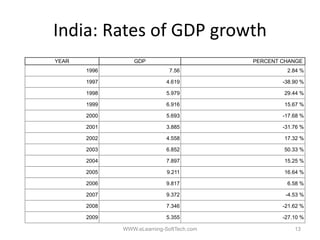
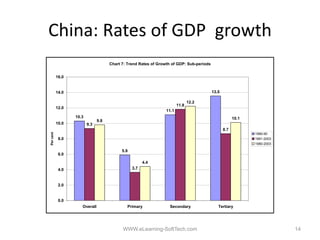
The document discusses transforming India through education and vocational training. It outlines the purpose of education and focuses on areas like vocational education and training, governance, the economy, and employment generation. It notes India's high dropout rates, low literacy rates compared to countries like China, and emphasizes the need to focus on vocational skills training to generate employment and improve productivity. The document concludes by discussing eLearning and its potential role in improving access to education.