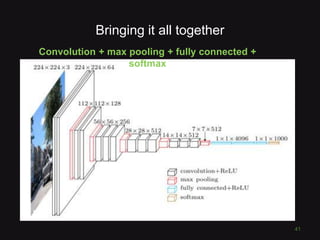
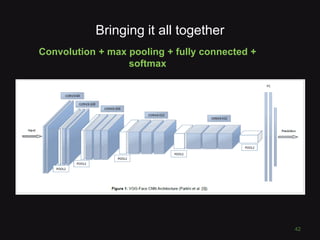
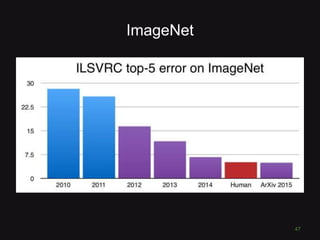
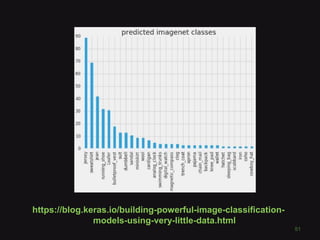
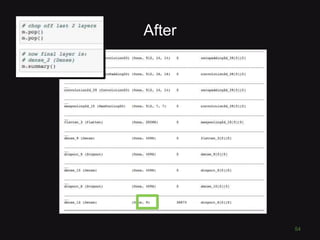
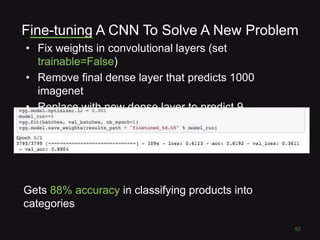
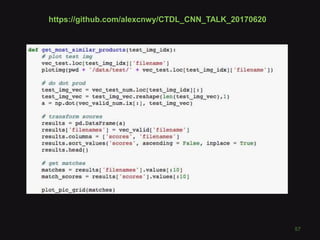
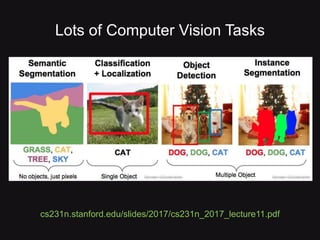
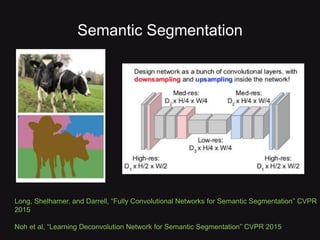
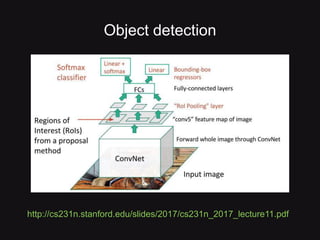
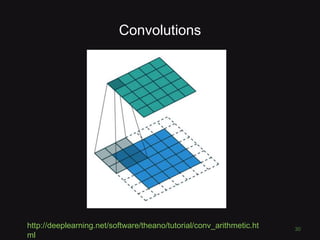
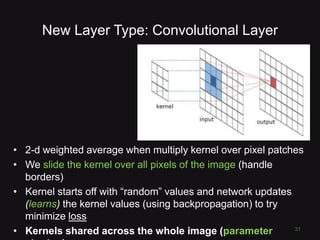
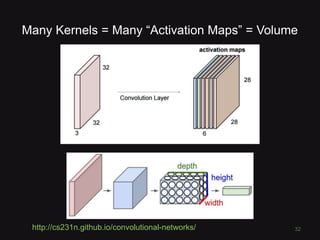
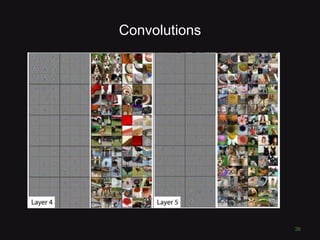
This document discusses convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and their applications in computer vision, providing resources and techniques for image classification, object detection, and more advanced topics like style transfer. It includes practical tips for training CNNs and mentions a hackathon challenge focused on detecting potholes in images. The document emphasizes the importance of using labeled training data and the benefits of fine-tuning pre-trained models.

















![What is a single neuron?
20
• 3 inputs [x1,x2,x3]
• 3 weights [w1,w2,w3]
• Element-wise multiply and sum
• Apply activation function f
• Often add a bias too (weight of 1) – not](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dl4cvslides-170915173401/85/Convolutional-Neural-Networks-for-Computer-vision-Applications-20-320.jpg)
![What is an Activation Function?
21
Sigmoid Tanh ReLU
Nonlinearities … “squashing functions” … transform neuron’s
output
NB: sigmoid output in [0,1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dl4cvslides-170915173401/85/Convolutional-Neural-Networks-for-Computer-vision-Applications-21-320.jpg)




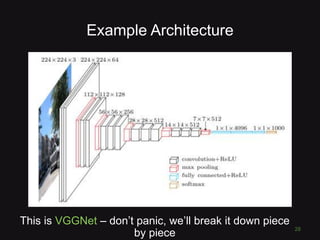
![What is a Convolutional Neural
Network?
27
“like a simple neural network but with
special types of layers that work well on
images”
(math works on numbers)
• Pixel = 3 colour channels (R, G, B)
• Pixel intensity = number in [0,255]
• Image has width w and height h
• Therefore image is w x h x 3 numbers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dl4cvslides-170915173401/85/Convolutional-Neural-Networks-for-Computer-vision-Applications-27-320.jpg)




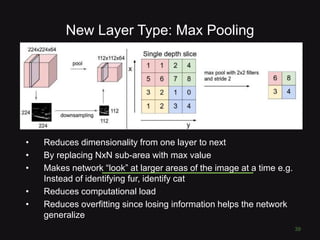
![Softmax
• Convert scores ∈ ℝ to probabilities ∈ [0,1]
• Then predict the class with highest
probability
40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dl4cvslides-170915173401/85/Convolutional-Neural-Networks-for-Computer-vision-Applications-40-320.jpg)