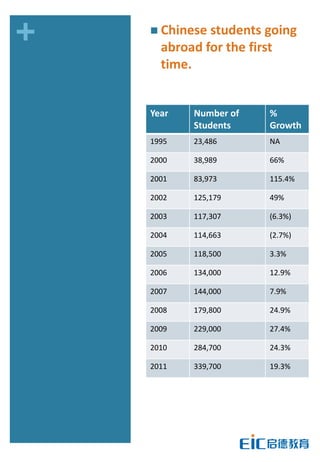
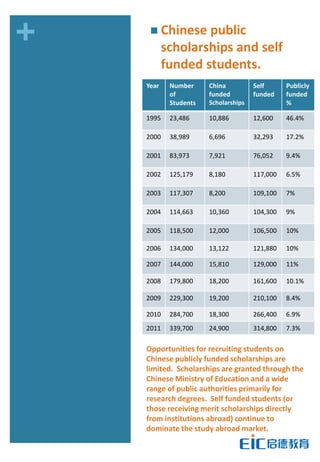
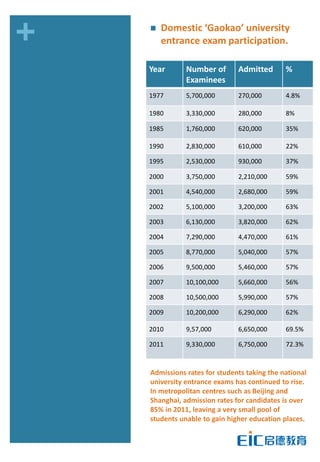
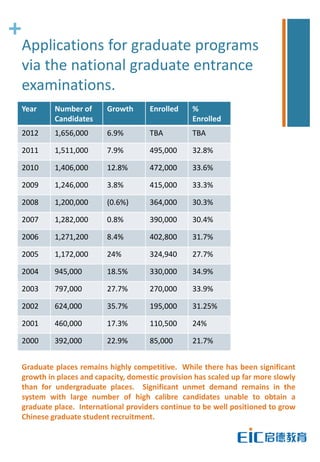
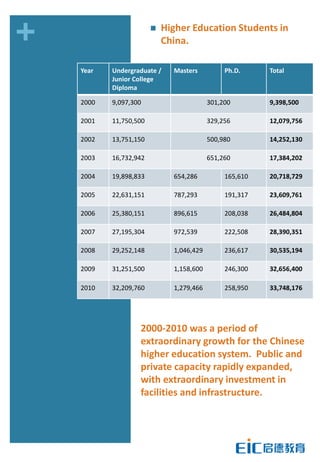
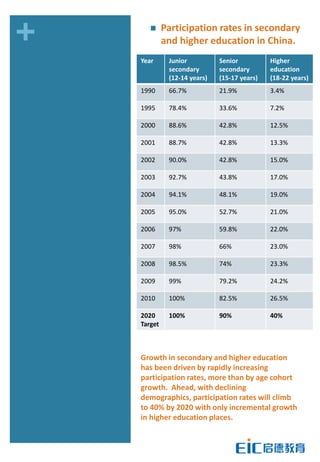
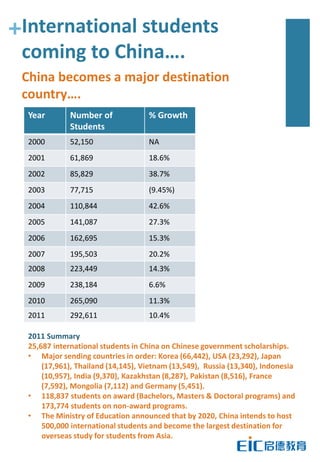
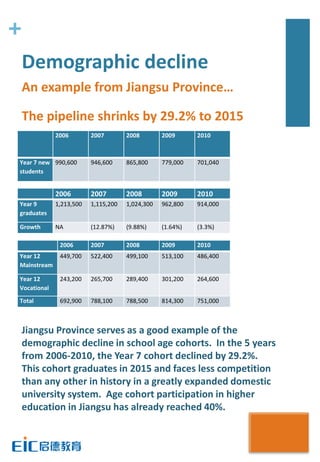
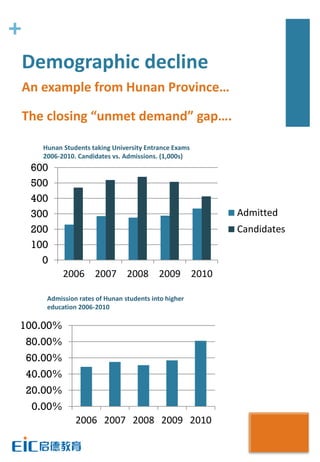
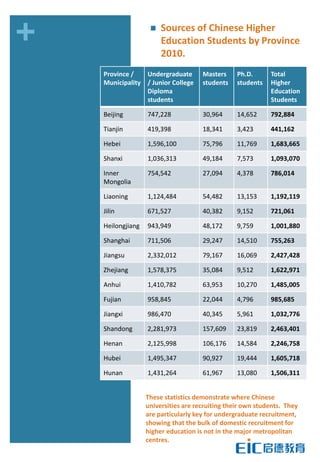
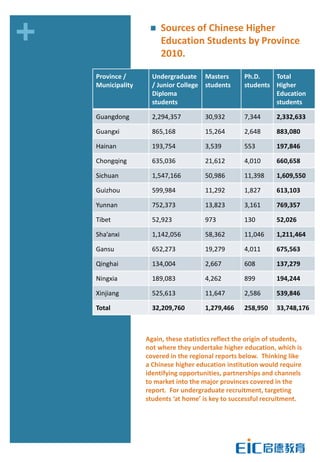
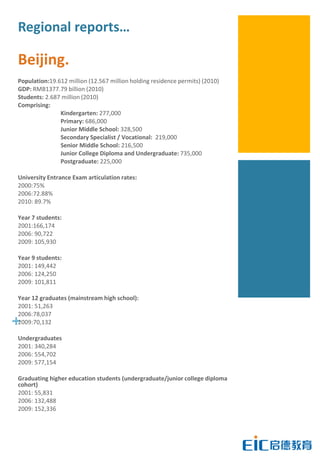
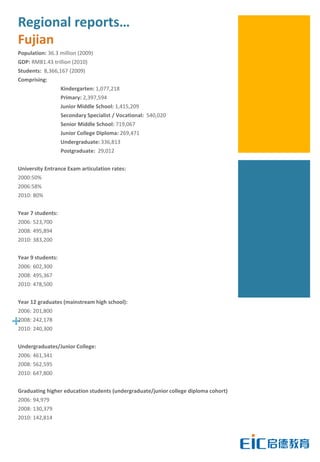
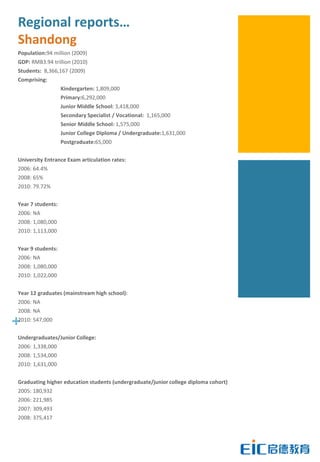
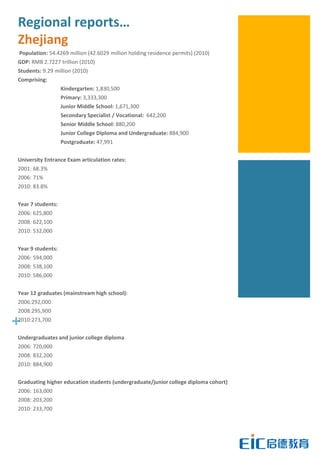
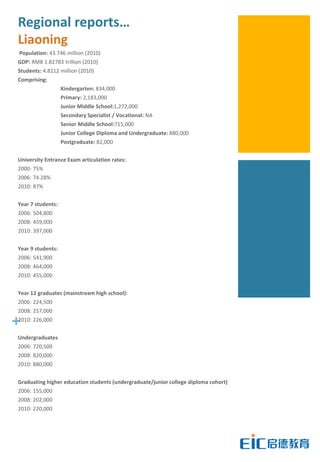
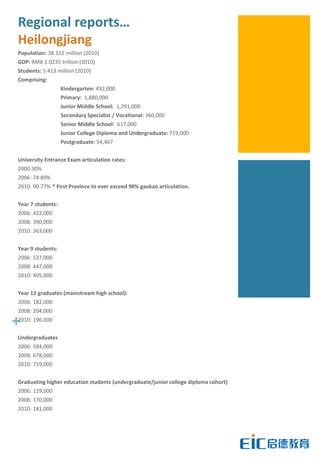
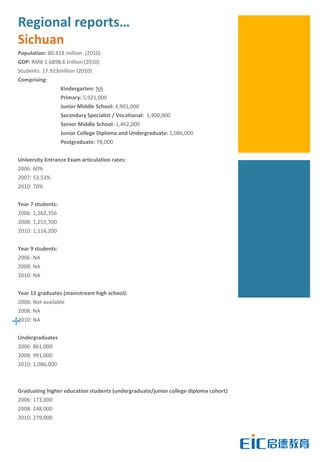
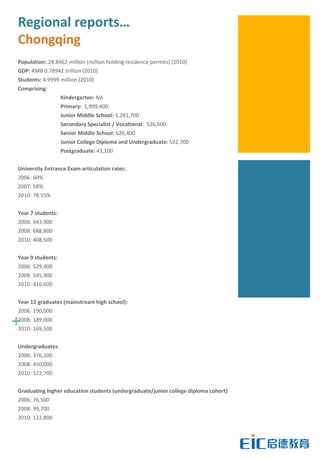
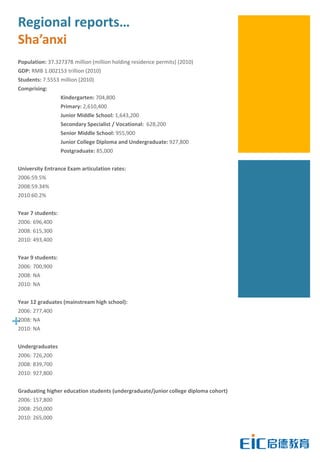
This document provides key education statistics for China, intended to help international educators understand the Chinese education market. It notes that from 2000-2010, China saw extraordinary growth in higher education participation, with the number of students growing from 9.3 million to over 33 million. However, with declining school age cohorts, only modest further increases in higher education capacity will be needed to accommodate students through 2020. While the number of students studying abroad continues to rise, domestic options are expanding as well. The report aims to help international partners position themselves successfully amid these changing dynamics in China.