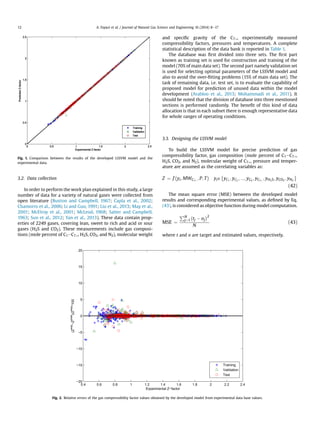
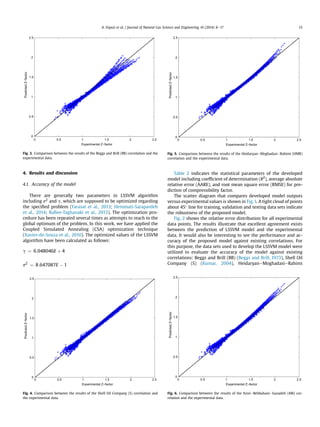
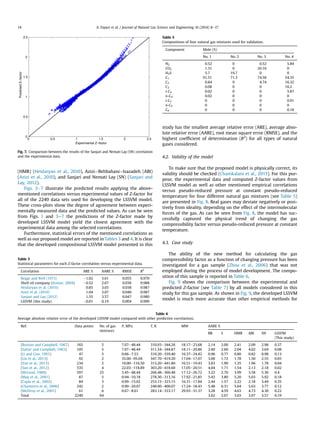
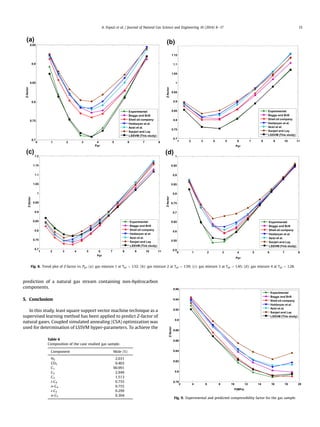
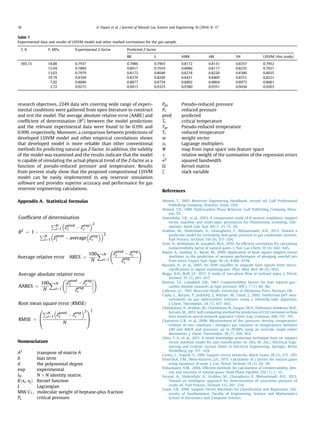
This document presents a new method for estimating natural gas compressibility factor (Z-factor) using least square support vector machine (LSSVM) modeling. The LSSVM model is developed and tested using a database of over 2,200 samples of sour and sweet gas compositions. The model predicts Z-factor as a function of gas composition, molecular weight, pressure, and temperature. Statistical analysis shows the LSSVM model outperforms existing empirical correlations with an average absolute relative error of 0.19% and correlation coefficient of 0.999. The accurate prediction of Z-factor is important for natural gas engineering calculations.