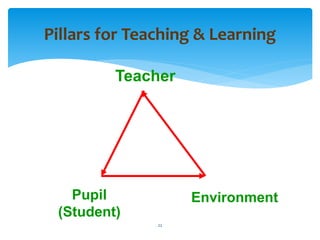
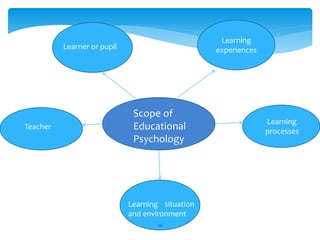
Here are some suggestions for applying
educational psychology:
- Apply principles of learning, development and motivation to lesson planning
- Consider individual differences when designing instruction
- Use assessment to inform teaching and provide feedback to students
- Continually reflect on your own teaching practices and ways to improve
- Consult educational psychology research when addressing challenges in the classroom
- Collaborate with other teachers to discuss strategies informed by theory
- Participate in professional development to stay current on new findings in the field