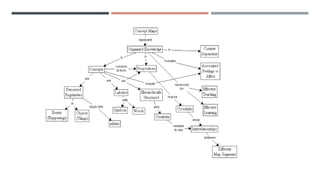
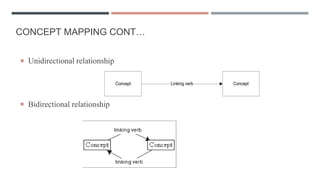
This document discusses concept mapping. It defines a concept map as a representation of spatial relationships between concepts, rather than physical space. Concept maps show an individual's psychological structure of knowledge through nodes representing concepts, lines representing relationships between concepts with arrows indicating direction, and labels describing the nature of the relationship. Concept maps can differ for individuals based on their conceptual understanding of a topic and can be structured hierarchically or as a non-hierarchical network.