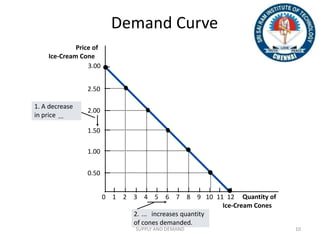
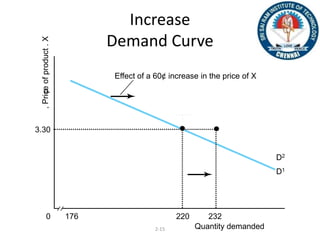
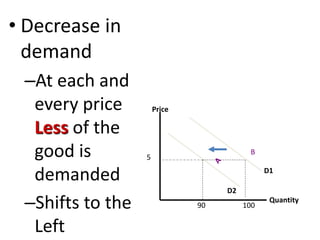
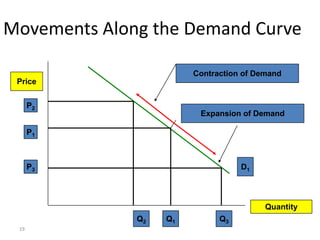
The document discusses the law of demand, which states that greater prices lead to lower quantities demanded and vice versa, considering factors like consumer preferences and related goods. It explains the demand curve, illustrating the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded, and mentions effects such as the income effect and substitution effect that shift demand. Additionally, it describes concepts like changes in demand, including increase, decrease, extension, and contraction along the demand curve.