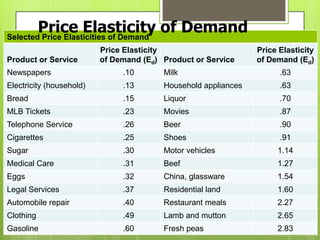
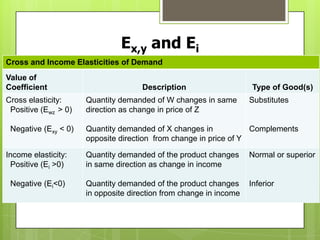
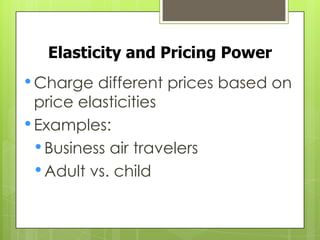
This document provides an overview of price elasticity of demand and supply, detailing how buyers' responsiveness to price changes varies based on elasticity levels (elastic, inelastic, unit elastic). It includes formulas for calculating elasticity, total revenue implications, and determinants such as substitutability and income proportion. Additionally, it discusses applications of different elasticities and how they affect pricing and revenue strategies.