The document discusses key concepts in economics including:
1) Economics is defined as the management of household resources, with different economists providing varying definitions focused on wealth, welfare, or scarcity.
2) Microeconomics examines decision-making by individuals and firms, while macroeconomics studies aggregate economic indicators like GDP and unemployment rates.
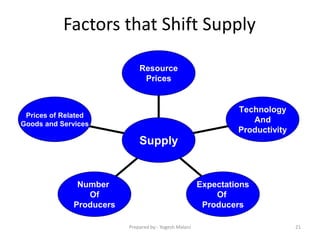
3) The law of demand states that as price increases, quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa. The supply curve slopes upward to show quantity supplied increases with rising price.