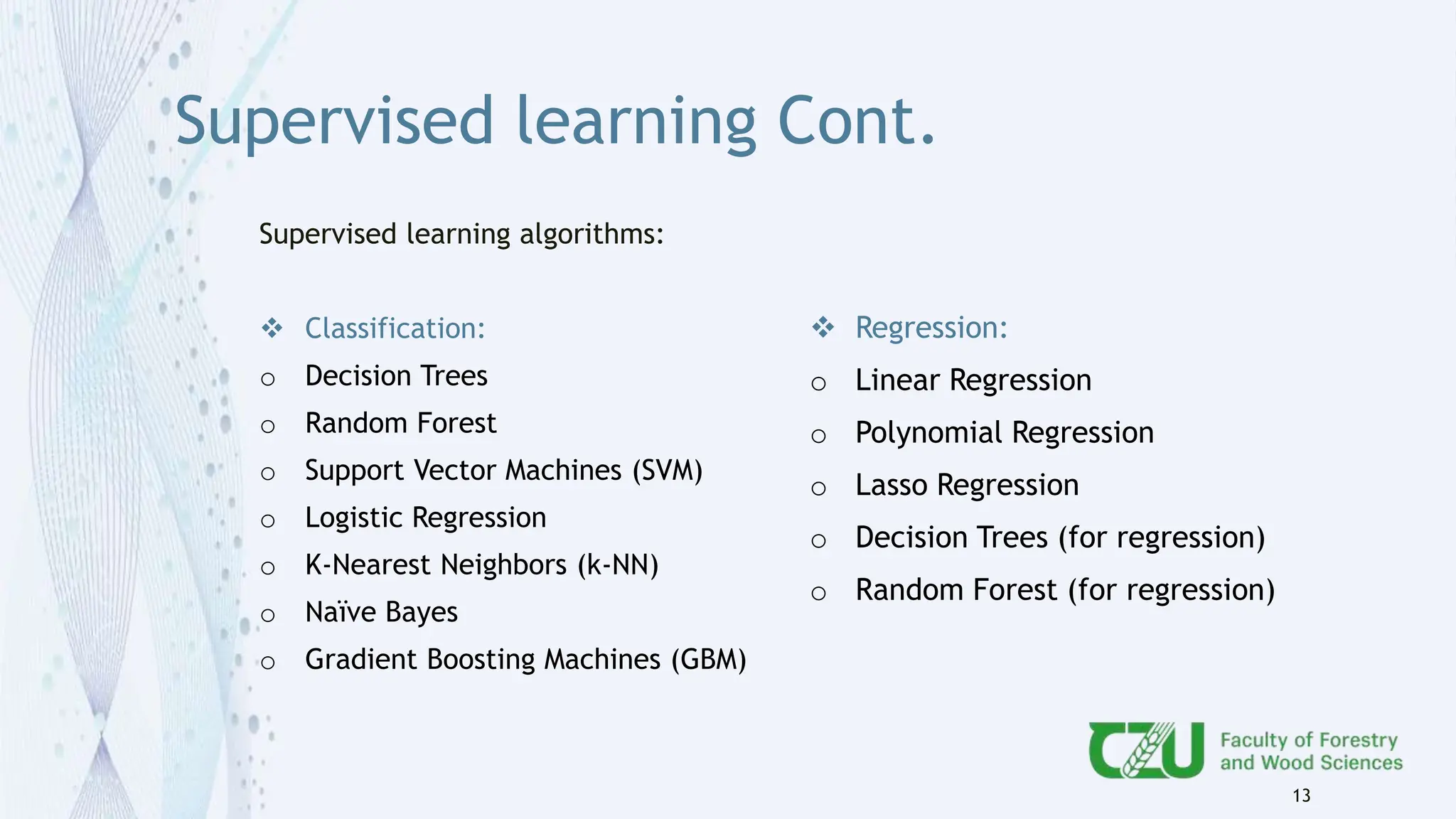
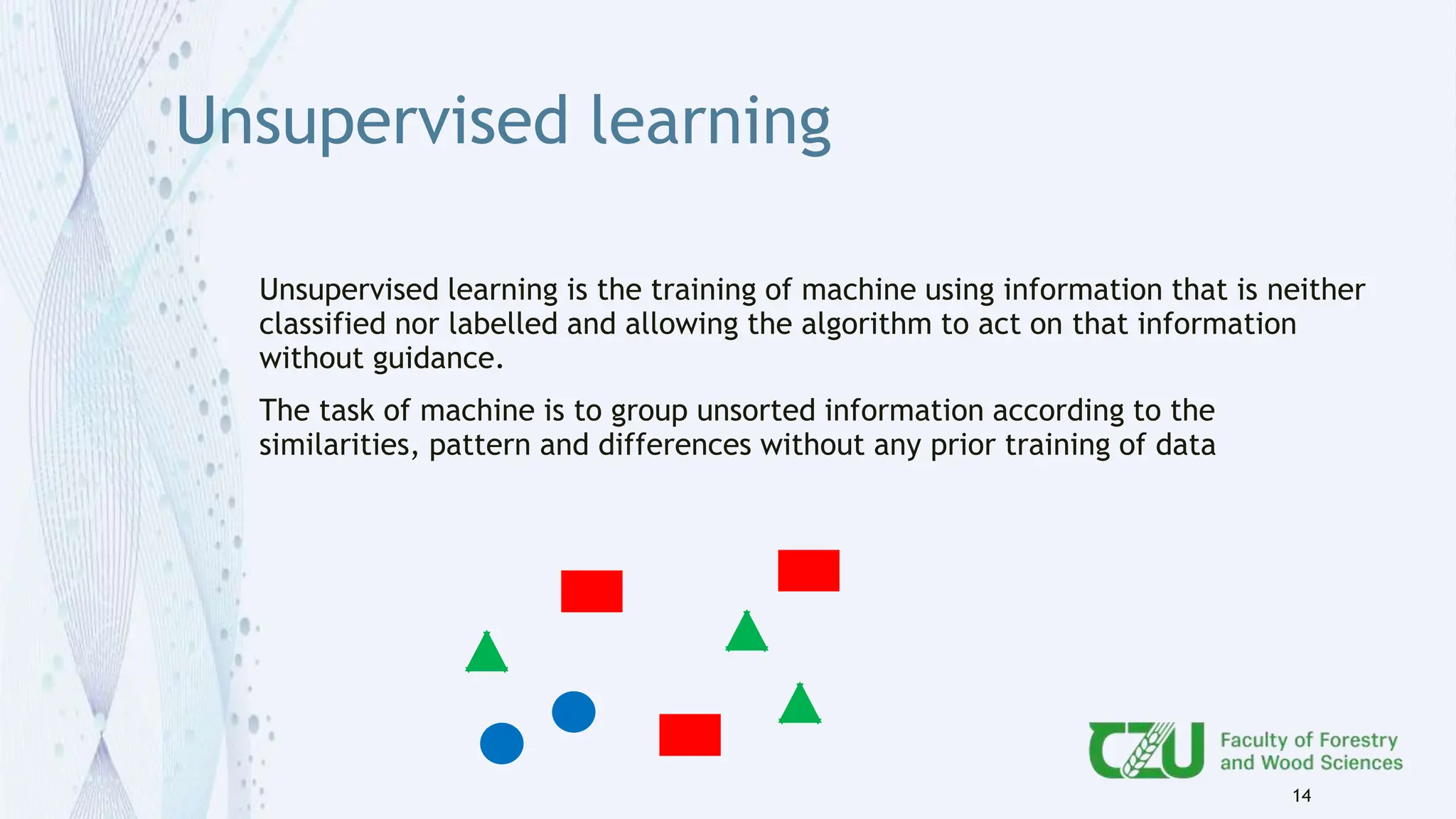
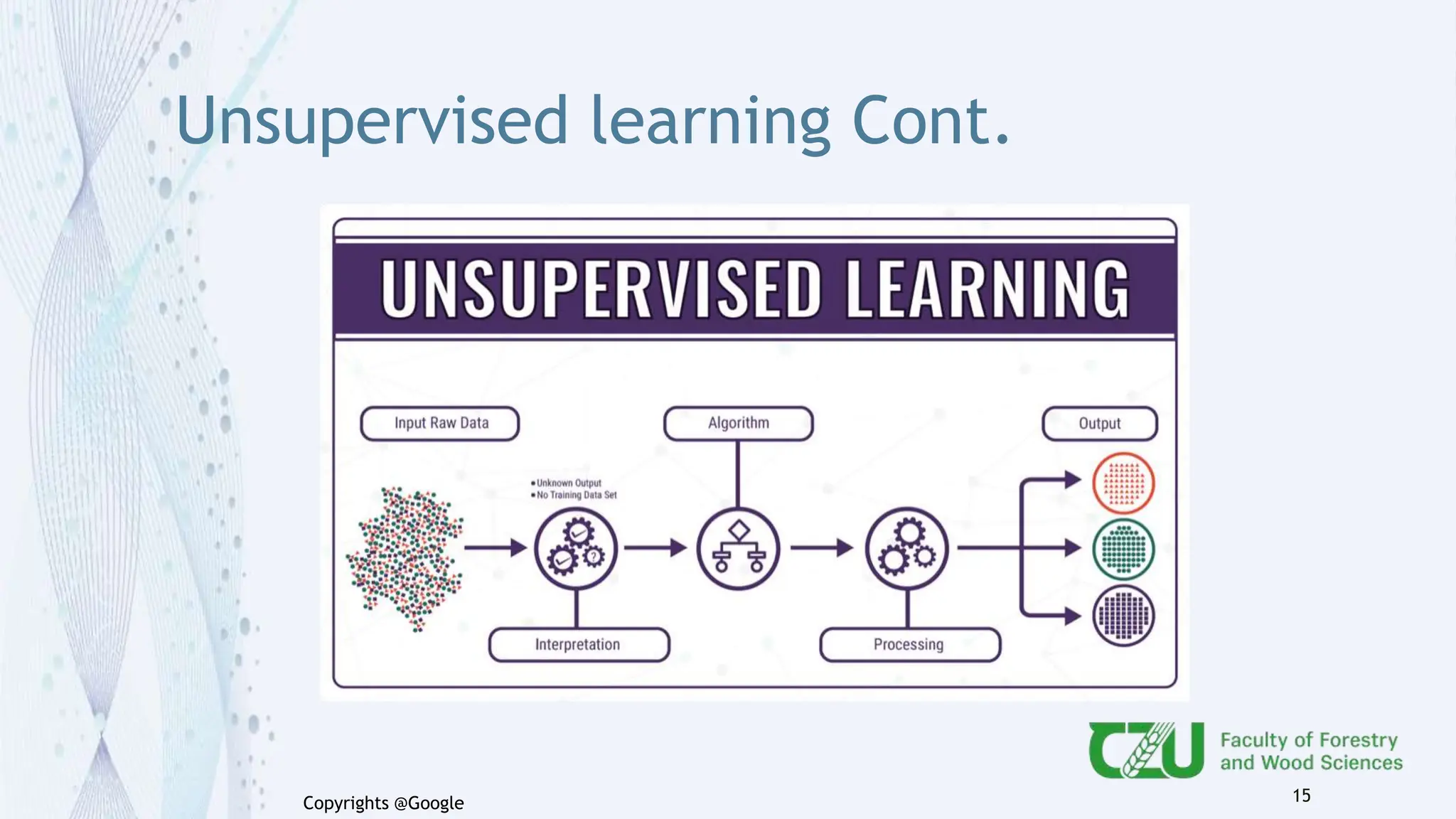
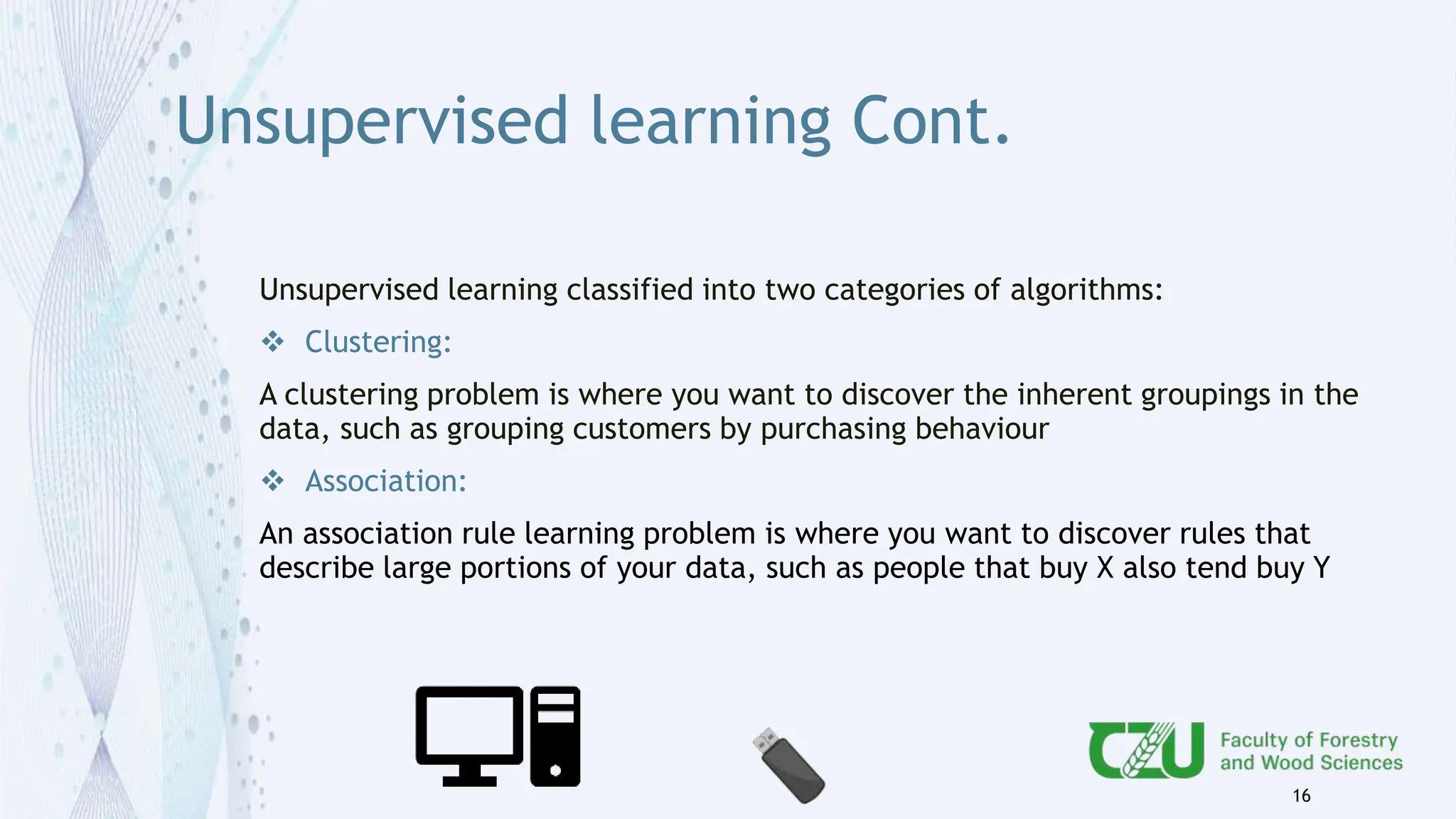
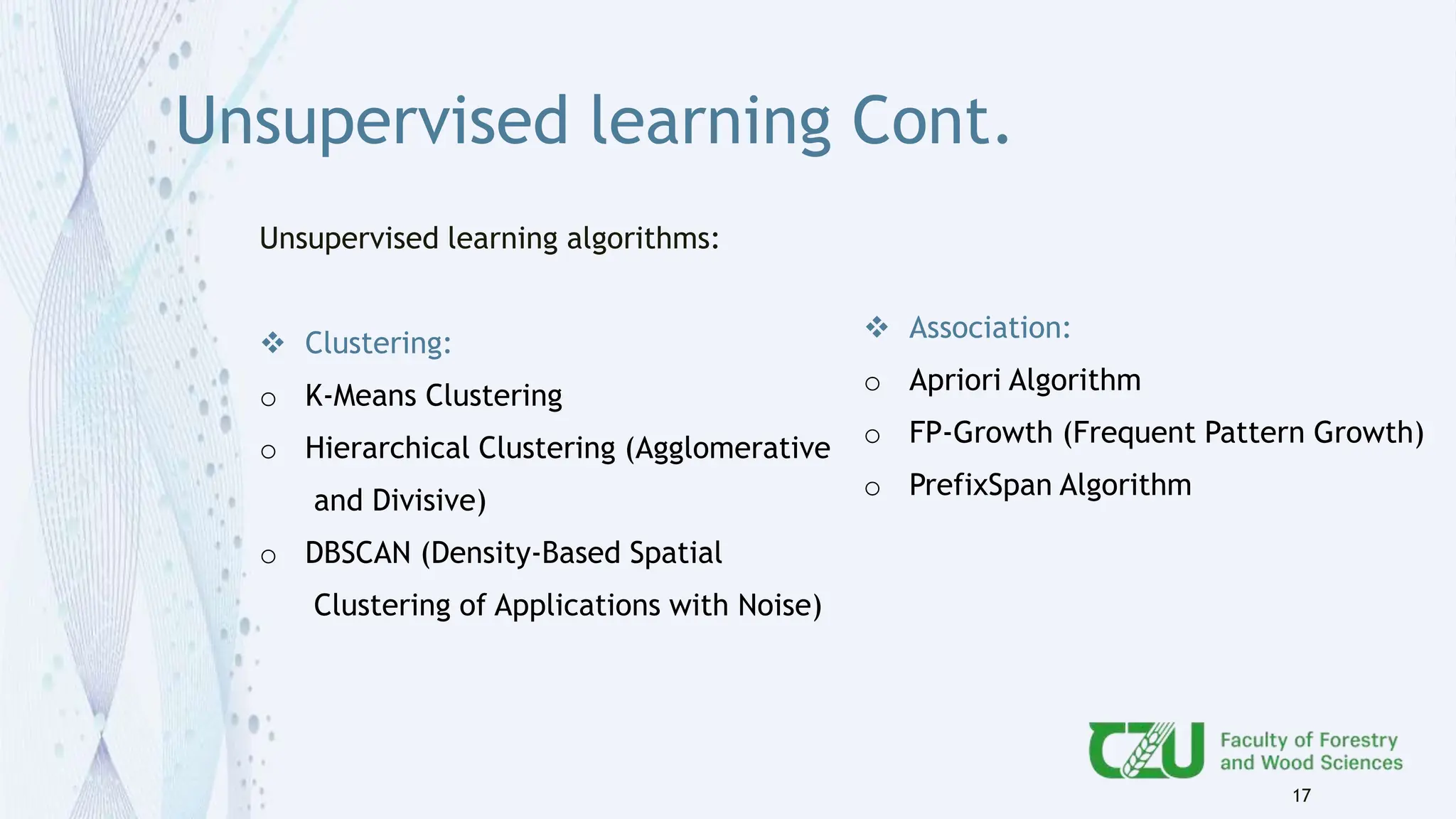
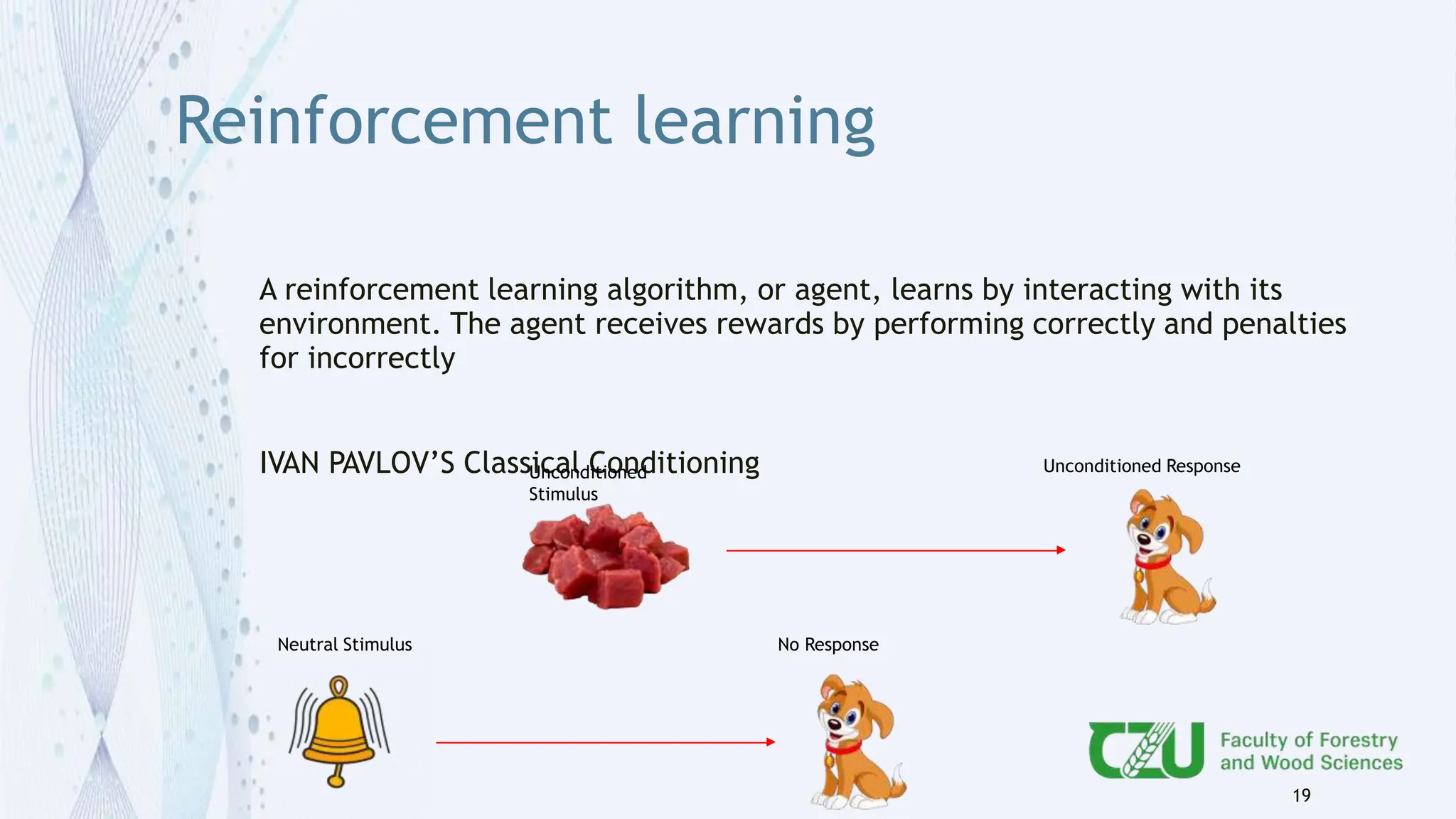
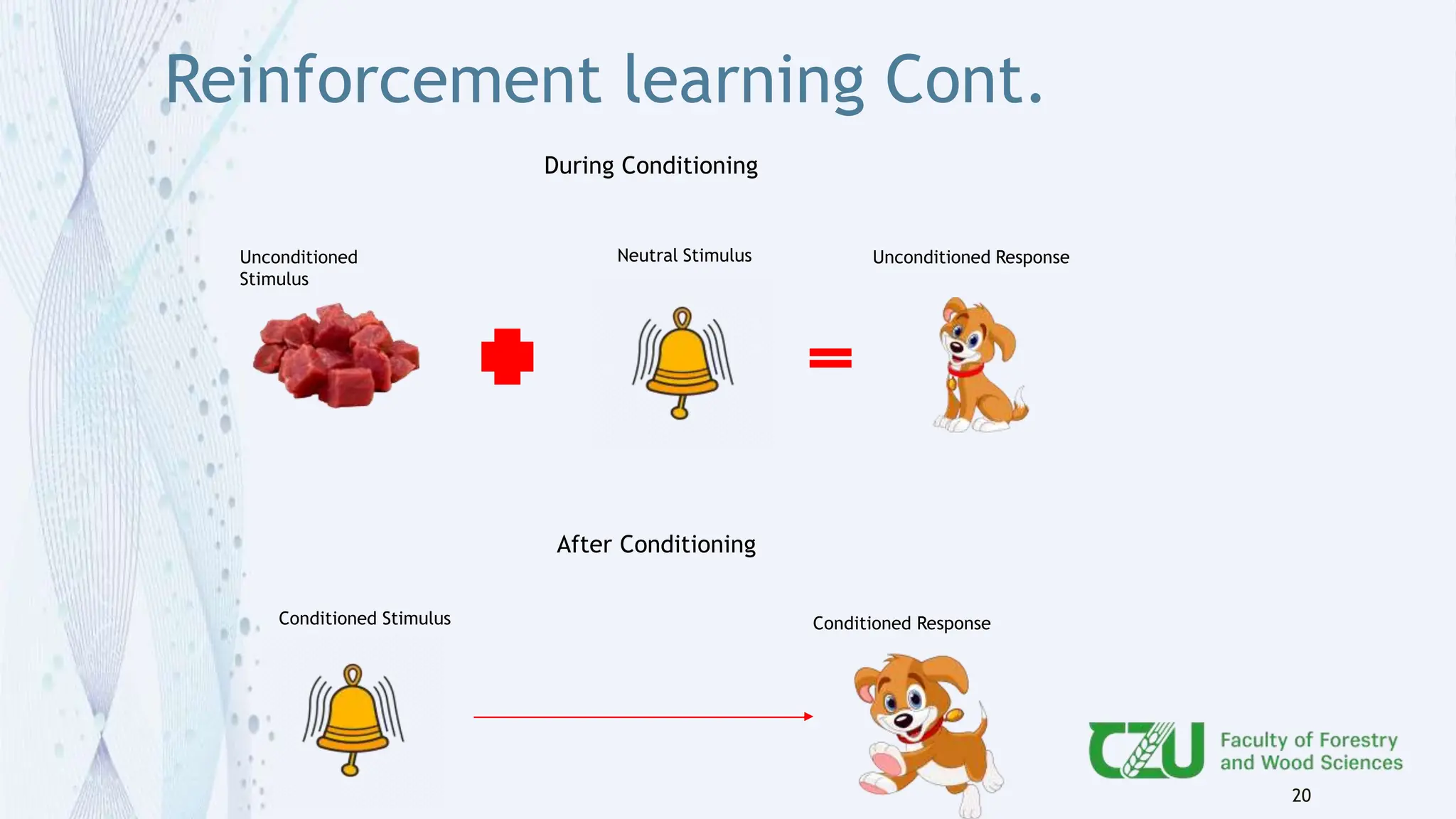
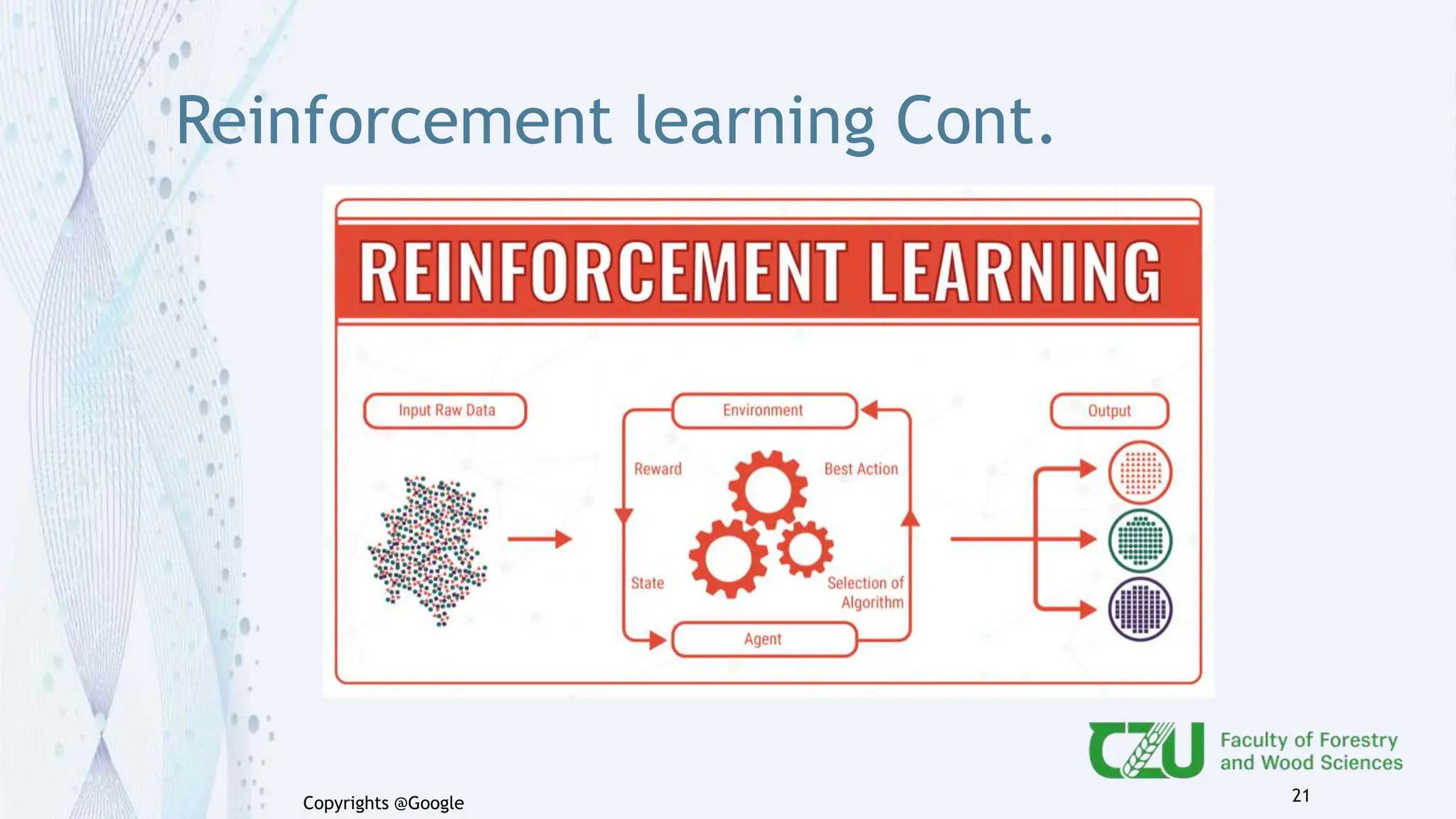
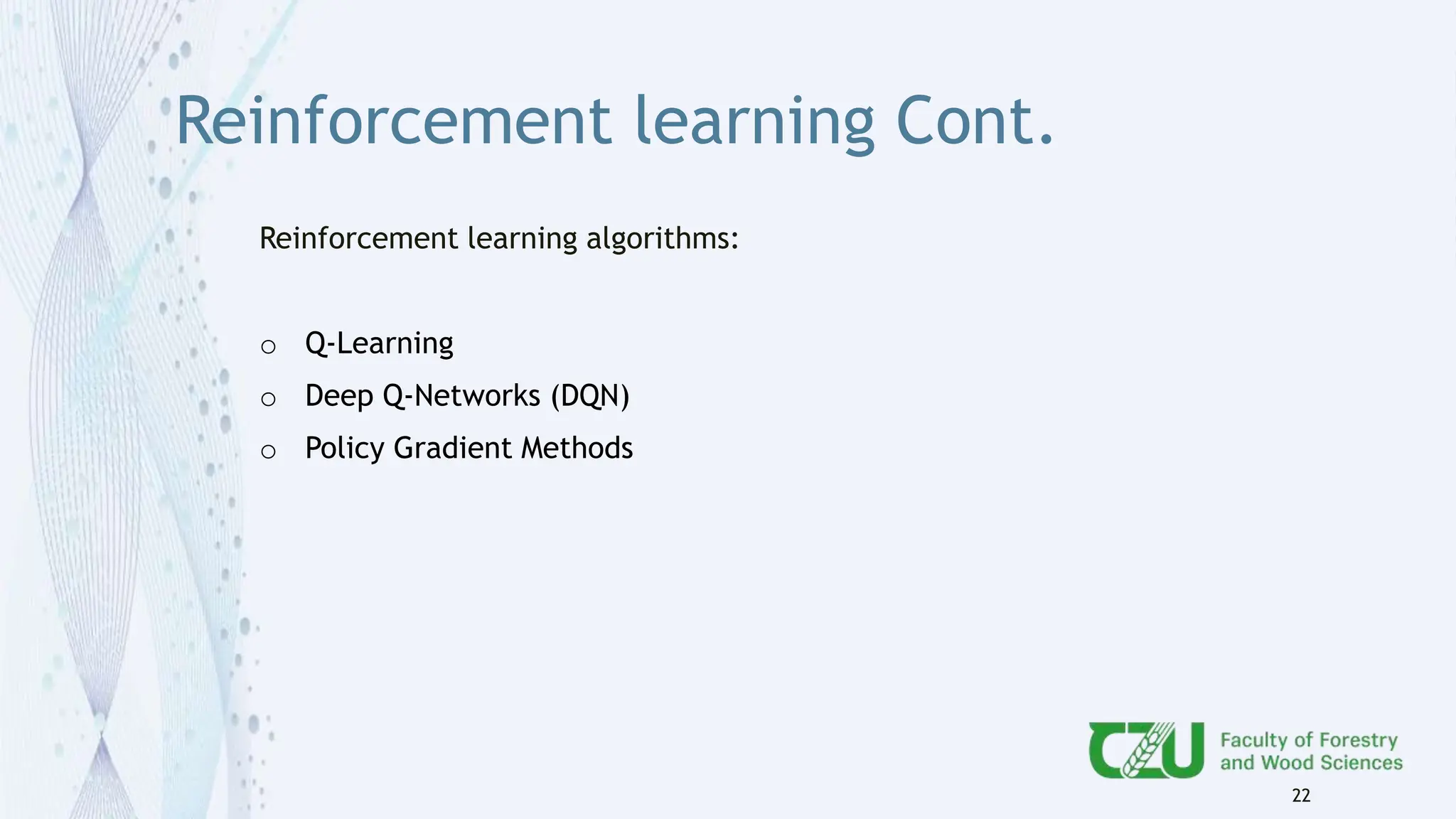
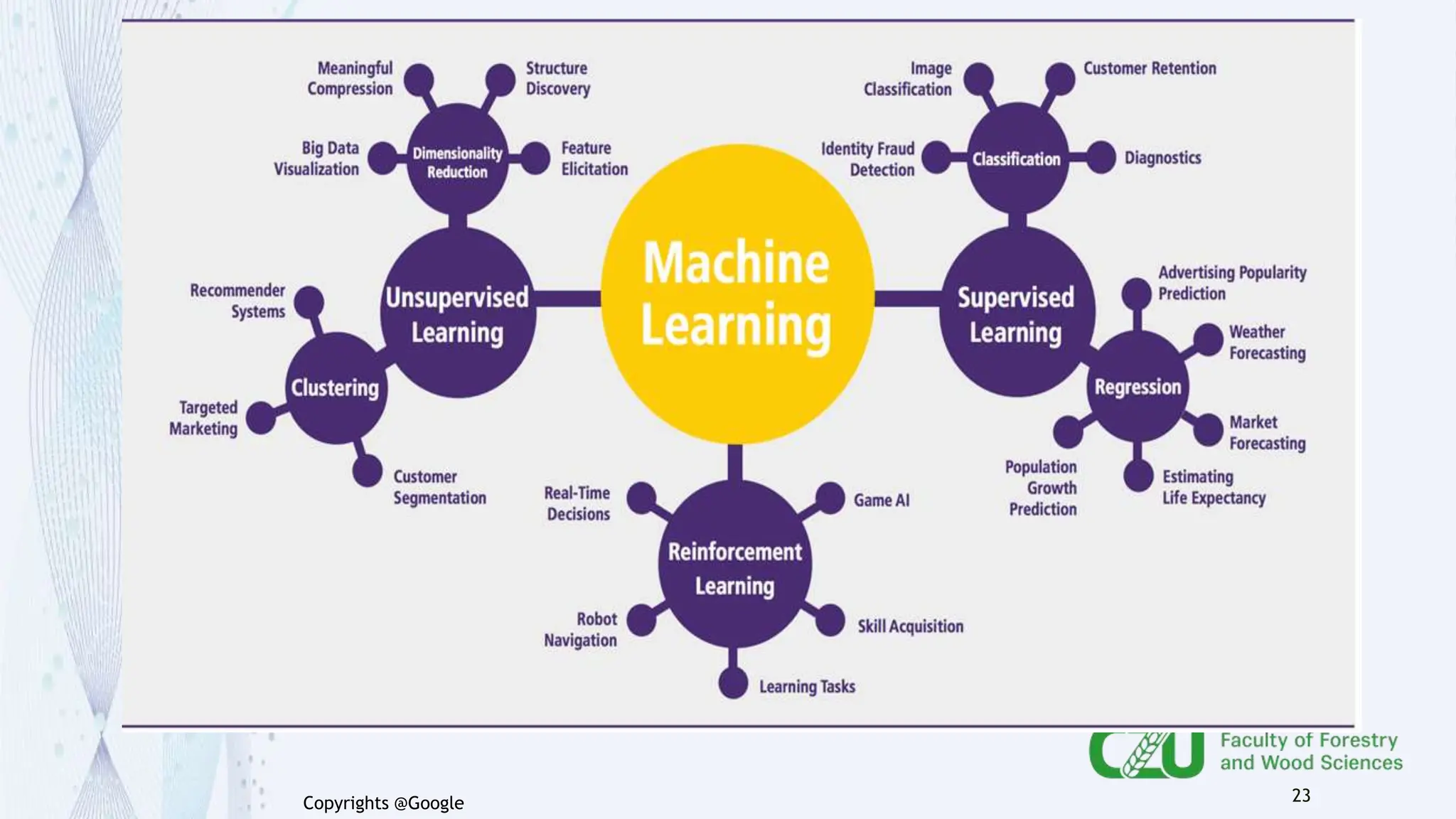
The document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI) and its subset, machine learning (ML), highlighting various types of learning including supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning. It details the algorithms used in each category, offers applications of ML in forestry, and discusses issues in machine learning such as biases and data quality. The author, Gokul K.S., is a PhD scholar at the Czech University of Life Sciences, with guidance from a supervisor at University College London.