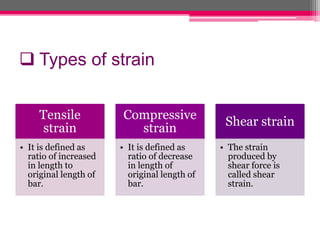
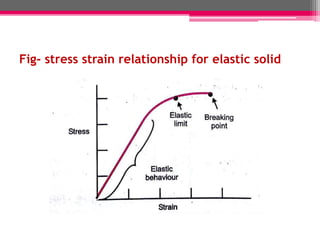
The document explains the concepts of deformation in solids, focusing on plastic and elastic deformations, stress (including types like direct, indirect, and combined stress), and strain. It defines stress as force per unit area and strain as the measure of deformation, introducing the elastic modulus to quantify material response under load based on Hooke's Law. The document details the characteristics of elastic and plastic deformation, highlighting their reversible and irreversible nature, respectively.