This document defines elasticity and discusses different types of elasticity, including:
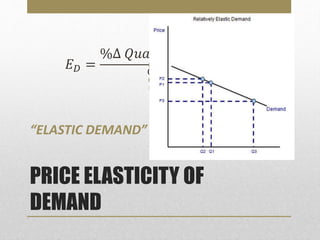
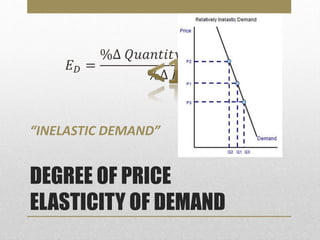
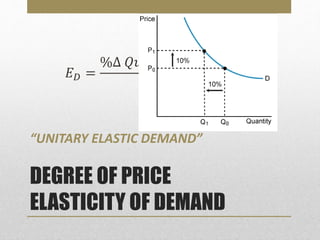
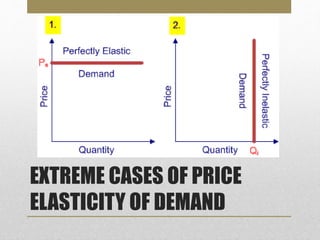
- Price elasticity of demand measures responsiveness of quantity demanded to price changes. It can be elastic, inelastic, or unitary.
- Income elasticity of demand measures responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in income. Goods can be normal, inferior, luxury, or necessity.
- Cross elasticity of demand measures responsiveness of demand for one good to price changes of other goods.
- Price elasticity of supply measures responsiveness of quantity supplied to price changes. Supply can be elastic, inelastic, or unitary. Determinants include time period and ability to adjust inputs.